|
Landau Distribution
In probability theory, the Landau distribution is a probability distribution named after Lev Landau. Because of the distribution's "fat" tail, the moments of the distribution, like mean or variance, are undefined. The distribution is a particular case of stable distribution. Definition The probability density function, as written originally by Landau, is defined by the complex integral: :p(x) = \frac \int_^ e^\, ds , where ''a'' is an arbitrary positive real number, meaning that the integration path can be any parallel to the imaginary axis, intersecting the real positive semi-axis, and \log refers to the natural logarithm. In other words it is the Laplace transform of the function s^s. The following real integral is equivalent to the above: :p(x) = \frac \int_0^\infty e^ \sin(\pi t)\, dt. The full family of Landau distributions is obtained by extending the original distribution to a location-scale family of stable distributions with parameters \alpha=1 and \beta=1, with ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landau Distribution PDF
Landau ( pfl, Landach), officially Landau in der Pfalz, is an autonomous (''kreisfrei'') town surrounded by the Südliche Weinstraße ("Southern Wine Route") district of southern Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It is a university town (since 1990), a long-standing cultural centre, and a market and shopping town, surrounded by vineyards and wine-growing villages of the Palatinate (wine region), Palatinate wine region. Landau lies east of the Palatinate forest, on the German Wine Route. It contains the districts (''Ortsteile'') of Arzheim, Dammheim, Godramstein, Mörlheim, Mörzheim, Nussdorf, Queichheim, and Wollmesheim. History Landau was first mentioned as a settlement in 1106. It was in the possession of the counts of Leiningen-Dagsburg-Landeck, whose arms, differenced by an Escutcheon (heraldry), escutcheon of the Imperial eagle, served as the arms of Landau until 1955. The town was granted a charter in 1274 by King Rudolph I of Germany, Rudolf I of Kingdom of Germany, Germany, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laplace Transform
In mathematics, the Laplace transform, named after its discoverer Pierre-Simon Laplace (), is an integral transform In mathematics, an integral transform maps a function from its original function space into another function space via integration, where some of the properties of the original function might be more easily characterized and manipulated than in ... that converts a Function (mathematics), function of a Real number, real Variable (mathematics), variable (usually t, in the ''time domain'') to a function of a Complex number, complex variable s (in the complex frequency domain, also known as ''s''-domain, or s-plane). The transform has many applications in science and engineering because it is a tool for solving differential equations. In particular, it transforms ordinary differential equations into algebraic equations and convolution into multiplication. For suitable functions ''f'', the Laplace transform is the integral \mathcal\(s) = \int_0^\infty f(t)e^ \, dt. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Laws
In statistics, a power law is a functional relationship between two quantities, where a relative change in one quantity results in a proportional relative change in the other quantity, independent of the initial size of those quantities: one quantity varies as a power of another. For instance, considering the area of a square in terms of the length of its side, if the length is doubled, the area is multiplied by a factor of four. Empirical examples The distributions of a wide variety of physical, biological, and man-made phenomena approximately follow a power law over a wide range of magnitudes: these include the sizes of craters on the moon and of solar flares, the foraging pattern of various species, the sizes of activity patterns of neuronal populations, the frequencies of words in most languages, frequencies of family names, the species richness in clades of organisms, the sizes of power outages, volcanic eruptions, human judgments of stimulus intensity and many other quantit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability Distributions With Non-finite Variance
Probability is the branch of mathematics concerning numerical descriptions of how likely an event is to occur, or how likely it is that a proposition is true. The probability of an event is a number between 0 and 1, where, roughly speaking, 0 indicates impossibility of the event and 1 indicates certainty."Kendall's Advanced Theory of Statistics, Volume 1: Distribution Theory", Alan Stuart and Keith Ord, 6th Ed, (2009), .William Feller, ''An Introduction to Probability Theory and Its Applications'', (Vol 1), 3rd Ed, (1968), Wiley, . The higher the probability of an event, the more likely it is that the event will occur. A simple example is the tossing of a fair (unbiased) coin. Since the coin is fair, the two outcomes ("heads" and "tails") are both equally probable; the probability of "heads" equals the probability of "tails"; and since no other outcomes are possible, the probability of either "heads" or "tails" is 1/2 (which could also be written as 0.5 or 50%). These conce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuous Distributions
Continuity or continuous may refer to: Mathematics * Continuity (mathematics), the opposing concept to discreteness; common examples include ** Continuous probability distribution or random variable in probability and statistics ** Continuous game, a generalization of games used in game theory ** Law of Continuity, a heuristic principle of Gottfried Leibniz * Continuous function, in particular: ** Continuity (topology), a generalization to functions between topological spaces ** Scott continuity, for functions between posets ** Continuity (set theory), for functions between ordinals ** Continuity (category theory), for functors ** Graph continuity, for payoff functions in game theory * Continuity theorem may refer to one of two results: ** Lévy's continuity theorem, on random variables ** Kolmogorov continuity theorem, on stochastic processes * In geometry: ** Parametric continuity, for parametrised curves ** Geometric continuity, a concept primarily applied to the conic secti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
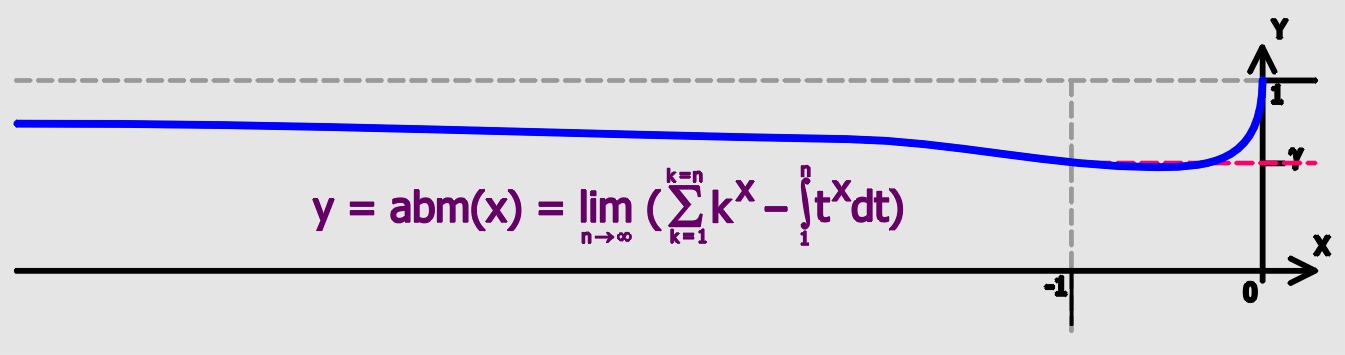
Euler's Constant
Euler's constant (sometimes also called the Euler–Mascheroni constant) is a mathematical constant usually denoted by the lowercase Greek letter gamma (). It is defined as the limiting difference between the harmonic series and the natural logarithm, denoted here by \log: :\begin \gamma &= \lim_\left(-\log n + \sum_^n \frac1\right)\\ px&=\int_1^\infty\left(-\frac1x+\frac1\right)\,dx. \end Here, \lfloor x\rfloor represents the floor function. The numerical value of Euler's constant, to 50 decimal places, is: : History The constant first appeared in a 1734 paper by the Swiss mathematician Leonhard Euler, titled ''De Progressionibus harmonicis observationes'' (Eneström Index 43). Euler used the notations and for the constant. In 1790, Italian mathematician Lorenzo Mascheroni used the notations and for the constant. The notation appears nowhere in the writings of either Euler or Mascheroni, and was chosen at a later time perhaps because of the constant's connect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lindhard Theory
In condensed matter physics, Lindhard theoryN. W. Ashcroft and N. D. Mermin, ''Solid State Physics'' (Thomson Learning, Toronto, 1976) is a method of calculating the effects of electric field screening by electrons in a solid. It is based on quantum mechanics (first-order perturbation theory) and the random phase approximation. It is named after Danish physicist Jens Lindhard, who first developed the theory in 1954. Thomas–Fermi screening and the plasma oscillations can be derived as a special case of the more general Lindhard formula. In particular, Thomas–Fermi screening is the limit of the Lindhard formula when the wavevector (the reciprocal of the length-scale of interest) is much smaller than the Fermi wavevector, i.e. the long-distance limit. The Lorentz–Drude expression for the plasma oscillations are recovered in the dynamic case (long wavelengths, finite frequency). This article uses cgs-Gaussian units. Formula The Lindhard formula for the longitudinal dielec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affine Transformations
In Euclidean geometry, an affine transformation or affinity (from the Latin, ''affinis'', "connected with") is a geometric transformation that preserves lines and parallelism, but not necessarily Euclidean distances and angles. More generally, an affine transformation is an automorphism of an affine space (Euclidean spaces are specific affine spaces), that is, a function which maps an affine space onto itself while preserving both the dimension of any affine subspaces (meaning that it sends points to points, lines to lines, planes to planes, and so on) and the ratios of the lengths of parallel line segments. Consequently, sets of parallel affine subspaces remain parallel after an affine transformation. An affine transformation does not necessarily preserve angles between lines or distances between points, though it does preserve ratios of distances between points lying on a straight line. If is the point set of an affine space, then every affine transformation on can be repres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landau Pdf
Landau ( pfl, Landach), officially Landau in der Pfalz, is an autonomous (''kreisfrei'') town surrounded by the Südliche Weinstraße ("Southern Wine Route") district of southern Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It is a university town (since 1990), a long-standing cultural centre, and a market and shopping town, surrounded by vineyards and wine-growing villages of the Palatinate wine region. Landau lies east of the Palatinate forest, on the German Wine Route. It contains the districts (''Ortsteile'') of Arzheim, Dammheim, Godramstein, Mörlheim, Mörzheim, Nussdorf, Queichheim, and Wollmesheim. History Landau was first mentioned as a settlement in 1106. It was in the possession of the counts of Leiningen-Dagsburg-Landeck, whose arms, differenced by an escutcheon of the Imperial eagle, served as the arms of Landau until 1955. The town was granted a charter in 1274 by King Rudolf I of Germany, who declared the town a Free Imperial Town in 1291; nevertheless Prince-Bishop Emich of S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Characteristic Function (probability Theory)
In probability theory and statistics, the characteristic function of any real-valued random variable completely defines its probability distribution. If a random variable admits a probability density function, then the characteristic function is the Fourier transform of the probability density function. Thus it provides an alternative route to analytical results compared with working directly with probability density functions or cumulative distribution functions. There are particularly simple results for the characteristic functions of distributions defined by the weighted sums of random variables. In addition to univariate distributions, characteristic functions can be defined for vector- or matrix-valued random variables, and can also be extended to more generic cases. The characteristic function always exists when treated as a function of a real-valued argument, unlike the moment-generating function. There are relations between the behavior of the characteristic function of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stable Distributions
In probability theory, a distribution is said to be stable if a linear combination of two independent random variables with this distribution has the same distribution, up to location and scale parameters. A random variable is said to be stable if its distribution is stable. The stable distribution family is also sometimes referred to as the Lévy alpha-stable distribution, after Paul Lévy, the first mathematician to have studied it.B. Mandelbrot, The Pareto–Lévy Law and the Distribution of Income, International Economic Review 1960 https://www.jstor.org/stable/2525289 Of the four parameters defining the family, most attention has been focused on the stability parameter, \alpha (see panel). Stable distributions have 0 < \alpha \leq 2, with the upper bound corresponding to the , and to the Cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |