|
La Sal Mountains
The La Sal Mountains or La Sal Range are a mountain range located in Grand and San Juan counties in the U.S. state of Utah, along the border with Colorado. The range rises above and southeast of Moab and north of the town of La Sal. This range is part of the Manti-La Sal National Forest and the southern Rocky Mountains. The maximum elevation is at Mount Peale, reaching above sea level. The range contains three clusters of peaks separated by passes. The peaks span a distance of about . The name of the range dates to Spanish times, when the Sierra La Sal (meaning the "Salt Mountains") was a prominent landmark on the Old Spanish Trail between Santa Fe and Los Angeles. Geology The range formed due to intrusion of igneous rocks and subsequent erosion of the surrounding less-resistant sedimentary rocks. The most abundant igneous rocks are porphyritic, with phenocrysts of hornblende and plagioclase: these rocks are called diorite in some accounts but trachyte in at least one o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arches National Park
Arches National Park is a national park in eastern Utah, United States. The park is adjacent to the Colorado River, north of Moab, Utah. More than 2,000 natural sandstone arches are located in the park, including the well-known Delicate Arch, as well as a variety of unique geological resources and formations. The park contains the highest density of natural arches in the world. The park consists of of high desert located on the Colorado Plateau. The highest elevation in the park is at Elephant Butte, and the lowest elevation is at the visitor center. The park receives an average of less than of rain annually. Administered by the National Park Service, the area was originally named a national monument on April 12, 1929, and was redesignated as a national park on November 12, 1971. The park received more than 1.6 million visitors in 2018. Park purpose As stated in the foundation document in U.S. National Park Service website: Geology The national park lies above an unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diorite
Diorite ( ) is an intrusive igneous rock formed by the slow cooling underground of magma (molten rock) that has a moderate content of silica and a relatively low content of alkali metals. It is intermediate in composition between low-silica (mafic) gabbro and high-silica ( felsic) granite. Diorite is found in mountain-building belts (''orogens'') on the margins of continents. It has the same composition as the fine-grained volcanic rock, andesite, which is also common in orogens. Diorite has been used since prehistoric times as decorative stone. It was used by the Akkadian Empire of Sargon of Akkad for funerary sculptures, and by many later civilizations for sculptures and building stone. Description Diorite is an intrusive igneous rock composed principally of the silicate minerals plagioclase feldspar (typically andesine), biotite, hornblende, and sometimes pyroxene. The chemical composition of diorite is intermediate, between that of mafic gabbro and felsic grani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Bare Peak Of La Sal
A, or a, is the first Letter (alphabet), letter and the first vowel of the Latin alphabet, Latin alphabet, used in the English alphabet, modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is English alphabet#Letter names, ''a'' (pronounced ), plural English alphabet#Letter names, ''aes''. It is similar in shape to the Greek alphabet#History, Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives. The Letter case, uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version can be written in two forms: the double-storey a and single-storey ɑ. The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type. In English grammar, "English articles, a", and its variant "English articles#Indefinite article, an", are Article (grammar)#Indefinite article, indefinite arti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ute Mountain
Ute Mountain, also known as Ute Peak or Sleeping Ute Mountain (; Ute: ''Wisuv Káruv'', Navajo: ''Dził Naajiní''), is a peak within the Ute Mountains, a small mountain range in the southwestern corner of Colorado. It is on the northern edge of the Ute Mountain Ute Tribe Reservation. The Reservation forms the southwestern corner of the state and of Montezuma County. Nomenclature for this peak and its range varies. The highest peak is sometimes known as Sleeping Ute Mountain; the entire range is also identified as one large mountain, called Sleeping Ute Mountain, on some maps; and the range is sometimes called the Sleeping Ute Mountains. All of these forms of the mountain's name and of the range's name can be found on various USGS maps, databases and reports. The Ute Mountains, with a collective profile commonly known as "The Sleeping Ute", are a dense cluster of peaks approximately in extent and stand in isolation from other mountains. Despite being much lower than Col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrizo Mountains
The Carrizo Mountains (36°50' N, 109°7'W) is a small, mostly circular mountain range 15 to 20 km (9 to 12 miles) in diameter located on the Colorado Plateau in northeastern Arizona. The range is about southwest of the Four Corners. The highest summit, Pastora Peak, is in elevation, whereas elevations on the surrounding plateau are near . The mountains are within the Navajo Nation. Teec Nos Pos, Arizona, the closest community, is adjacent at the northern foothills, on Teec Nos Pos Wash, from Pastora Peak, about 5-mi miles to the north from the mountain's perimeter; Teec Nos Pos had about 800 inhabitants in the 2000 census. Geology The Carrizo Mountains primarily consist of igneous rocks that intruded Permian through Cretaceous marine strata. The most common igneous rock type is porphyritic hornblende diorite. Intrusive forms include laccoliths, stocks, sills, and dikes. Ages of the igneous rocks range from 70 to 74 million years. Similar igneous-cored ranges of the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Mountains
The Henry Mountains is a mountain range located in the southeastern portion of the U.S. state of Utah that runs in a generally north-south direction, extending over a distance of about . They were named by Almon Thompson in honor of Joseph Henry, the first secretary of the Smithsonian Institution. The nearest town of any size is Hanksville, Utah, which is north of the mountains. The Henry Mountains were the last mountain range to be added to the map of the 48 contiguous U.S. states (1872), and before their official naming by Thompson were sometimes referred to as the "Unknown Mountains." In Navajo, the range is still referred to as ''Dził Bizhiʼ Ádiní'' ("mountain whose name is missing"). The great majority of the land within the Henry Mountains is owned by the U.S. Bureau of Land Management. A herd of 350 American Bison roams freely in the Henrys. Geography and geology The range is clustered into two main groups, with Highway 276 dividing the two portions. The northern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abajo Mountains
The Abajo Mountains, sometimes referred to as the Blue Mountains, is a small mountain range west of Monticello, Utah, south of Canyonlands National Park and north of Blanding, Utah. The mountain range is located within the Manti–La Sal National Forest. The highest point within the range is Abajo Peak at . This mountain range, like both the La Sal Range and Henry Mountains in the same part of the Colorado Plateau, is formed about igneous intrusions that are relatively resistant to erosion. Some of these intrusions form laccoliths emplaced at depths of a few kilometers. The predominant igneous rock is porphyritic hornblende diorite. Ages of intrusion in the Abajo Mountains fall in the interval from 22 to 29 million years. These mountain ranges are part of the Colorado Plateau province west of the greater ranges of the Rocky Mountains The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Moun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
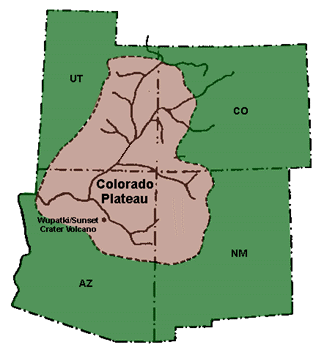
Colorado Plateau
The Colorado Plateau, also known as the Colorado Plateau Province, is a physiographic and desert region of the Intermontane Plateaus, roughly centered on the Four Corners region of the southwestern United States. This province covers an area of 336,700 km2 (130,000 mi2) within western Colorado, northwestern New Mexico, southern and eastern Utah, northern Arizona, and a tiny fraction in the extreme southeast of Nevada. About 90% of the area is drained by the Colorado River and its main tributaries: the Green, San Juan, and Little Colorado. Most of the remainder of the plateau is drained by the Rio Grande and its tributaries. The Colorado Plateau is largely made up of high desert, with scattered areas of forests. In the south-west corner of the Colorado Plateau lies the Grand Canyon of the Colorado River. Much of the Plateau's landscape is related to the Grand Canyon in both appearance and geologic history. The nickname "Red Rock Country" suggests the brightly colored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin ''creta'', "chalk", which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation ''Kreide''. The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now- extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was ice free, and forests extended to the poles. During this time, new groups of mammals and birds appeared. During the Early Cretaceous, flowering plants appeared and began to rapidly diversify, becoming the dominant group of plants across the Earth b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic Era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia. The Permian witnessed the diversification of the two groups of amniotes, the synapsids and the sauropsids ( reptiles). The world at the time was dominated by the supercontinent Pangaea, which had formed due to the collision of Euramerica and Gondwana during the Carboniferous. Pangaea was surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa. The Carboniferous rainforest collapse left behind vast regions of desert within the continental interior. Amniotes, which could better cope with these drier conditions, rose to dominance in place of their am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laccolith
A laccolith is a body of intrusive rock with a dome-shaped upper surface and a level base, fed by a conduit from below. A laccolith forms when magma (molten rock) rising through the Earth's crust begins to spread out horizontally, prying apart the host rock strata. The pressure of the magma is high enough that the overlying strata are forced upward, giving the laccolith its dome-like form. Over time, erosion can expose the solidified laccolith, which is typically more resistant to weathering than the host rock. The exposed laccolith then forms a hill or mountain. The Henry Mountains of Utah, US, are an example of a mountain range composed of exposed laccoliths. It was here that geologist Grove Karl Gilbert carried out pioneering field work on this type of intrusion. Laccolith mountains have since been identified in many other parts of the world. Description A laccolith is a type of igneous intrusion, formed when magma forces its way upwards through the Earth's crust b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |