|
Landkreis Groß Wartenberg
The Groß Wartenberg district, known until 1888 as the Wartenberg district, was a Prussian district in Silesia from 1742 to 1945. Its capital was the town of Groß Wartenberg, which was known until 1888 as ''Polnisch Wartenberg''. The area of this district now lies within the Lower Silesian Voivodeship of Poland. History After conquering most of Silesia, King Frederick the Great introduced Prussian administrative structures in Lower Silesia by cabinet order on November 25, 1741. This included the establishment of two war and domain chambers in Breslau and Glogau as well as their subdivision into districts and the establishment of district administrators on January 1, 1742. Leonhard Moritz von Prittwitz-Gaffron was appointed as the first district administrator of the Wartenberg district. In the course of the Stein-Hardenberg Reforms in 1815, the district was assigned to Regierungsbezirk Breslau in the Province of Silesia. During the district reform of 1818 in Regierungsbezir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schlesien Kr Groß Wartenberg
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is split into two main subregions, Lower Silesia in the west and Upper Silesia in the east. Silesia has a diverse culture, including architecture, costumes, cuisine, traditions, and the Silesian language (minority in Upper Silesia). Silesia is along the Oder River, with the Sudeten Mountains extending across the southern border. The region contains many historical landmarks and UNESCO World Heritage Sites. It is also rich in mineral and natural resources, and includes several important industrial areas. The largest city and Lower Silesia's capital is Wrocław; the historic capital of Upper Silesia is Opole. The biggest metropolitan area is the Upper Silesian metropolitan area, the centre of which is Katowice. Parts of the Czech city of Ostrava and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1919 in the Palace of Versailles, exactly five years after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, which led to the war. The other Central Powers on the German side signed separate treaties. Although the armistice of 11 November 1918 ended the actual fighting, it took six months of Allied negotiations at the Paris Peace Conference to conclude the peace treaty. The treaty was registered by the Secretariat of the League of Nations on 21 October 1919. Of the many provisions in the treaty, one of the most important and controversial was: "The Allied and Associated Governments affirm and Germany accepts the responsibility of Germany and her allies for causing all the loss and damage to which the Allied and Associated Governments and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1742 Establishments In Prussia
Year 174 ( CLXXIV) was a common year starting on Friday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Gallus and Flaccus (or, less frequently, year 927 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 174 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Empress Faustina the Younger accompanies her husband, Marcus Aurelius, on various military campaigns and enjoys the love of the Roman soldiers. Aurelius gives her the title of ''Mater Castrorum'' ("Mother of the Camp"). * Marcus Aurelius officially confers the title ''Fulminata'' ("Thundering") to the Legio XII Fulminata. Asia * Reign in India of Yajnashri Satakarni, Satavahana king of the Andhra. He extends his empire from the center to the north of India. By topic Art and Science * ''Meditations'' by Marcus Aurelius is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oleśnica County
__NOTOC__ Oleśnica County ( pl, powiat oleśnicki) is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, south-western Poland. It was created on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. The county covers an area of . Its administrative seat is the town of Oleśnica, and it also contains the towns of Syców, Twardogóra, Bierutów and Międzybórz. As of 2019 the total population of the county is 107,090. The most populated towns are Oleśnica with 37,169 inhabitants and Syców is 10,397 inhabitants. Neighbouring counties Oleśnica County is bordered by Milicz County and Ostrów Wielkopolski County to the north, Ostrzeszów County, Kępno County and Namysłów County to the east, Oława County to the south, and Wrocław County and Trzebnica County to the west. Administrative division The county is subdivided into eight gmina The gmina (Polish: , plural ''gminy'' , from German ''Gemeinde'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Districts Of Prussia
Prussian districts (german: Kreise, literally "circles") were administrative units in the former Kingdom of Prussia, part of the German Empire from 1871 to 1918, and its successor state, the Free State of Prussia, similar to a county or a shire. They were established in the course of the Stein-Hardenberg Reforms from 1815 to 1818 at an intermediate level, between the higher provinces and the government districts (''Regierungsbezirke''), and the lower municipal governments ('' Gemeinden''). Then part of a modern and highly effective public administration structure, they served as a model for the present-day districts of Germany In the aftermath of World War I, the Prussian districts of Eupen and Malmedy (Belgium) were annexed by Belgium in 1925, thereby causing the presence of a German-speaking minority. Administration After the Napoleonic Wars and the 1815 Congress of Vienna, the Prussian lands were re-arranged into ten provinces, three of them—East Prussia, West Prussia and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czech Language
Czech (; Czech ), historically also Bohemian (; ''lingua Bohemica'' in Latin), is a West Slavic language of the Czech–Slovak group, written in Latin script. Spoken by over 10 million people, it serves as the official language of the Czech Republic. Czech is closely related to Slovak, to the point of high mutual intelligibility, as well as to Polish to a lesser degree. Czech is a fusional language with a rich system of morphology and relatively flexible word order. Its vocabulary has been extensively influenced by Latin and German. The Czech–Slovak group developed within West Slavic in the high medieval period, and the standardization of Czech and Slovak within the Czech–Slovak dialect continuum emerged in the early modern period. In the later 18th to mid-19th century, the modern written standard became codified in the context of the Czech National Revival. The main non-standard variety, known as Common Czech, is based on the vernacular of Prague, but is now spoken as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Language
Polish (Polish: ''język polski'', , ''polszczyzna'' or simply ''polski'', ) is a West Slavic language of the Lechitic group written in the Latin script. It is spoken primarily in Poland and serves as the native language of the Poles. In addition to being the official language of Poland, it is also used by the Polish diaspora. There are over 50 million Polish speakers around the world. It ranks as the sixth most-spoken among languages of the European Union. Polish is subdivided into regional dialects and maintains strict T–V distinction pronouns, honorifics, and various forms of formalities when addressing individuals. The traditional 32-letter Polish alphabet has nine additions (''ą'', ''ć'', ''ę'', ''ł'', ''ń'', ''ó'', ''ś'', ''ź'', ''ż'') to the letters of the basic 26-letter Latin alphabet, while removing three (x, q, v). Those three letters are at times included in an extended 35-letter alphabet, although they are not used in native words. The traditional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Language
German ( ) is a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language mainly spoken in Central Europe. It is the most widely spoken and Official language, official or co-official language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, and the Italy, Italian province of South Tyrol. It is also a co-official language of Luxembourg and German-speaking Community of Belgium, Belgium, as well as a national language in Namibia. Outside Germany, it is also spoken by German communities in France (Bas-Rhin), Czech Republic (North Bohemia), Poland (Upper Silesia), Slovakia (Bratislava Region), and Hungary (Sopron). German is most similar to other languages within the West Germanic language branch, including Afrikaans, Dutch language, Dutch, English language, English, the Frisian languages, Low German, Luxembourgish, Scots language, Scots, and Yiddish. It also contains close similarities in vocabulary to some languages in the North Germanic languages, North Germanic group, such as Danish lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
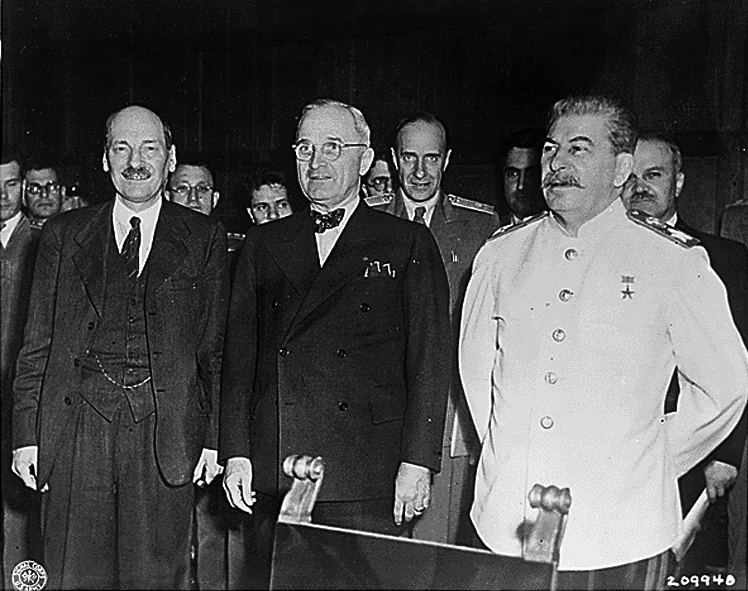
Potsdam Agreement
The Potsdam Agreement (german: Potsdamer Abkommen) was the agreement between three of the Allies of World War II: the United Kingdom, the United States, and the Soviet Union on 1 August 1945. A product of the Potsdam Conference, it concerned the military occupation and reconstruction of Germany, its border, and the entire European Theatre of War territory. It also addressed Germany's demilitarisation, reparations, the prosecution of war criminals and the Flight and expulsion of Germans (1944–1950), mass expulsion of ethnic Germans from various parts of Europe. Executed as a communiqué, the agreement was not a peace treaty according to international law, although it created accomplished facts. It was superseded by the Treaty on the Final Settlement with Respect to Germany signed on 12 September 1990. As De Gaulle had not been invited to the Conference, the French resisted implementing the Potsdam Agreements within their occupation zone. In particular, the French refused to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish People's Republic
The Polish People's Republic ( pl, Polska Rzeczpospolita Ludowa, PRL) was a country in Central Europe that existed from 1947 to 1989 as the predecessor of the modern Republic of Poland. With a population of approximately 37.9 million near the end of its existence, it was the second-most populous communist and Eastern Bloc country in Europe. It was also one of the main signatories of the Warsaw Pact alliance. The largest city and official capital since 1947 was Warsaw, followed by the industrial city of Łódź and cultural city of Kraków. The country was bordered by the Baltic Sea to the north, the Soviet Union to the east, Czechoslovakia to the south, and East Germany to the west. The Polish People's Republic was a socialist one-party state, with a unitary Marxist–Leninist government headed by the Polish United Workers' Party (PZPR). The country's official name was the "Republic of Poland" (') between 1947 and 1952 in accordance with the transitional Small Constitutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, after 1922, the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. The army was established in January 1918. The Bolsheviks raised an army to oppose the military confederations (especially the various groups collectively known as the White Army) of their adversaries during the Russian Civil War. Starting in February 1946, the Red Army, along with the Soviet Navy, embodied the main component of the Soviet Armed Forces; taking the official name of "Soviet Army", until its dissolution in 1991. The Red Army provided the largest land force in the Allied victory in the European theatre of World War II, and its invasion of Manchuria assisted the unconditional surrender of Imperial Japan. During operations on the Eastern Front, it accounted for 75–80% of casual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
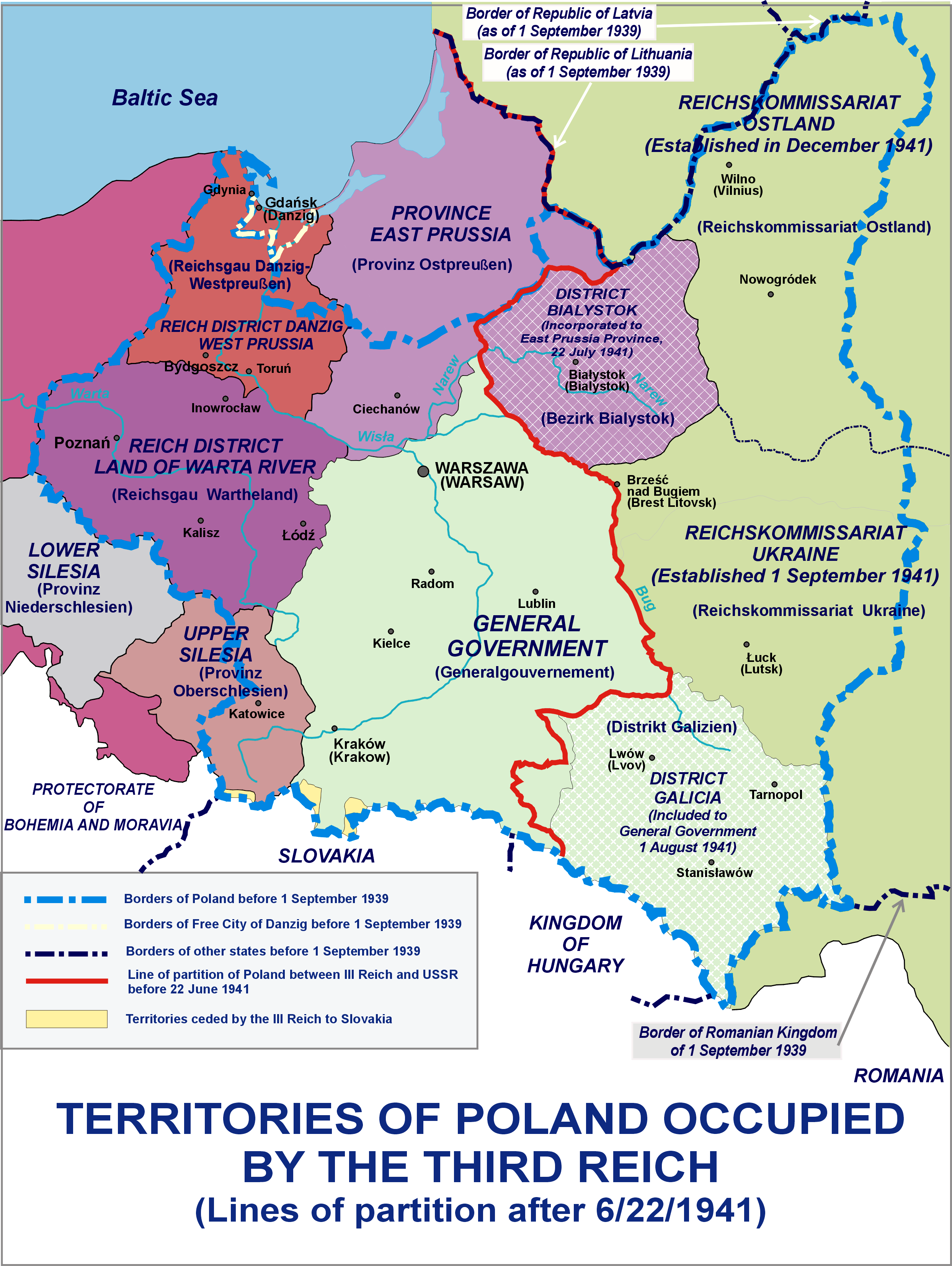
Reichsgau Wartheland
The ''Reichsgau Wartheland'' (initially ''Reichsgau Posen'', also: ''Warthegau'') was a Nazi German ''Reichsgau'' formed from parts of Polish territory annexed in 1939 during World War II. It comprised the region of Greater Poland and adjacent areas. Parts of ''Warthegau'' matched the similarly named pre-Versailles Prussian province of Posen. The name was initially derived from the capital city, Posen (Poznań), and later from the main river, Warthe (Warta). During the Partitions of Poland from 1793, the bulk of the area had been annexed by the Kingdom of Prussia until 1807 as South Prussia. From 1815 to 1849, the territory was within the autonomous Grand Duchy of Posen, which was the Province of Posen until Poland was re-established in 1918–1919 following World War I. The area is currently the Greater Poland Voivodeship. Invasion and occupation of Poland After the invasion of Poland, the conquered territory of Greater Poland was split between four ''Reichsgaue'' and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)