|
Lambda Aquarii
Lambda Aquarii, informally known as Hydor (), is a variable star in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. The name is Latinized from the Bayer designation λ Aquarii. The apparent visual magnitude of this star ranges from 3.57 down to 3.80, which is bright enough to be visible with the naked eye. It lies just 0.39 degrees south of the ecliptic and so is subject to lunar occultations. The star is eclipsed by the sun from about 1-4 March; thus the star can be viewed the whole night, crossing the sky, in early September, in the current epoch. Lambda Aquarii is located at a distance of approximately from the Sun based on parallax, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −10.5 km/s. The stellar classification of Lambda Aquarii is , indicating this is an aging red giant star with an underabundance of iron showing in its spectrum. This star is on the asymptotic giant branch and is generating energy through the nuclear fusion of hydrogen and helium along con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquarius (constellation)
Aquarius is an celestial equator, equatorial constellation of the zodiac, between Capricornus and Pisces (constellation), Pisces. Its name is Latin for "water-carrier" or "cup-carrier", and its old astronomical symbol is (♒︎), a representation of water. Aquarius is one of the oldest of the recognized constellations along the zodiac (the Sun's apparent path). It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is found in a region often called the Sea (astronomy), Sea due to its profusion of constellations with watery associations such as Cetus the whale, Pisces (constellation), Pisces the fish, and Eridanus (constellation), Eridanus the river. At apparent magnitude 2.9, Beta Aquarii is the brightest star in the constellation. History and mythology Aquarius is identified as "The Great One" in the Babylonian star catalogues and represents the god Ea (god), Ea himself, who is commonly depic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iota Aquarii
Iota Aquarii, Latinised from ι Aquarii, is the Bayer designation for a binary star system in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent magnitude of +4.279. Based upon parallax measurements made during the ''Hipparcos'' mission, the distance to this star is around . The system is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −10 km/s. The binary nature of this system was reported in 2009 following a radial velocity survey using the HARPS instrument. A 2010 infrared search for companions around this star was unsuccessful. The presence of a stellar companion was confirmed through direct spectral detection in 2016. The companion shows a significant velocity variation over a 77-day interval, suggesting a short orbital period. The spectrum of the primary, component A, fits a stellar classification of B8 V, showing that this is a B-type main-sequence star. It is roughly 124 million years old and is spinnin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
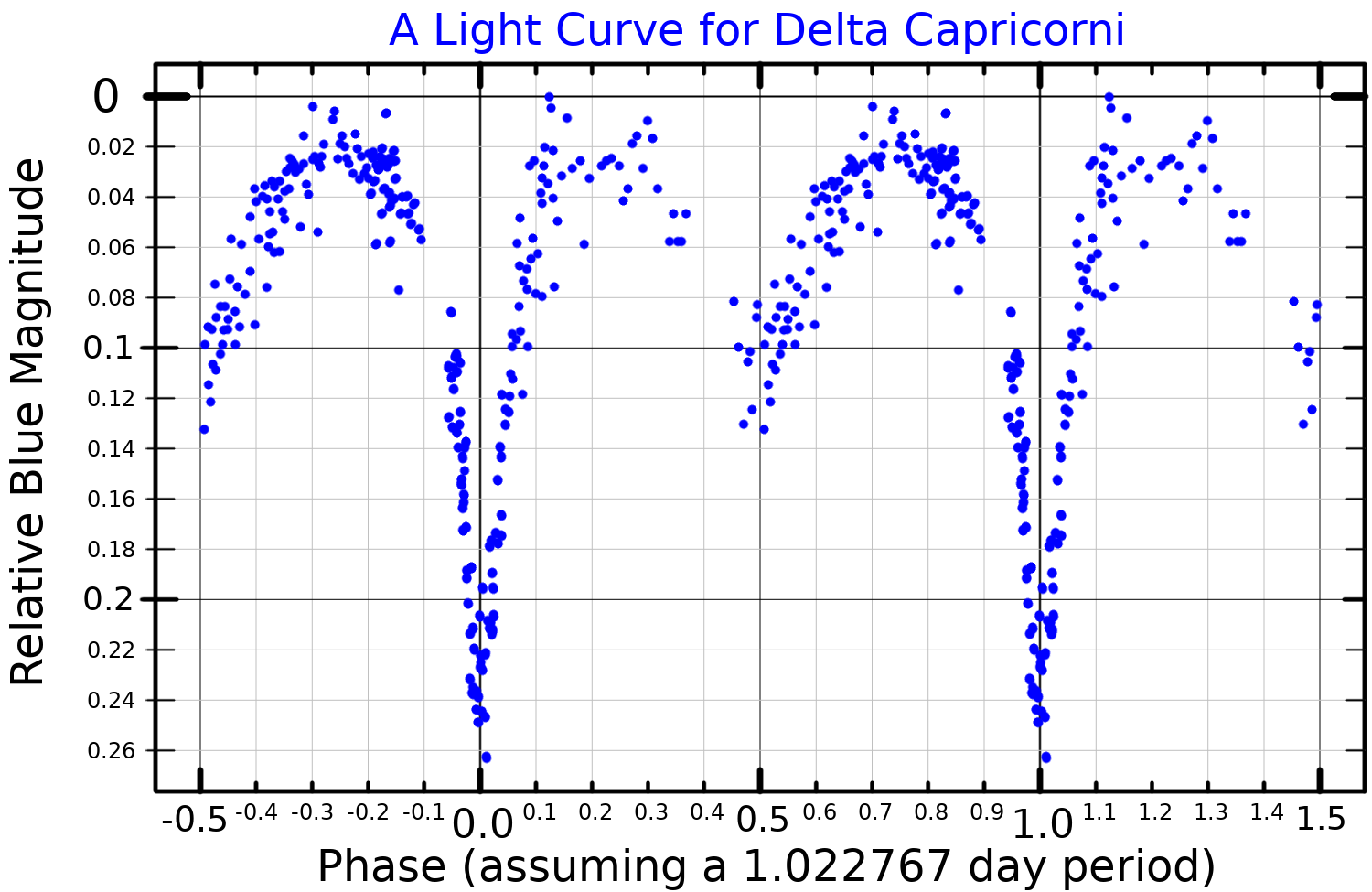
Delta Capricorni
Delta Capricorni, or δ Capricorni, is a binary star located 38,7 light-years from the Sun in the constellation of Capricornus (the Sea Goat). The system consists of an eclipsing binary, Delta Capricorni A, and two visual companions that are over 10 magnitudes fainter, labeled B and C. Delta Capricorni A's two components are designated Delta Capricorni Aa (formally named Deneb Algedi , the traditional name of the system) and Ab. The primary star, Aa, is a white giant and the combined light of Aa and Ab makes it the brightest star in the constellation. Delta Capricorni is 2.6 degrees south of the ecliptic and can be occulted by the Moon, and (rarely) by planets. Nomenclature ''δ Capricorni'' ( Latinised to ''Delta Capricorni'') is the system's Bayer designation. The designations of the three constituents as ''Delta Capricorni A'', ''B'' and ''C'', and those of ''A's'' components – ''Delta Capricorni Aa'' and ''Ab'' – derive from the convention used by the Washin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Capricorni
Gamma Capricorni or γ Capricorni, formally named Nashira (), is a giant star in the constellation of Capricornus. Based on parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, it is located at a distance of approximately 157 light-years from the Sun. The star is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −31 km/s. It is 2.56 degrees south of the ecliptic, so it can be occulted by the Moon, and (rarely) by planets. Nomenclature ''γ Capricorni'' ( Latinised to ''Gamma Capricorni'') is the star's Bayer designation. It bore the traditional name ''Nashira'', derived from the Arabic سعد ناشرة ''sa'd nashirah'' "the lucky one" or "bearer of good news". In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) to catalogue and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN approved the name ''Nashira'' for this star on 21 August 2016 and it is now so included in the List of IAU-approved Star Names. In Chinese, (), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epsilon Capricorni
Epsilon Capricorni, Latinized from ε Capricorni, is a possible binary star system in the constellation Capricornus. It has the traditional star name Kastra, meaning "fort" or "military camp" in Latin. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 3.09 mas as seen from the Earth, the star is located about 1,060 light years from the Sun. It can be seen with the naked eye, having a combined apparent visual magnitude of 4.62. In Chinese, (), meaning '' Line of Ramparts'', refers to an asterism consisting of ε Capricorni, κ Capricorni, γ Capricorni, δ Capricorni, ι Aquarii, σ Aquarii, λ Aquarii, φ Aquarii, 27 Piscium, 29 Piscium, 33 Piscium and 30 Piscium. Consequently, the Chinese name for ε Capricorni itself is (, en, the Second Star of Line of Ramparts.) The binary system has an orbital period of 129 days. The primary, component Aa, is a Be star that is surrounded by ionized gas that is producing the emission lines in the spectrum. This circ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kappa Capricorni
Kappa Capricorni (κ Cap, κ Capricorni) is a solitary star in the constellation Capricornus. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +4.73. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 11.09 mas as seen from the Earth, the star is located about 294 light years from the Sun. This is a yellow-hued, evolved, G-type giant star with a stellar classification of G8 III. There is a 91% probability that it is currently on the horizontal branch, rather than the red giant branch. As such, it is a red clump giant with an estimated 2.43 times the mass of the Sun and has expanded to 13.28 times the radius of the Sun. The star is about 1.2 billion years old and has a projected rotational velocity that is too small to be measured. It radiates 107 times the solar luminosity from its photosphere at an effective temperature The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total amou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encampment (Chinese Constellation)
The Encampment mansion () is one of the 28 mansions of the Chinese constellations. It is one of the northern mansions of the Black Tortoise The Black Tortoise () is one of the Four Symbols of the Chinese constellations. Despite its English name, it is usually depicted as a tortoise entwined together with a snake. The name used in East Asian languages does not mention either anima .... Asterisms References {{DEFAULTSORT:Encampment (Chinese Constellation) Chinese constellations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Astronomy
Astronomy in China has a long history stretching from the Shang dynasty, being refined over a period of more than 3,000 years. The ancient Chinese people have identified stars from 1300 BCE, as Chinese star names later categorized in the twenty-eight mansions have been found on oracle bones unearthed at Anyang, dating back to the mid-Shang dynasty. The core of the "mansion" (宿 ''xiù'') system also took shape around this period, by the time of King Wu Ding (1250–1192 BCE). Detailed records of astronomical observations began during the Warring States period (fourth century BCE) and flourished from the Han period onward. Chinese astronomy was equatorial, centered on close observation of circumpolar stars, and was based on different principles from those in traditional Western astronomy, where heliacal risings and settings of zodiac constellations formed the basic ecliptic framework. Joseph Needham has described the ancient Chinese as the most persistent and accurate obser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Hinckley Allen
In astronomy, stars have a variety of different stellar designations and names, including catalogue designations, current and historical proper names, and foreign language names. Only a tiny minority of known stars have proper names; all others have only designations from various catalogues or lists, or no identifier at all. Hipparchus in the 2nd century BC enumerated about 850 naked-eye stars. Johann Bayer in 1603 listed about twice this number. Only in the 19th century did star catalogues list the naked-eye stars exhaustively. The Bright Star Catalogue, which is a star catalogue listing all stars of apparent magnitude 6.5 or brighter, or roughly every star visible to the naked eye from Earth, contains 9,096 stars. The most voluminous modern catalogues list on the order of a billion stars, out of an estimated total of 200 to 400 billion in the Milky Way. Proper names may be historical, often transliterated from Arabic or Chinese names. Such transliterations can vary so there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proclus
Proclus Lycius (; 8 February 412 – 17 April 485), called Proclus the Successor ( grc-gre, Πρόκλος ὁ Διάδοχος, ''Próklos ho Diádokhos''), was a Greek Neoplatonist philosopher, one of the last major classical philosophers of late antiquity. He set forth one of the most elaborate and fully developed systems of Neoplatonism and, through later interpreters and translators, exerted an influence on Byzantine philosophy, Early Islamic philosophy, and Scholastic philosophy. Biography The primary source for the life of Proclus is the eulogy ''Proclus, or On Happiness'' that was written for him upon his death by his successor, Marinus, Marinus' biography set out to prove that Proclus reached the peak of virtue and attained eudaimonia. There are also a few details about the time in which he lived in the similarly structured ''Life of Isidore'' written by the philosopher Damascius in the following century. According to Marinus, Proclus was born in 412 AD in Cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Effective Temperature
The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total amount of electromagnetic radiation. Effective temperature is often used as an estimate of a body's surface temperature when the body's emissivity curve (as a function of wavelength) is not known. When the star's or planet's net emissivity in the relevant wavelength band is less than unity (less than that of a black body), the actual temperature of the body will be higher than the effective temperature. The net emissivity may be low due to surface or atmospheric properties, including greenhouse effect. Star The effective temperature of a star is the temperature of a black body with the same luminosity per ''surface area'' () as the star and is defined according to the Stefan–Boltzmann law . Notice that the total (bolometric) luminosity of a star is then , where is the stellar radius. The definition of the stellar radius is obviously not straightf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |