|
Lai Tay Script
The Lai Tay script, ( vi, Chữ Thái Lai Tay), is a writing system used by the Tai Yo people of Quỳ Châu District, to write the Tai Yo language. Names The Lai Tay script means "the script of the Tai". It is also known by various other names such as the ''Yo Lai Tay'' script, ''Nge An script'', ''Tai Yo script'', ''Thai Lai Tay script'', ''Quy Chau script''. Origin The scholar Ferlus classifies the Lai Tay script as a part of the Khmer family of writing systems, which the scholar divides into two groups: the central scripts consisting of the ancient Sukhothai and Fakkham scripts, which developed into the modern Thai and Lao scripts, and the peripheral scripts of the Tai peoples of Vietnam, which include the Tai Dam, Tai Don, Tai Daeng, Lai Tay and Lai Pao scripts. Ferlus suggest that the Tai peoples all adopted the same first model of writing borrowed from the Khmers, by simple contact during exchanges, without proper learning. Subsequently, the Tai migrated and occup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tai Yo Language
Tai Yo ( th, ไทญ้อ), also known as Tai Mène and Nyaw, is a Tai languages, Tai language of Southeast Asia. It is closely related to Tai Pao language, Tai Pao of Vietnam, where it may have originated. It was once written in a unique script, the Tai Yo script, but that is no longer in use. The language is known regionally in Laos and Thailand as ''Tai Mène'' and ''Tai Nyaw'' and, in Vietnam as ''Tai Do'' (old-fashioned English transcription) and ''Tai Quy Chau''. Superficially, Tai Yo appears to be a Southwestern Tai language but this is only because of centuries of language contact and it is properly classified with the Northern Tai languages. The Lao Nyo language, ''Nyaw''/''Nyo'' spoken in central Thailand and western Cambodia is not the same as Tai Yo.Thananan (2014) Tai Mène (Tai Maen) The Mène people of Laos claim to be from Xieng Mène (also Xieng My) in Vietnam. These two names correspond to the following two towns in Nghệ An Province, Vietnam, located near Qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sukhothai Script
The Sukhothai script, also known as the ''proto-Thai script'' and ''Ram Khamhaeng alphabet'', is a Brahmic script which originated in the Sukhothai Kingdom. The script is found on the Ram Khamhaeng Inscription and the ''Lö Thai inscription''. History Origin The source of the Sukhothai script was cursive Khmer script, Khmer letters, which were formed by dissections, truncations and removal of flourishes from the original Khmer script. Scholar Michel Ferlus has demonstrated that certain peculiarities of ancient and modern Tai scripts can only be explained by inadequacies and gaps in the ancient Khmer script, in particular the pre-Angkorian Khmer script. The Sukhothai script is first attested on the Ram Khamhaeng stele, which is dated between 1283 and 1290, but it is the result of the modification of an unattested pre-existing script, based on the Khmer script. Ferlus theorizes that the pre-existing script may have developed during the pre-Angkorian period (7th-8th centuries), whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Script
Chinese characters () are logograms developed for the writing of Chinese. In addition, they have been adapted to write other East Asian languages, and remain a key component of the Japanese writing system where they are known as ''kanji''. Chinese characters in South Korea, which are known as ''hanja'', retain significant use in Korean academia to study its documents, history, literature and records. Vietnam once used the ''chữ Hán'' and developed chữ Nôm to write Vietnamese before turning to a romanized alphabet. Chinese characters are the oldest continuously used system of writing in the world. By virtue of their widespread current use throughout East Asia and Southeast Asia, as well as their profound historic use throughout the Sinosphere, Chinese characters are among the most widely adopted writing systems in the world by number of users. The total number of Chinese characters ever to appear in a dictionary is in the tens of thousands, though most are graphic v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abugida
An abugida (, from Ge'ez language, Ge'ez: ), sometimes known as alphasyllabary, neosyllabary or pseudo-alphabet, is a segmental Writing systems#Segmental writing system, writing system in which consonant-vowel sequences are written as units; each unit is based on a consonant letter, and vowel notation is secondary. This contrasts with a full alphabet, in which vowels have status equal to consonants, and with an abjad, in which vowel marking is absent, Abjad#Impure abjads, partial, or optional (although in less formal contexts, all three types of script may be termed alphabets). The terms also contrast them with a syllabary, in which the symbols cannot be split into separate consonants and vowels. Related concepts were introduced independently in 1948 by James Germain Février (using the term ) and David Diringer (using the term ''semisyllabary''), then in 1959 by Fred Householder (introducing the term ''pseudo-alphabet''). The Ethiopian Semitic languages, Ethiopic term "abugi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tai Peoples
Tai peoples are the populations who speak (or formerly spoke) the Tai languages. There are a total of about 93 million people of Tai ancestry worldwide, with the largest ethnic groups being Dai, Thais, Isan, Tai Yai (Shan), Lao, Tai Ahom, and Northern Thai peoples. The Tai are scattered through much of South China and Mainland Southeast Asia, with some (''e.g.'' Tai Ahom, Tai Khamti, Tai Phake, Tai Aiton) inhabiting parts of Northeast India. Tai peoples are both culturally and genetically very similar and therefore primarily identified through their language. Names Speakers of the many languages in the Tai branch of the Tai–Kadai language family are spread over many countries in Southern China, Indochina and Northeast India. Unsurprisingly, there are many terms used to describe the distinct Tai peoples of these regions. According to Michel Ferlus, the ethnonyms Tai/Thai (or Tay/Thay) would have evolved from the etymon *k(ə)ri: 'human being' through the following cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tai Viet Script
The Tai Viet script (Tai Dam: ("Tai script"), Vietnamese: Chữ Thái Việt) ( th, อักษรไทดำ, ) is a Brahmic script used by the Tai Dam people and various other Thai people in Vietnam and Thailand.Bảng chữ cái tiếng Thái (Việt Nam), các quy tắc cơ bản Lịch sử văn hóa Thái, 26/06/2018. In vietnamese. History According to Thai authors, the is probably derived from the old Thai writing of the kingdom of Sukhotai.[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making it the world's sixteenth-most populous country. Vietnam borders China to the north, and Laos and Cambodia to the west. It shares maritime borders with Thailand through the Gulf of Thailand, and the Philippines, Indonesia, and Malaysia through the South China Sea. Its capital is Hanoi and its largest city is Ho Chi Minh City (commonly known as Saigon). Vietnam was inhabited by the Paleolithic age, with states established in the first millennium BC on the Red River Delta in modern-day northern Vietnam. The Han dynasty annexed Northern and Central Vietnam under Chinese rule from 111 BC, until the first dynasty emerged in 939. Successive monarchical dynasties absorbed Chinese influences through Confucianism and Buddhism, and expanded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lao Script
Lao script or Akson Lao ( lo, ອັກສອນລາວ, links=no ) is the primary script used to write the Lao language and other minority languages in Laos. Its earlier form, the Tai Noi script, was also used to write the Isan language, but was replaced by the Thai script. It has 27 consonants ( ), 7 consonantal ligatures ( ), 33 vowels (/ ), and 4 tone marks ( ). The Lao alphabet was adapted from the Khmer script, which itself was derived from the Pallava script, a variant of the Grantha script descended from the Brāhmī script, which was used in southern India and South East Asia during the 5th and 6th centuries AD. Akson Lao is a sister system to the Thai script, with which it shares many similarities and roots. However, Lao has fewer characters and is formed in a more curvilinear fashion than Thai. Lao is written from left to right. Vowels can be written above, below, in front of, or behind consonants, with some vowel combinations written before, over, and after. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
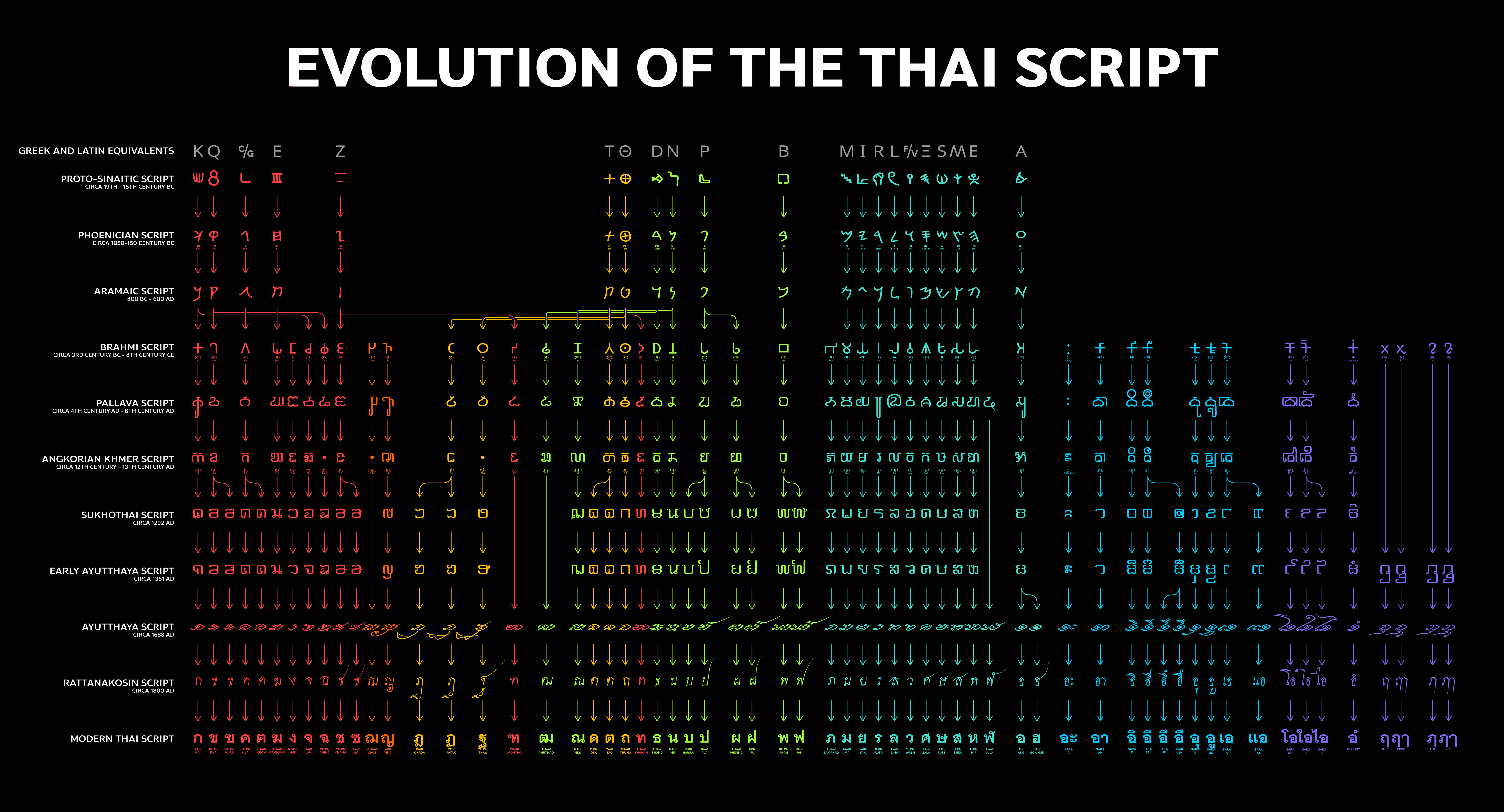
Thai Script
The Thai script ( th, อักษรไทย, ) is the abugida used to write Thai, Southern Thai and many other languages spoken in Thailand. The Thai alphabet itself (as used to write Thai) has 44 consonant symbols ( th, พยัญชนะ, ''phayanchana''), 16 vowel symbols ( th, สระ, ''sara'') that combine into at least 32 vowel forms and four tone diacritics ( th, วรรณยุกต์ or วรรณยุต, or ) to create characters mostly representing syllables. Although commonly referred to as the "Thai alphabet", the script is in fact not a true alphabet but an abugida, a writing system in which the full characters represent consonants with diacritical marks for vowels; the absence of a vowel diacritic gives an implied 'a' or 'o'. Consonants are written horizontally from left to right, and vowels following a consonant in speech are written above, below, to the left or to the right of it, or a combination of those. History The Thai alphabet is deri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fakkham Script
The Fakkham script ( th, อักษรฝักขาม, "''Tamarind pod-script''") or Thai Lanna script is a Brahmic script, used historically in the Lan Na Kingdom. The script was frequently used in Lan Na stone inscriptions. Origin The Fakkham script, was derived from the old Sukhothai script (also known as ''Proto-Thai script''), and used extensively in Lan Na between the beginning of the 15th century and the end of the 16th century. The Fakkham script was possibly introduced to Lan Na by a religious mission from Sukhothai. The script was named after its similarity to the shape of tamarind pods, because the letters became elongated and somewhat more angular rather than square and perpendicular like its ancestor the Sukhothai script. Several letters had noticeable "tails" extending above and below the main writing line. History The Fakkham script was used extensively in the territories controlled by the kings of Chiang Mai, the Lan Na kingdom, between the beginning of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Sinaitic Alphabet
Proto-Sinaitic (also referred to as Sinaitic, Proto-Canaanite when found in Canaan, the North Semitic alphabet, or Early Alphabetic) is considered the earliest trace of alphabetic writing and the common ancestor of both the Ancient South Arabian script and the Phoenician alphabet, which led to many modern alphabets including the Greek alphabet. According to common theory, Canaanites or Hyksos who spoke a Semitic language repurposed Egyptian hieroglyphs to construct a different script. The script is attested in a small corpus of inscriptions found at Serabit el-Khadim in the Sinai Peninsula, Egypt, dating to the Middle Bronze Age (2100–1500 BC). The earliest Proto-Sinaitic inscriptions are mostly dated to between the mid-19th (early date) and the mid-16th (late date) century BC. However, the discovery of the Wadi el-Hol inscriptions near the Nile River indicates that the script originated in Egypt. The evolution of Proto-Sinaitic and the various Proto-Canaanite scripts during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)