|
Lahaina Roads
Lahaina Roads, also called the Lahaina Roadstead, is an anchorage in the ʻAuʻau Channel lying off the town of Lahaina on the island of Maui in the Hawaiian archipelago and U.S. state of Hawaii. It lies in the lee of the West Maui Mountains, with the surrounding islands of Lānai (and to a lesser extent, Molokai and Kahoolawe) adding to its general shelter from dangerous winds and large waves. It is most vulnerable to both from the south in the long open fetch between southern Maui and Kahoolawe, as during a "Kona storm" from that direction. While protected from the trade winds (that hit the opposite side of West Maui) it is also subject to frequent heavy gusts and short sharp chop due to thermally induced gusts driven offshore from the West Mauis, and occasional wraparound from heavy winds in the Pailolo Channel between Maui and Molokai. The Roads lie in the Pacific Ocean in the area . Through the 1940s, it was an alternative anchorage to Pearl Harbor for the U.S. Pacific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anchorage (maritime)
An anchorage is a location at sea where ships can lower anchors. Anchorages are where anchors are lowered and utilised, whereas moorings usually are tethering to buoys or something similar. The locations usually have conditions for safe anchorage in protection from weather conditions, and other hazards. The purpose of resting a ship at sea securely can be for waiting to enter ports, as well as taking on cargo or passengers where insufficient port facilities exist. Some coastlines without port facilities have extensive anchorage locations. In the days of large-scale sailing ship operations, a ship could wait at an anchorage for the wind to change, allowing it to continue its journey. The mooring of large ships in locations with adequate conditions for secure berthing is an engineering task requiring considerable technical skill. History See also * Roadstead * Sea anchor A sea anchor (also known as a parachute anchor, drift anchor, drift sock, para-anchor or boat br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Oceania in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), this largest division of the World Ocean—and, in turn, the hydrosphere—covers about 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of its total surface area, larger than Earth's entire land area combined .Pacific Ocean . '' Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the |
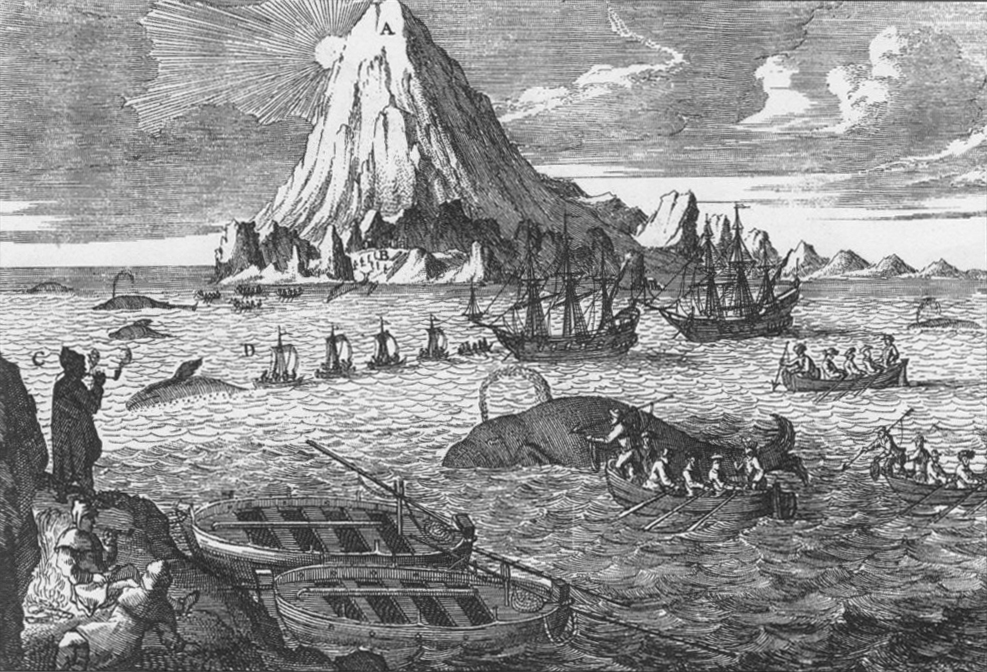
Whaling In The Hawaiian Kingdom
Whaling is the process of hunting of whales for their usable products such as meat and blubber, which can be turned into a type of oil that became increasingly important in the Industrial Revolution. It was practiced as an organized industry as early as 875 AD. By the 16th century, it had risen to be the principal industry in the Basque coastal regions of Spain and France. The industry spread throughout the world, and became increasingly profitable in terms of trade and resources. Some regions of the world's oceans, along the animals' migration routes, had a particularly dense whale population, and became the targets for large concentrations of whaling ships, and the industry continued to grow well into the 20th century. The depletion of some whale species to near extinction led to the banning of whaling in many countries by 1969, and to an international cessation of whaling as an industry in the late 1980s. The earliest known forms of whaling date to at least 3000 BC. Coastal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Channels Of Hawaii
In an archipelago like the Hawaiian Islands the water between islands is typically called a '' channel'' or ''passage''. Described here are the channels between the islands of Hawaiʻi, arranged from northwest to southeast. Kaulakahi Channel The Kaulakahi Channel separates the islands of Niʻihau and Kauaʻi. It is wide. Kaulakahi translates to "the single flame (streak of color)." Kaʻieʻie Waho Channel The Kaʻieʻie Waho Channel, also called the Kauai Channel,The Road Atlas of United States, Canada & Mexico (Rand McNally, 2004) p. 30. separates the islands of Kauaʻi and Oʻahu, at a distance of . Kaʻieʻie Waho means "Outer Kaʻieʻie," named after the ʻieʻie vine (''Freycinetia arborea''). The maximum depth of the channel is over 11000 feet. Kaiwi Channel The Kaiwi Channel (also known as the Molokai Channel) separates the islands of Oʻahu and Molokaʻi, and is wide. Maximum depth is . ''Ka Iwi'' means "the bone." There are annual paddleboarding and out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
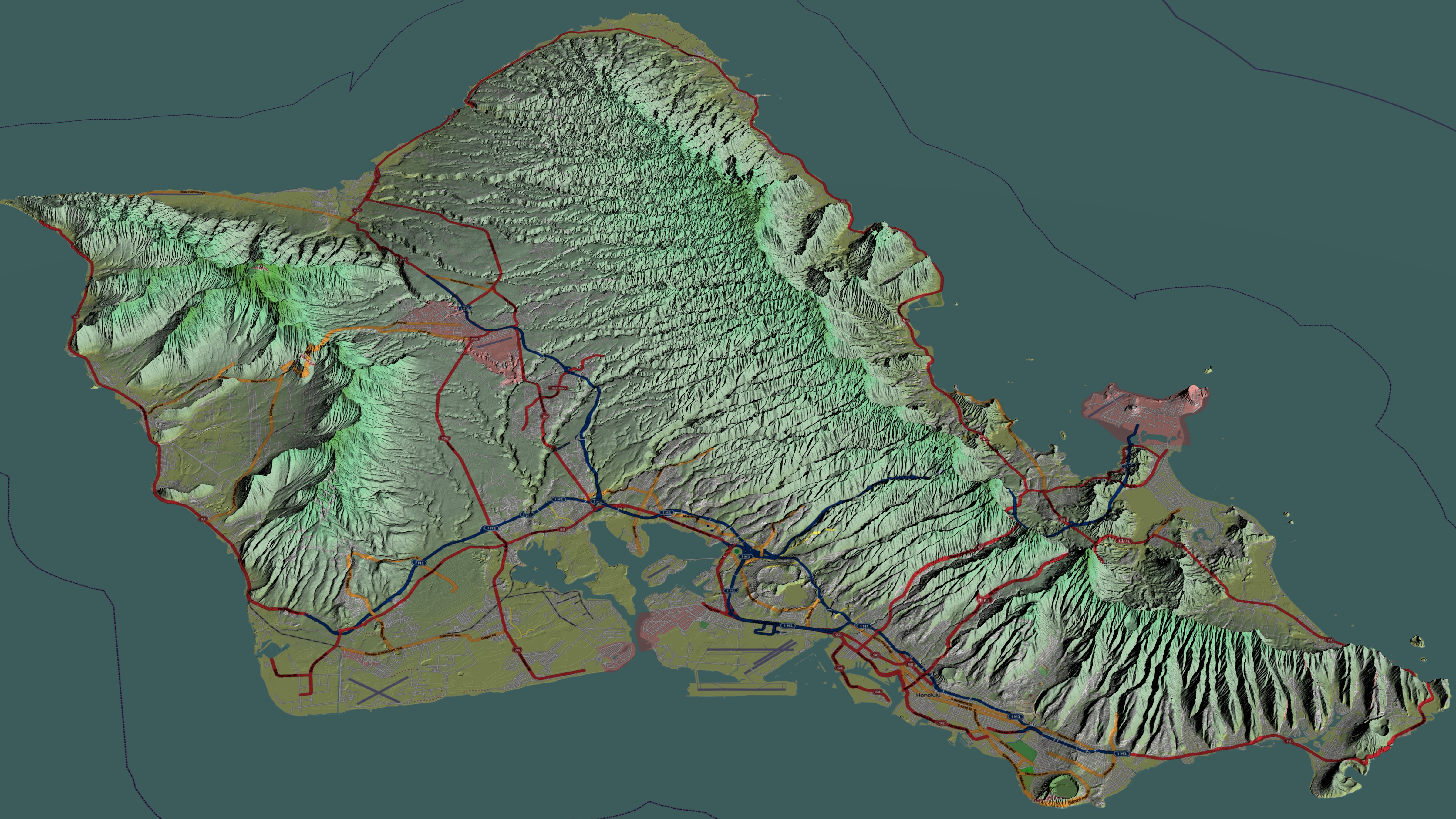
Oahu
Oahu () (Hawaiian language, Hawaiian: ''Oʻahu'' ()), also known as "The Gathering place#Island of Oʻahu as The Gathering Place, Gathering Place", is the third-largest of the Hawaiian Islands. It is home to roughly one million people—over two-thirds of the population of the U.S. state of Hawaii. The island of O’ahu and the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands constitute the City and County of Honolulu, Hawaii, City and County of Honolulu. The state capital, Honolulu, is on Oʻahu's southeast coast. Oʻahu had a population of 1,016,508 according to the 2020 U.S. Census, up from 953,207 people in 2010 (approximately 70% of the total 1,455,271 population of the State of Hawaii, with approximately 81% of those living in or near the Honolulu urban area). Name The Island of O{{okinaahu in Hawaii is often nicknamed (or translated as) ''"The Gathering Place"''. It appears that O{{okinaahu grew into this nickname; it is currently the most populated Hawaiian islands, Hawaiian Island, how ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ford Island
Ford Island ( haw, Poka Ailana) is an islet in the center of Pearl Harbor, Oahu, in the U.S. state of Hawaii. It has been known as Rabbit Island, Marín's Island, and Little Goats Island, and its native Hawaiian name is ''Mokuumeume''. The island had an area of when it was surveyed in 1825, which was increased during the 1930s to with fill dredged out of Pearl Harbor by the United States Navy to accommodate battleships. It was the site of an ancient Hawaiian fertility ritual, which was stopped by Christian missionaries during the 1830s. The island was given by Kamehameha I to Spanish deserter Francisco de Paula Marín, and later returned to the monarchy. After the island was bought at auction by James Isaac Dowsett and sold to Caroline Jackson, it became the property of Dr. Seth Porter Ford by marriage and was renamed Ford Island. After Ford's death, his son sold the island to the John Papa ʻĪʻī estate and it was converted into a sugarcane plantation. In 1916, part of Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attack On Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Territory of Hawaii, just before 8:00a.m. (local time) on Sunday, December 7, 1941. The United States was a neutral country at the time; the attack led to its formal entry into World War II the next day. The Japanese military leadership referred to the attack as the Hawaii Operation and Operation AI, and as Operation Z during its planning. Japan intended the attack as a preventive action. Its aim was to prevent the United States Pacific Fleet from interfering with its planned military actions in Southeast Asia against overseas territories of the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, and those of the United States. Over the course of seven hours there were coordinated Japanese attacks on the US-held Philippines, Guam, and Wake Island and on the British Empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kido Butai
The , also known as the ''Kidō Butai'' ("Mobile Force"), was a name used for a combined carrier battle group comprising most of the aircraft carriers and carrier air groups of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) during the first eight months of the Pacific War. At the time of its best-known operation, the attack on Pearl Harbor, in December 1941, the 1st Air Fleet was the world's largest fleet of aircraft carriers. In its second generation, 1st Air Fleet was a land-based fleet of "kichi kōkūtai" (base air unit(s)). Origins In 1912, the British Royal Navy had established its own flying branch, the Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS). The IJN was modeled on the Royal Navy and the IJN Admiralty sought establishment of their own Naval Air Service. The IJN had also observed technical developments in other countries and saw military potential of the airplane. In 1913, the IJN seaplane carrier ''Wakamiya'' was converted into a seaplane tender and aircraft were purchased. The 1st and 2nd Air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pearl Harbor
Pearl Harbor is an American lagoon harbor on the island of Oahu, Hawaii, west of Honolulu. It was often visited by the Naval fleet of the United States, before it was acquired from the Hawaiian Kingdom by the U.S. with the signing of the Reciprocity Treaty of 1875. Much of the harbor and surrounding lands are now a United States Navy deep-water naval base. It is also the headquarters of the United States Pacific Fleet. The U.S. government first obtained exclusive use of the inlet and the right to maintain a repair and coaling station for ships here in 1887. The surprise attack by the Imperial Japanese Navy on December 7, 1941, led the United States to declare war on the Empire of Japan, making the attack on Pearl Harbor the immediate cause of the United States' entry into World War II. History Pearl Harbor was originally an extensive shallow embayment called ''Wai Momi'' (meaning, “Waters of Pearl”) or ''Puuloa'' (meaning, “long hill”) by the Hawaiians. Puuloa was r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trade Winds
The trade winds or easterlies are the permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The trade winds blow mainly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisphere, strengthening during the winter and when the Arctic oscillation is in its warm phase. Trade winds have been used by captains of sailing ships to cross the world's oceans for centuries. They enabled colonial expansion into the Americas, and trade routes to become established across the Atlantic Ocean and the Pacific Ocean. In meteorology, they act as the steering flow for tropical storms that form over the Atlantic, Pacific, and southern Indian oceans and make landfall in North America, Southeast Asia, and Madagascar and East Africa. Shallow cumulus clouds are seen within trade wind regimes and are capped from becoming taller by a trade wind inversion, which is caused by descending air aloft from within the subtropical ridge. The weak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Channels Of The Hawaiian Islands
In an archipelago like the Hawaiian Islands the water between islands is typically called a '' channel'' or ''passage''. Described here are the channels between the islands of Hawaiʻi, arranged from northwest to southeast. Kaulakahi Channel The Kaulakahi Channel separates the islands of Niʻihau and Kauaʻi. It is wide. Kaulakahi translates to "the single flame (streak of color)." Kaʻieʻie Waho Channel The Kaʻieʻie Waho Channel, also called the Kauai Channel,The Road Atlas of United States, Canada & Mexico (Rand McNally, 2004) p. 30. separates the islands of Kauaʻi and Oʻahu, at a distance of . Kaʻieʻie Waho means "Outer Kaʻieʻie," named after the ʻieʻie vine (''Freycinetia arborea''). The maximum depth of the channel is over 11000 feet. Kaiwi Channel The Kaiwi Channel (also known as the Molokai Channel) separates the islands of Oʻahu and Molokaʻi, and is wide. Maximum depth is . ''Ka Iwi'' means "the bone." There are annual paddleboarding and outrigge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kahoolawe
Kahoolawe (Hawaiian: ), anglicized as Kahoolawe (), is the smallest of the eight main volcanic islands in the Hawaiian Islands. Kahoolawe is located about southwest of Maui and also southeast of Lānaʻi, and it is long by wide, with a total land area of . The highest point on Kahoolawe is the crater of Lua Makika at the summit of Puu Moaulanui, which is about above sea level. Kahoolawe is relatively dry (average annual rainfall is less than ) because the island's low elevation fails to generate much orographic precipitation from the northeastern trade winds, and Kahoʻolawe is located in the rain shadow of eastern Maui's volcano, Haleakalā. More than one quarter of Kahoolawe has been eroded down to saprolitic hardpan soil, largely on exposed surfaces near the summit. Kahoolawe has always been sparsely populated, due to its lack of fresh water. During World War II and the following decades, Kahoolawe was used as a training ground and bombing range by the Armed Forces of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)