|
Landwirtschaftliche Hochschule Berlin
The Agricultural University of Berlin (german: Landwirtschaftliche Hochschule Berlin) was an agricultural university in Berlin, Germany. Established in 1881, it was closed in 1934, and incorporated as a faculty into the Humboldt University of Berlin. History Academic teaching in agricultural science began in Germany only after the publishing of ''Grundsätze der deutschen Landwirtschaft'' (Principles of the German Agriculture) by Johann Beckmann (1739–1811) in 1779. After the foundation of the first agricultural institute in Celle, establishment of several educational institutions in this field followed in Germany. Mid-1860s, the then Prussian Minister of Agriculture, Count Heinrich Friedrich August von Itzenplitz (1799-1883), set up an agricultural institute in Berlin, which was subordinated to the Ministry, and was affiliated to the university. The institute was initially housed in a private home in the Behrensstraße, and then moved to the Dorotheenstraße in 1873. On 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
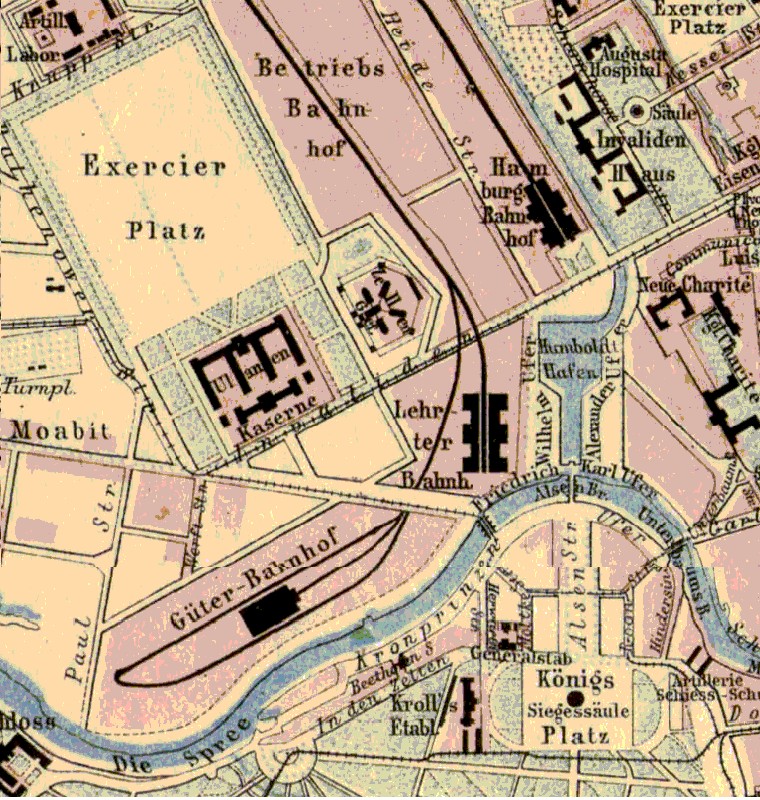
Invalidenstraße
The Invalidenstraße is a street in Berlin, Germany. It runs east to west for through the districts of Mitte and Moabit. The street originally connected three important railway stations in the northern city centre: the Stettiner Bahnhof (today Nordbahnhof), the Hamburger Bahnhof and the Lehrter Bahnhof, the present-day Berlin Hauptbahnhof. History The street was laid out in the 13th century and originally named ''Spandauer Heerweg''. It was renamed after a hostel erected in 1748 by the order of King Frederick II of Prussia, the ''Invalidenhaus'', which served the veterans that fought in the Silesian Wars. Today the remaining parts of this building house offices for the Federal Ministry of Economics. On western Invalidenstraße was the site of the notorious Moabit cell prison and large barracks of the Prussian Uhlans (''Uhlanenkaserne''). East-West border crossing After World War II Invalidenstraße was divided between East and West Berlin and the ''Sandkrugbrücke'' crossi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technical University Of Berlin
The Technical University of Berlin (official name both in English and german: link=no, Technische Universität Berlin, also known as TU Berlin and Berlin Institute of Technology) is a public research university located in Berlin, Germany. It was the first German university to adopt the name "Technische Universität" (Technical University). The university alumni and professor list includes several US National Academies members, two National Medal of Science laureates and ten Nobel Prize laureates. TU Berlin is a member of TU9, an incorporated society of the largest and most notable German institutes of technology and of the Top International Managers in Engineering network, which allows for student exchanges between leading engineering schools. It belongs to the Conference of European Schools for Advanced Engineering Education and Research. The TU Berlin is home of two innovation centers designated by the European Institute of Innovation and Technology. The university is labeled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1881 Establishments In Germany
Events January–March * January 1– 24 – Siege of Geok Tepe: Russian troops under General Mikhail Skobelev defeat the Turkomans. * January 13 – War of the Pacific – Battle of San Juan and Chorrillos: The Chilean army defeats Peruvian forces. * January 15 – War of the Pacific – Battle of Miraflores: The Chileans take Lima, capital of Peru, after defeating its second line of defense in Miraflores. * January 24 – William Edward Forster, chief secretary for Ireland, introduces his Coercion Bill, which temporarily suspends habeas corpus so that those people suspected of committing an offence can be detained without trial; it goes through a long debate before it is accepted February 2. * January 25 – Thomas Edison and Alexander Graham Bell form the Oriental Telephone Company. * February 13 – The first issue of the feminist newspaper ''La Citoyenne'' is published by Hubertine Auclert. * February 16 – The Canadia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Educational Institutions Established In 1881
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty. Various researchers emphasize the role of critical thinking in order to distinguish education from indoctrination. Some theorists require that education results in an improvement of the student while others prefer a value-neutral definition of the term. In a slightly different sense, education may also refer, not to the process, but to the product of this process: the mental states and dispositions possessed by educated people. Education originated as the transmission of cultural heritage from one generation to the next. Today, educational goals increasingly encompass new ideas such as the liberation of learners, skills needed for modern society, empathy, and complex vocational skills. Types of education are commonly divided into formal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Von Münstermann
Carl von Münstermann (December 20, 1843 in Werne - 20 September 1930 in Berlin-Wilmersdorf) was a German engineer and land improvement officer. He was a professor of culture and technology at the Agricultural University of Berlin The Agricultural University of Berlin (german: Landwirtschaftliche Hochschule Berlin) was an agricultural university in Berlin, Germany. Established in 1881, it was closed in 1934, and incorporated as a faculty into the Humboldt University of Ber ... (Landwirtschaftliche Hochschule Berlin). References Engineers from North Rhine-Westphalia German agronomists 1843 births 1930 deaths People from Werne {{Germany-engineer-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugo Hagen
Hugo Hagen (1818 – 14 April 1871, Berlin) was a German sculptor. Life He was a student of Ludwig Wilhelm Wichmann. From 1842 to 1857, he was an assistant in the studios of Christian Daniel Rauch, where he contributed to creating the statues of Frederick the Great on the Unter den Linden, Albrecht Thaer at Humboldt University and Immanuel Kant in Königsberg. In 1865, he became the Director of the "Rauch-Museum". After the early death of Hermann Schievelbein, he helped complete the monument to Heinrich Friedrich Karl vom Stein. He also assisted Rudolf Siemering to complete Johann Gottfried Schadow's "Münzfrieses" (Coin Friezes) on the Old Berlin Mint. Ironically, many of his own works were left incomplete when he died. Selected major works * 1860/1861: Group, "Grace with Pegasus", on the roof of the Altes Museum * 1862: Monument for Friedrich Wilhelm, Count Brandenburg on the Leipziger Platz * 1866/1869: Johann Gottfried Schadow Monument on the porch of the Altes Muse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Daniel Rauch
Christian Daniel Rauch (2 January 1777 – 3 December 1857) was a German sculptor. He founded the Berlin school of sculpture, and was the foremost German sculptor of the 19th century. Life Rauch was born at Arolsen in the Principality of Waldeck in the Holy Roman Empire. His father was employed at the court of Prince Frederick II of Hesse, and in 1790 the lad was apprenticed to the court sculptor of Arolsen, Friedrich Valentin. In 1795, he became assistant to Johann Christian Ruhl, the court sculptor of Kassel. After the death of his father in 1796 and his older brother in 1797, he moved to Berlin where he was appointed groom of the chamber in the king's household. He abandoned sculpture temporarily, but his new position provided a wider field for improvement, and he soon used the opportunity and practised his art in spare hours. He came under the influence of Johann Gottfried Schadow. In 1802, he exhibited his "Sleeping Endymion." Queen Louisa of Prussia, surprising him ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atrium (architecture)
In architecture, an atrium (plural: atria or atriums) is a large open-air or skylight-covered space surrounded by a building. Atria were a common feature in Ancient Roman dwellings, providing light and ventilation to the interior. Modern atria, as developed in the late 19th and 20th centuries, are often several stories high, with a glazed roof or large windows, and often located immediately beyond a building's main entrance doors (in the lobby). Atria are a popular design feature because they give their buildings a "feeling of space and light." The atrium has become a key feature of many buildings in recent years. Atria are popular with building users, building designers and building developers. Users like atria because they create a dynamic and stimulating interior that provides shelter from the external environment while maintaining a visual link with that environment. Designers enjoy the opportunity to create new types of spaces in buildings, and developers see atria as prest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
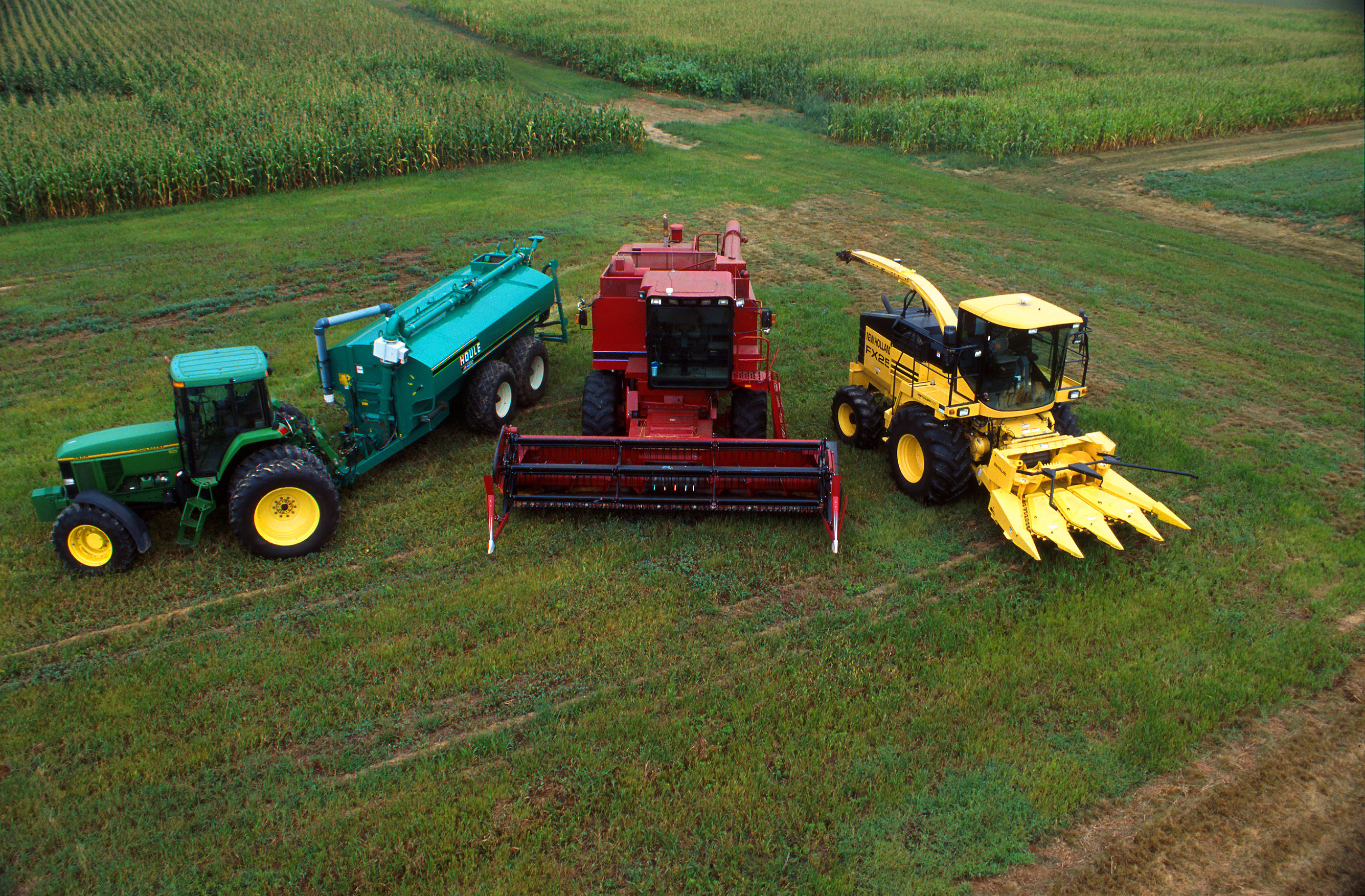
Agricultural Machinery
Agricultural machinery relates to the mechanical structures and devices used in farming or other agriculture. There are many types of such equipment, from hand tools and power tools to tractors and the countless kinds of farm implements that they tow or operate. Diverse arrays of equipment are used in both organic and nonorganic farming. Especially since the advent of mechanised agriculture, agricultural machinery is an indispensable part of how the world is fed. History The Industrial Revolution With the coming of the Industrial Revolution and the development of more complicated machines, farming methods took a great leap forward. Instead of harvesting grain by hand with a sharp blade, wheeled machines cut a continuous swath. Instead of threshing the grain by beating it with sticks, threshing machines separated the seeds from the heads and stalks. The first tractors appeared in the late 19th century. Steam power Power for agricultural machinery was originally supplied by o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Heinrich Von Thünen
Johann Heinrich von Thünen (24 June 1783 – 22 September 1850), sometimes spelled Thuenen, was a prominent nineteenth century economist and a native of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, now in northern Germany.He "ranks alongside Marx as the greatest German economist of the nineteenth century" (Fernand Braudel). Work Thünen's model of agricultural land use Thünen was a Mecklenburg landowner, who in the first volume of his treatise ''The Isolated State'' (1826), developed the first serious treatment of spatial economics and economic geography, connecting it with the theory of rent. The importance lies less in the pattern of land use predicted than in its analytical approach. Thünen developed the basics of the theory of marginal productivity in a mathematically rigorous way, summarizing it in the formula in which :R = Y(p - c) - YFm \, where R = land rent; Y = yield per unit of land; c = production expenses per unit of commodity; p=market price per unit of commodity; F = freight rat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albrecht Daniel Thaer
Albrecht Daniel Thaer (; 14 May 1752 – 26 October 1828) was a German agronomist and a supporter of the humus theory for plant nutrition. Biography Family and early life Albrecht Daniel Thaer was born in Celle, a neat little town in Hanover, on 14 May 1752. His father, Johann Friedrich Thaer, was physician to the Court, and born in Liebenwerda, in Saxony; his mother, Sophie Elisabeth, was the daughter of J. Saffe, receiver of rents and taxes of the district of Celle. Albert was the first born, and had three sisters, Christine, Albertine, and Wilhelmine, of which the first died in infancy, the second was married to Captain Schweppe, and the youngest to the well-known privy councillor, Doctor Jacobi.John Sinclair. "Memoir of Thaer" in: A.D. Thaer. ''The Principles of Agriculture, Volume 1.'' William Shaw and Cuthbert W. Johnson (tr.). Ridgway, 1844. p. i-xvi. At the University of Göttingen he finished his medical studies, and afterwards practised medicine in his native plac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |