|
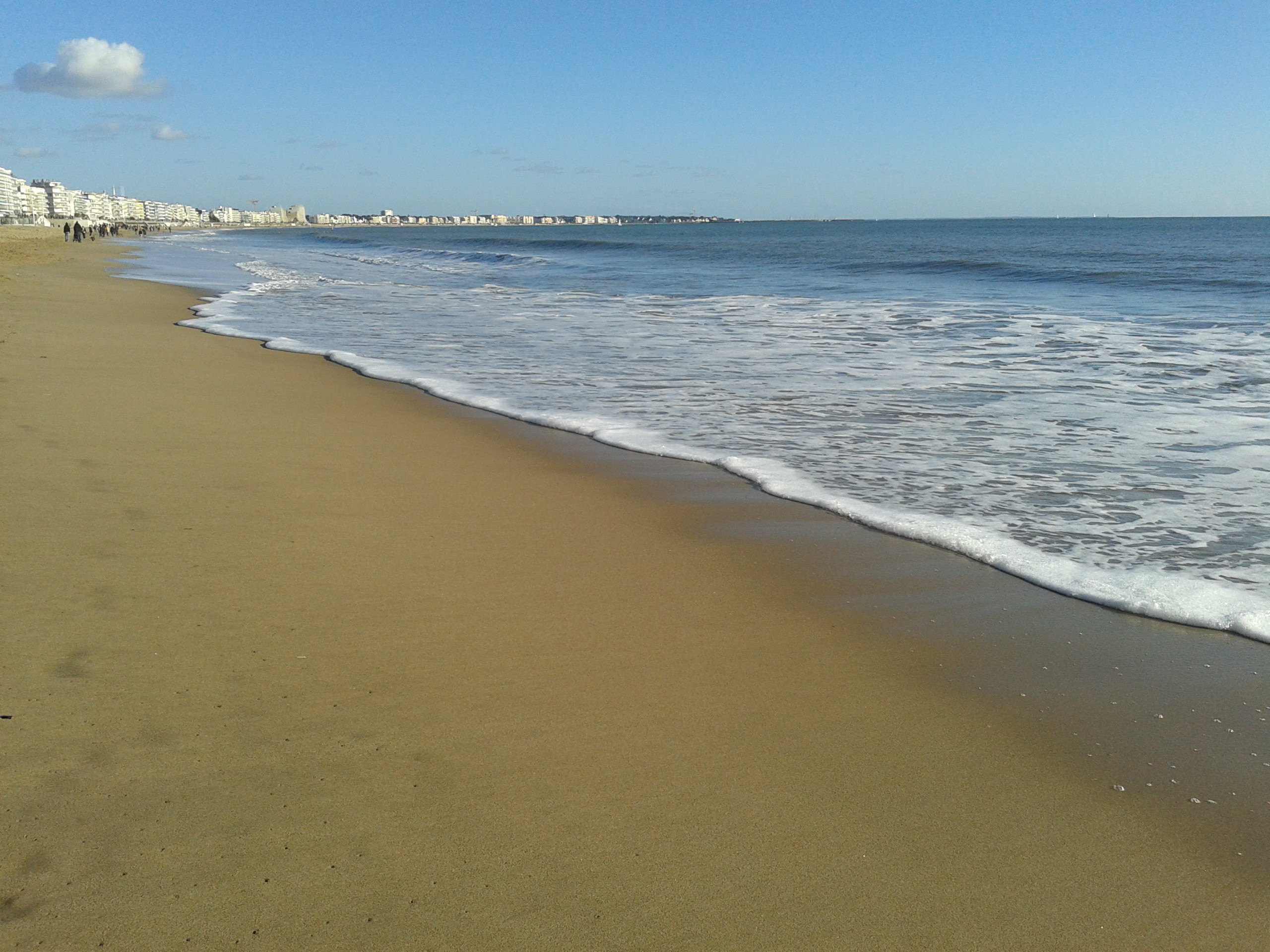
La Baule-Escoublac
La Baule-Escoublac (; br, Ar Baol-Skoubleg, ), commonly referred to as La Baule, is a commune in the Loire-Atlantique department, Pays de la Loire, western France. A century-old seaside resort in southern Brittany with villas, casino, luxury hotels and an original mix of old Breton and seaside culture with a 9 kilometre long sand beach, La Baule has long been home to French high society's seaside residences. During July and August each year, the population of La Baule increases dramatically with many Parisians staying for weeks and regular day-trippers from Nantes. Parisians can take the train in Paris Montparnasse Station and it is about 3 hours to go to La Baule. Despite this, La Baule is still virtually unknown outside France. History In 1779, a violent storm buried the village of Escoublac, near the current location of La Baule, under sand. Escoublac was rebuilt further inland. At that time, the very unstable dunes were occupied only by customs officers, who gave them the nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Baule-les-Pins
La Baule-les-Pins is a quartier of La Baule-Escoublac, Loire-Atlantique, France.Rough Guides (Firm), David Abram -The Rough Guide to France 2003 - Page 493 1843530562 La Baule has two gare SNCFs, the barely-used eponym An eponym is a person, a place, or a thing after whom or which someone or something is, or is believed to be, named. The adjectives which are derived from the word eponym include ''eponymous'' and ''eponymic''. Usage of the word The term ''epon ...ous station, and the main La-Baule-Escoublac. References Seaside resorts in France {{LoireAtlantique-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communauté D'agglomération De La Presqu'île De Guérande Atlantique
Communauté d'agglomération de la Presqu'île de Guérande Atlantique (also: ''Cap Atlantique'') is the ''communauté d'agglomération'', an intercommunal structure, centred on the towns of La Baule-Escoublac and Guérande. It is located in the Loire-Atlantique and Morbihan departments, in the Pays de la Loire and Brittany regions, western France. Created in 2017, its seat is in La Baule-Escoublac.CA de la Presqu'île de Guérande Atlantique (CAP ATLANTIQUE) (N° SIREN : 244400610) BANATIC. Retrieved 18 November 2022. Its area is 386.1 km2. Its population was 75,119 in 2019. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
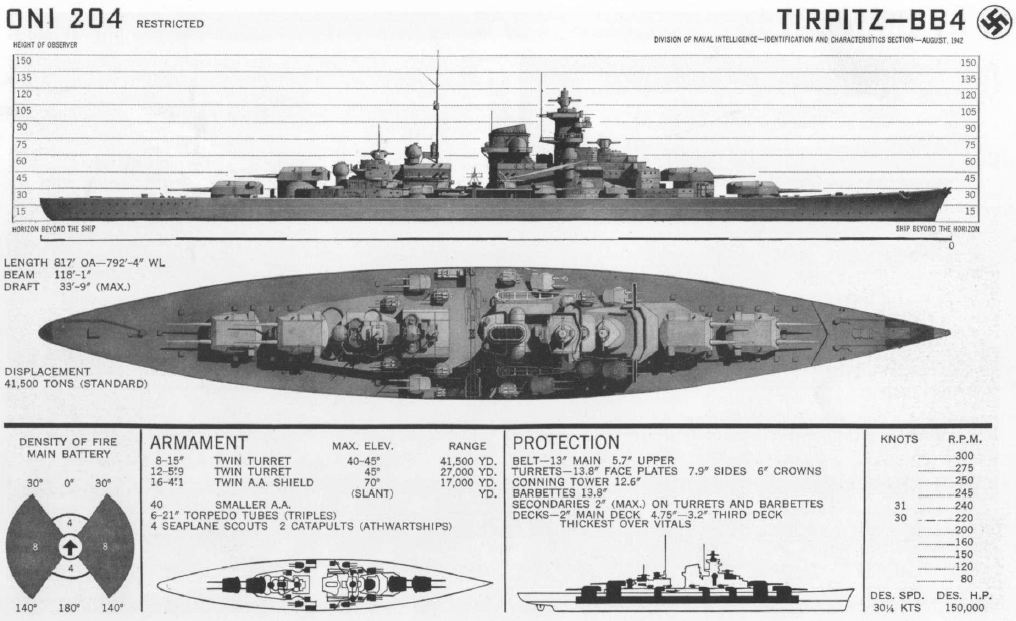
German Battleship Tirpitz
''Tirpitz'' was the second of two s built for Nazi Germany's ''Kriegsmarine'' (navy) prior to and during the Second World War. Named after Grand Admiral Alfred von Tirpitz, the architect of the ''Kaiserliche Marine'' (Imperial Navy), the ship was laid down at the Kriegsmarinewerft Wilhelmshaven in November 1936 and her hull was launched two and a half years later. Work was completed in February 1941, when she was commissioned into the German fleet. Like her sister ship, , ''Tirpitz'' was armed with a main battery of eight guns in four twin turrets. After a series of wartime modifications she was 2000 tonnes heavier than ''Bismarck'', making her the heaviest battleship ever built by a European navy. After completing sea trials in early 1941, ''Tirpitz'' briefly served as the centrepiece of the Baltic Fleet, which was intended to prevent a possible break-out attempt by the Soviet Baltic Fleet. In early 1942, the ship sailed to Norway to act as a deterrent against an Allied inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gérard Lecointe
Gérard Pierre Louis François Armand Lecointe (7 July 1912, in Poitiers, France – 30 January 2009, in La Baule-Escoublac, France) was a French ''général de corps d'armée''. He served in World War II and the Cold War and saw colonial service in French North Africa. He was the last commander of French forces in Algeria, and completed his career as commander-in-chief of the French Forces in Germany. Biography Early life and career Lecointe was born in Poitiers on 7 July 1912, the son of ''Capitaine'' (Captain) Henri Lecointe, an Officer of the Legion of Honor. He attended high school in Douai, where he won eleven awards for excellence. He originally planned to attend the ''École Polytechnique'', but instead chose to attend the military academy at Saint-Cyr, which he entered in 1930 at the age of eighteen in the "Joffre class." While at the school, he was promoted from cadet to aspirant in 1931. Lecointe graduated from Saint-Cyr in 1932 and was appointed ''sous-lieutenant'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henri Anger
Henri Anger (8 June 1907 – 1989) was a French journalist and writer. Entered at '' Télégramme de Brest et de l'Ouest'' in 1944, he became its chief editor in 1965. He used to sign his columns under the pseudonym Kerdaniel. After he finished his studies at lycée de Nantes, he became a journalist at age 16 for ''Le Populaire de Nantes''. Henri Anger won the 1983 edition of thPrix Roland de Jouvenelawarded by the Académie française with his novel ''Une petite fille en colère'' as well as the 1988 edition of the Prix des Deux Magots The Prix des Deux Magots is a major French literary prize. It is presented to new works, and is generally awarded to works that are more off-beat and less conventional than those that receive the more mainstream Prix Goncourt. The name derives from ... with his novel ''La Mille-et-Unième Rue''. Works *1979: ''Chatte allaitant un ourson'', Grasset *1980: ''L'An Quarante'', Grasset *1982: ''Une Petite fille en colère'', Gallimard *1987: ''L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Grover-Williams
William Charles Frederick Grover-Williams (born William Charles Frederick Grover, 16 January 1903 – 18 March 1945 (or shortly thereafter)), also known as "W Williams", was a British Grand Prix motor racing driver and special agent who worked for the Special Operations Executive (SOE) inside France. As a racing driver, he is best known for winning the first Monaco Grand Prix and as an SOE agent he organised and coordinated the Chestnut network, before being captured and executed by the Nazis. Personal and early life Grover-Williams was born in Montrouge, Hauts-de-Seine, France, on 16 January 1903 to Frederick and Hermance Grover. Frederick Grover was an English horse breeder who had settled in Montrouge. Frederick met a French woman, Hermance Dagan, and they were soon married. Their first child was Elizabeth, born in 1897. William had two other siblings – Alice and Frederic. Born to an English father and a French mother, Grover-Williams grew up fluent in both the French a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lluís Companys
Lluís Companys i Jover (; 21 June 1882 – 15 October 1940) was a Catalan politician who served as president of Catalonia from 1934 and during the Spanish Civil War. Companys was a lawyer close to labour movement and one of the most prominent leaders of the Republican Left of Catalonia (ERC) political party, founded in 1931. He had a key role in the events of the proclamation and first steps of the Second Spanish Republic. Appointed president of the Generalitat of Catalonia in 1934, after the death of the previous president, Francesc Macià, his government tried to consolidate the recently acquired Catalan self-government and implement a progressive agenda, despite the internal difficulties. In disagreement with the accession of the right-wing party CEDA to the Spanish government in October 1934, he proclaimed a new Catalan State, for which he was imprisoned between 1934 and 1936. He was still in charge of the Catalan Government during the Spanish Civil War, remaining loyal t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Côte D'amour
The Côte d'Amour is a name given to part of the north western Atlantic coast of the Pays de la Loire region in France. It runs from Le Traict de Pen Bé to the mouth of the Loire in Saint-Nazaire, both of which are in the Loire-Atlantique department. Many municipalities of Côte d'Amour are also part of what it is called noBretagne Plein Sud( en, Lower Brittany. The department of Loire-Atlantique was part of Brittany until 1941). The coastline includes the peninsula of Guérande (in French "Presqu'île de Guérande", including the following localities and seaside resorts from south to north: Saint-Nazaire, Pornichet, La Baule-Escoublac, Le Pouliguen, Le Croisic, Batz-sur-Mer, Guérande, La Turballe, Piriac-sur-Mer and Mesquer. Etymology In 1913, the newspaper ''La Mouette'' organised an opinion poll to give a name to the shore and that is when it became "La Côte d'Amour". Despite popular assumptions, the name is not related to sex. History Until the 19th century, the area con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Prix Motor Racing
Grand Prix motor racing, a form of motorsport competition, has its roots in organised automobile racing that began in France as early as 1894. It quickly evolved from simple road races from one town to the next, to endurance tests for car and driver. Innovation and the drive of competition soon saw speeds exceeding , but because early races took place on open roads, accidents occurred frequently, resulting in deaths both of drivers and of spectators. A common abbreviation used for Grand Prix racing is "GP" or "GP racing". Grand Prix motor racing eventually evolved into formula racing, and one can regard Formula One as its direct descendant. Each event of the Formula One World Championships is still called a ''Grand Prix''; Formula One is also referred to as "Grand Prix racing". Some IndyCar championship races are also called "Grands Prix". Origins of organized racing Motor racing was started in France, as a direct result of the enthusiasm with which the French public e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pornichet
Pornichet (; br, link=no, Pornizhan) is a commune in the Loire-Atlantique department in western France. Geography Location Pornichet is a coastal town of the Côte d'Amour, located ten kilometers west of the centre of Saint-Nazaire. The adjacent communes are Saint-Nazaire and La Baule-Escoublac. Physical geography The town of Pornichet is located * on the line ''sillon de Guérande'', orientated NW-SE; the town border is located on the ''Route de Guérande'', D392d, at approximately 4 km from the shore, at a place called ''Pont de Terre'' (railway junction) at the ''Quatre Vents''; * on a coastal rock belt located upfront of the ''sillon de Guérande'' (same orientation), between two rock heads, the ''Pointe du Bec'' and the ''Pointe de la Lande'' (border with Saint-Nazaire), separated of 4.25 km; * on sandy terranes part of the sand dune unit of ''Escoublac'', between the place named ''Mazy'' (border with La Baule-Escoublac) and the ''Pointe du Bec'' (length: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quiberon
Quiberon (; , ) is a commune in the French department of Morbihan, administrative region of Brittany, western France. It is situated on the southern part of the Quiberon peninsula, the northern part being the commune of Saint-Pierre-Quiberon. It is primarily known as a seaside resort for French tourists during summer, and for its history of sardine production. Quiberon is connected to the mainland by a tombolo. History During the Seven Years' War the bay was the site of the Battle of Quiberon Bay (1759) between the French and British fleets. Then later in July 1795 during the period of the French Revolution, Quiberon was also used by French Royalist exiles, with assistance from the British, as the base for a failed invasion of Brittany (traditionally a royalist area). The invasion was defeated by the Revolutionaries under General Lazare Hoche. In the 19th century, Nicolas Appert, a chemist, developed a technique that permitted the sterilization of food. Thanks to this process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



