|
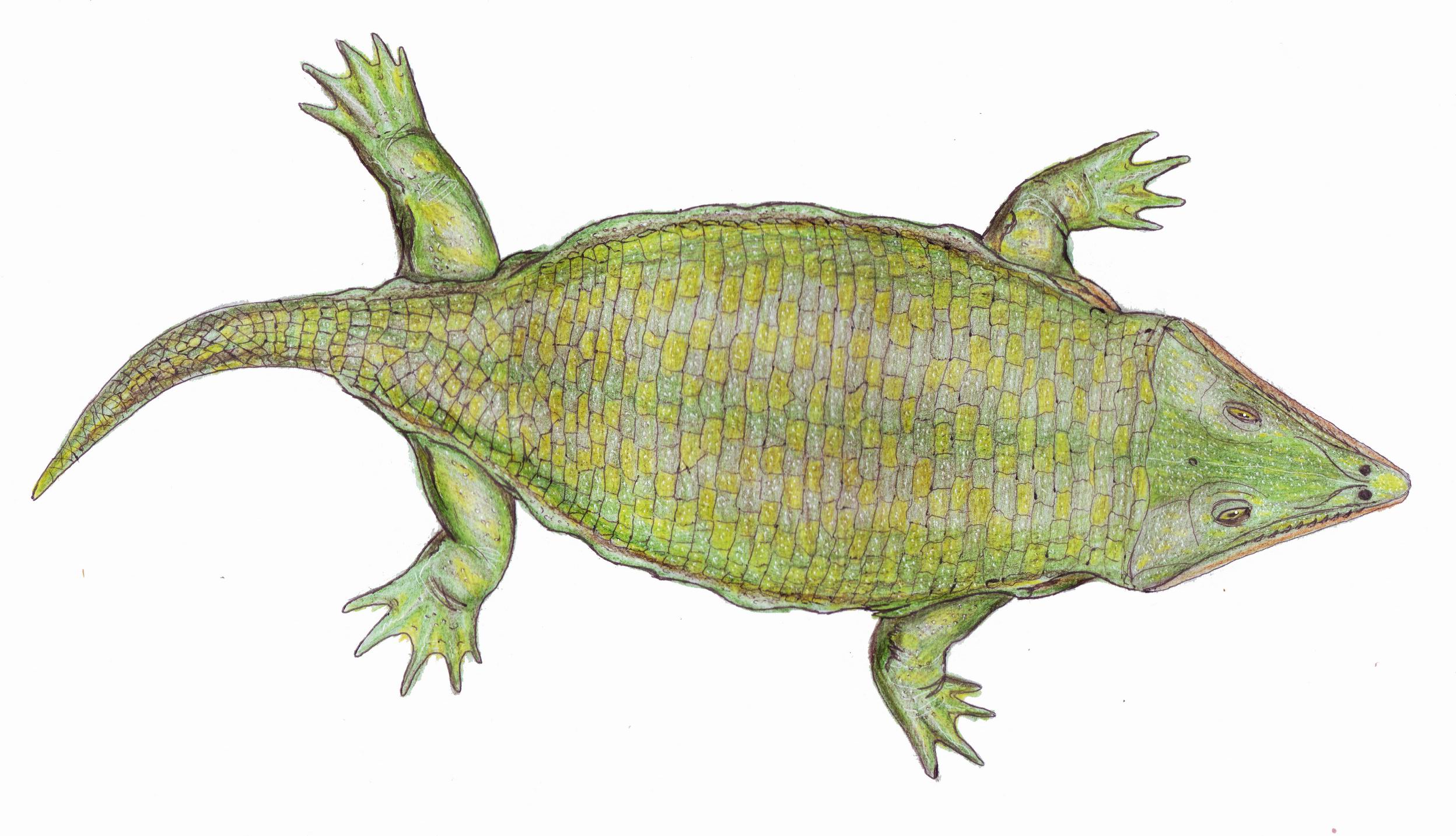
Lapillopsis
''Lapillopsis'' is an extinct genus of stereospondyl temnospondyl within the family Lapillopsidae. Fossils belonging to the genus have been found in the Arcadia Formation ( Rewan Group) of Queensland, Australia. History of study The type species and only known species is ''Lapillopsis nana,'' named in 1990 by Australian scientists Anne Warren and Mark Hutchinson. The name is derived from the Latin ''lapillus'' (pebble) and Greek -''opsis'' (appearance) in reference to the material of this species being collected from within small rocky nodules. There are two known specimens, both nearly complete skulls with associated mandibles and associated postcranial elements. An additional fourteen specimens from the same locality were described by Australian paleontologist Adam Yates in 1999. Anatomy ''Lapillopsis'' was differentiated from the closely related '' Rotaurisaurus'' from Australia by several features: (1) a deep, semi-elliptical otic notch; (2) an abbreviated posterior sk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lapillopsidae
Lapillopsidae is a family of Temnospondyli Temnospondyli (from Greek τέμνειν, ''temnein'' 'to cut' and σπόνδυλος, ''spondylos'' 'vertebra') is a diverse order of small to giant tetrapods—often considered primitive amphibians—that flourished worldwide during the Carb .... ''Lapillopsis'' was found as the sister to ''Rotaurisaurus'' in a 1999 analysis that found the Lapillopsidae as basal stereospondyls. ''Lapillopsis'' was found as a sister to Dissorophoidea by a 2017 analysis. Another relative of ''Lapillopsis'', ''Manubrantlia'' was described from the Early Triassic of India. Yates & Sengupta, 2002. A lapillopsid temnospondyl from the Early Triassic of India. Alcheringa 26: 201-208. https://doi.org/10.1080/03115510208619252 References * Stereospondyls Triassic temnospondyls {{triassic-animal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcadia Formation (Australia)
The Arcadia Formation is a geological formation located within central-eastern Queensland, Australia, which has been aged between the Induan–Olenekian epoch of the Early-Triassic period. It is most well known for its abundance of Early-Triassic aged fossils, most notably its high diversity of amphibians. Description The Arcadia Formation is a sequence of sandstones and mudstones deposited as a result of freshwater rivers and lakes during the Induan–Olenekian epoch. The Arcadia Formation represents one of the oldest known Mesozoic formations within the entirety of Australia, as well as containing relatively well-preserved specimens for its age and country. At the time at which the Arcadia Formation was building up, the then region of today's Australia was still recovering from the recent Permian–Triassic extinction event which had resulted in the global biodiversity remaining at a low level throughout much of the lower Triassic. The world currently was generally a hot and ari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotaurisaurus
''Rotaurisaurus'' is an extinct genus of amphibian-grade tetrapod from the family Lapillopsidae. This genus is known only from an incomplete crushed skull and associated left jaw, together given the designation UTGD (University of Tasmania Geological Department) 87795. The generic name, ''Rotaurisaurus'', is a combination of Latin words translating to "circle-eared lizard". This references the shape of its otic notches, which acquire a circular form due to being partially enclosed by the tabular bones at the back of the skull. The specific name, ''contundo'', references the specimen's poor level of preservation, as it is derived from the Latin word for "squashed". The skull was discovered in 1960 at the Crisp and Gunn Quarry near Hobart, Tasmania. This quarry contains rock layers from the Knocklofty Formation, which is dated to the early Triassic Period. For years this skull was believed to belong to a juvenile individual of '' Chomatobatrachus halei'', a species of lydekkerinid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Prehistoric Amphibians
This list of prehistoric amphibians is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all genera from the fossil record that have ever been considered to be amphibians, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera that are now considered invalid, doubtful ('' nomina dubia''), or were not formally published (''nomina nuda''), as well as junior synonyms of more established names, and genera that are no longer considered amphibians. Modern forms are excluded from this list. The list currently includes 454 names. Naming conventions and terminology Naming conventions and terminology follow the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature. Technical terms used include: * Junior synonym: A name which describes the same taxon as a previously published name. If two or more genera are formally designated and the type specimens are later assigned to the same genus, the first to be published (in chronological order) is the senior synon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lydekkerinidae
Lydekkerinidae is a family of stereospondyl temnospondyls that lived in the Early Triassic period. During this time period, lydekkerinids were widely distributed, with putative remains reported from Russia, Greenland, India, South Africa, Madagascar, Australia, and Antarctica. In contrast to most other stereospondyls, lydekkerinids were relatively small-bodied (most with skulls less than 10 cm in length). The type genus is ''Lydekkerina'', the namesake of the family and the best-known lydekkerinid. Description The identification of features shared among lydekkerinids (synapomorphies) necessarily varies depending on which taxa are considered to belong to this group (see further in next section). In the most expansive concept, the family includes the eponymous ''Lydekkerina'' (and junior synonyms like '''Broomulus''' and '''Limnoiketes'''), ''Eolydekkerina'' from South Africa, ''Deltacephalus'' from Madagascar, ''Luzocephalus'' from Russia and Greenland (which includes the '''Aqui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissorophoidea
Dissorophoideans are a clade of medium-sized, temnospondyl amphibians that appeared during the Moscovian in Euramerica, and continued through to the Late Permian and the Early Triassic of Gondwana. They are distinguished by various details of the skull, and many forms seem to have been well adapted for life on land. Since 2008, Lissamphibia has been progressively widely considered part of this clade, but this position is still disputed by some authors. It is possible that the small Permo-Carboniferous Micromelerpetontidae and the large Late Permian Melosauridae may also belong in this clade. Phylogeny An extensive phylogenetic analysis of dissorophoids conducted in 2016 and 2018 found that the families Dissorophidae and Trematopidae are more closely related to each other than either is to the family Amphibamidae. Following a 2008 study, the Dissorophidae-Trematopidae clade was called Olsoniformes. Below is the cladogram from the 2018 analysis: References * Huttenlocker, Ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic Temnospondyls Of Australia
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the chief terrestrial vertebrates during this time. A specialized subgroup of archosaurs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereospondyls
The Stereospondyli are a group of extinct Temnospondyli, temnospondyl amphibians that existed primarily during the Mesozoic period. They are known from all seven continents and were common components of many Triassic ecosystems, likely filling a similar ecological niche to modern crocodilians prior to the diversification of pseudosuchian archosaurs. Classification and anatomy The group was first defined by Zittel (1888) on the recognition of the distinctive vertebral anatomy of the best known stereospondyls of the time, such as ''Mastodonsaurus'' and ''Metoposaurus''. The term 'stereospondylous' as a descriptor of vertebral anatomy was coined the following year by Fraas, referring to a vertebral position consisting largely or entirely of the intercentrum in addition to the neural arch. While the name 'Stereospondyli' is derived from the stereospondylous vertebral condition, there is a diversity of vertebral morphologies among stereospondyls, including the diplospondylous ('Tupil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lydekkerina
''Lydekkerina'' is an extinct genus of stereospondyl temnospondyl. It is the type genus of the family Lydekkerinidae. Fossils have been collected from Early Triassic deposits in South Africa and Australia. The type species is '' L. huxleyi'', first described in 1889. While most other stereospondyls were semiaquatic, ''Lydekkerina'' was exclusively terrestrial. Description ''Lydekkerina'' was a relatively small temnospondyl, growing up to around in length. Skulls range in length from in the smallest known individual to up to in larger individuals. The skull is wedge-shaped and has a parabolic outline with convex lateral margins. Shallow pits cover the surface of the skull. Teeth line the palate as well as the jaws, and some skulls even bear large ectopterygoid tusks on the underside of the skull. ''Lydekkerina'' can be distinguished from other lydekkerinids on the basis of several skull characteristics. One such feature is the presence of vomerine shagreen, tiny bumps cove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countries of Namibia, Botswana, and Zimbabwe; and to the east and northeast by Mozambique and Eswatini. It also completely enclaves the country Lesotho. It is the southernmost country on the mainland of the Old World, and the second-most populous country located entirely south of the equator, after Tanzania. South Africa is a biodiversity hotspot, with unique biomes, plant and animal life. With over 60 million people, the country is the world's 24th-most populous nation and covers an area of . South Africa has three capital cities, with the executive, judicial and legislative branches of government based in Pretoria, Bloemfontein, and Cape Town respectively. The largest city is Johannesburg. About 80% of the population are Black South Afri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karoo Basin
The Karoo Supergroup is the most widespread stratigraphy, stratigraphic unit in Africa south of the Kalahari Desert. The group (stratigraphy), supergroup consists of a sequence of units, mostly of nonmarine origin, deposited between the Pennsylvanian (geology), Late Carboniferous and Early Jurassic, a period of about 120 million years. In southern Africa, rocks of the Karoo Supergroup cover almost two thirds of the present land surface, including all of Lesotho, almost the whole of Free State (province), Free State, and large parts of the Eastern Cape, Northern Cape, Mpumalanga and KwaZulu-Natal Provinces of South Africa. Karoo supergroup outcrops are also found in Namibia, Eswatini, Zambia, Zimbabwe and Malawi, as well as on other continents that were part of Gondwana. The basins in which it was deposited formed during the formation and breakup of Pangea.McCarthy, T., Rubridge, B. (2005). ''The Story of Earth and Life.'' pp. 161, 187–241. Struik Publishers, Cape Town The type lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micropholis (amphibian)
''Micropholis'' (Greek mikros''' = small and '''pholis''' = scale) is an extinct genus of dissorophoid temnospondyl. Fossils have been found from the ''Lystrosaurus'' Assemblage Zone of the Karoo Basin in South Africa and are dated to the Induan (Early Triassic). Fossils have also been found from the lower Fremouw of Antarctica.''Micropholis'' is the only post-Permian dissorophoid and the only dissorophoid in what is presently the southern hemisphere and what would have been termed Gondwana during the amalgamation of Pangea. History of study ''Micropholis'' was one of the first dissorophoids to be named by English paleontologist Thomas Huxley in 1859 based on a partial skull. ''Micropholis stowii'' (properly ''Micropholis stowi'')'','' the type species, is named for George William Stow, the South African geologist and ethnologist who discovered the specimen and who proposed that it represented some extinct amphibian. English paleontologist Richard Owen later named a new genus a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |