|
LW9
LW9 is a para-alpine and para-Nordic standing skiing ''sport class'', a classification defined by the International Paralympic Committee (IPC) for people with upper and lower limb function problems, and includes cerebral palsy skiers classified CP5, CP6 and CP7, along with people with hemiplegia or amputations. For international skiing competitions, classification is done through IPC Alpine Skiing or IPC Nordic Skiing. A national federation such as Alpine Canada handles classification for domestic competitions. This classification is separated into two subclasses including LW9.1 and LW9.2. Para-Alpine skiers in this classification have their choice regarding how many skis and ski poles they wish to user, along with the type of ski poles they wish to utilize. In para-Nordic skiing, skiers use two skis and have an option to use one or two ski poles. Outriggers are one type of ski pole LW9 skiers can use, which requires its own techniques to use. As there are a broad range of di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Patterson (skier)
James Lawrence Paterson, is an Australian Paralympic skier who has cerebral palsy. Personal life Paterson was from Terrigal, New South Wales and a marine mechanic for Halvorsen Boats. After the 1994 Winter Paralympics, 1994 Games, Paterson thanked the Terrigal community and his employer for supporting his overseas preparation. Skiing career At the 1994 Winter Paralympics, 1994 Lillehammer Winter Paralympics, Paterson competed in four events and won a silver medal in the Men's Downhill LW9 event and a bronze medal in the Men's Giant Slalom LW9 event. In 1996, at the IPC Alpine Skiing World Championships, he won a silver medal and two bronze medals. At the 1998 Winter Paralympics, he was team captain and competed in four events. He won a gold medal in the Men's Downhill LW1,3,5/7,9 event and a bronze medal in the Men's Slalom LW9 event Between 1997 and 1999, he was an Australian Institute of Sport Athlete with a Disability scholarship holder. His last major international compet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CP7 (classification)
CP7 is a disability sport classification specific to cerebral palsy. In many sports, it is grouped inside other classifications to allow people with cerebral palsy to compete against people with other different disabilities but with the same level of functionality. Sportspeople in this class can walk but may appear to have a limp as half their body is affected by cerebral palsy. Sports which are open to this classification include athletics, football, skiing, standing volleyball, and swimming. In athletics, they compete in the T37/F37 class. CP7 alpine skiers compete in LW9/1 and LW9/2 in para-alpine, and in LW9 for para-Nordic skiing. CP7 swimmers are often classified in S7, S8, S9 or S10. Definition and participation Cerebral Palsy-International Sports and Recreation Association defined this class in January 2005 as, "Hemiplegic This Class is for the true ambulant hemiplegic athlete. A Class 7 athlete has Spasticity Grade 3 to 2 in one half of the body. They walk wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Para-Nordic Skiing Classification
Para-Nordic skiing classification is the classification system for para-Nordic skiing which includes the biathlon and cross-country events. The classifications for Para-Nordic skiing mirrors the classifications for Para-Alpine skiing with some exceptions. A functional mobility and medical classification is in use, with skiers being divided into three groups: standing skiers, sit skiers and visually impaired skiers. International classification is governed by International Paralympic Committee, Nordic Skiing (IPC-NS). Other classification is handled by national bodies. Before the IPC-NS took over classification, a number of organizations handled classification based on the type of disability. The first classification system for the sport was developed in Scandinavia and was a medical system for skiers with amputations. At the time, other types of disability were not eligible for classification. In developing a system for use at the first Winter Paralympics, organisers want ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
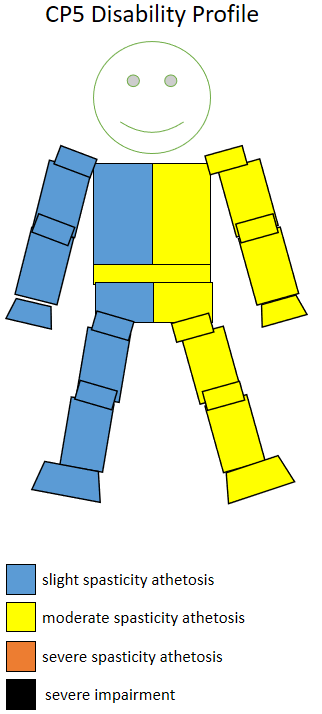
CP5 (classification)
CP5 is a disability sport classification specific to cerebral palsy. In many sports, it is grouped inside other classifications to allow people with cerebral palsy to compete against people with other different disabilities but the same level of functionality. Sportspeople in this class have greater functional control of their upper body, and are generally ambulant with the use of an assistive device. Quick movements can upset their balance. Sports that CP5 athletes are eligible to participate in include athletics, cycling, football, swimming, skiing wheelchair tennis, archery, para-equestrian, powerlifting, rowing, shooting, sledge hockey, sailing, table tennis, wheelchair basketball, wheelchair curling, and wheelchair fencing. In some of these sports, different classification systems or names for CP5 are used. Definition and participation Cerebral Palsy-International Sports and Recreation Association (CP-ISRA) defined this class in January 2005 as, "Diplegic - Moderate invo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CP6 (classification)
CP6 is a disability sport classification specific to cerebral palsy. In many sports, it is grouped inside other classifications to allow people with cerebral palsy to compete against people with other different disabilities but the same level of functionality. Sportspeople in this class are ambulatory, and able to walk without the use of an assistive device. Their bodies are constantly in motion. The running form of people in this class is often better than their form while walking. Some of the sports that CP6 sportspeople are eligible to participate in at the elite level include athletics, cycling, football, skiing, swimming, race running, para-taekwondo, wheelchair tennis, archery, para-equestrian, powerlifting, rowing, sailing, shooting, sledge hockey, table tennis, wheelchair basketball, wheelchair fencing, and table tennis In some of these sports, different classification systems or names for CP6 are used. Definition and participation Cerebral Palsy-International Sports ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Para-alpine Skiing
Paralympic alpine skiing is an adaptation of alpine skiing for athletes with a disability. The sport evolved from the efforts of disabled veterans in Germany and Austria during and after the Second World War. The sport is governed by the International Paralympic Committee Sports Committee. The primary equipment used includes outrigger skis, sit-skis, and mono-skis. Para-alpine skiing disciplines include the Downhill, Super-G, Giant slalom, Slalom, Super Combined and Snowboard. Para-alpine skiing classification is the classification system for para-alpine skiing designed to ensure fair competition between alpine skiers with different types of disabilities. The classifications are grouped into three general disability types: standing, blind and sitting. A factoring system was created for para-alpine skiing to allow the three classification groupings to fairly compete against each other in the same race despite different functional skiing levels and medical challenges. Alpine ski ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ski Binding
A ski binding is a device that connects a ski boot to the ski. Before the 1933 invention of ski lifts, skiers went uphill and down and cross-country on the same gear. As ski lifts became more prevalent, skis—and their bindings—became increasingly specialized, differentiated between alpine (downhill) and Nordic ( cross-country, Telemark, and ski jumping) styles of skiing. Until the point of divergence in the mid-20th century, bindings held the toe of a flexible, leather boot against the ski and allowed the heel to rise off the ski, typically with a form of strap or cable around the heel. To address injuries resulting from falls while skiing downhill on such equipment, ski bindings emerged with the ability to release the toe of the boot sideways, in early models, and to release the boot forward and aft, in later models. Downhill ski bindings became standardized to fit plastic ski boots and incorporated a built-in brake that drags in the snow after the ski detaches from the boot. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American College Of Sports Medicine
The American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM), headquartered in Indianapolis, Indiana, is a sports medicine and exercise science membership organization. Founded in 1954, ACSM holds conferences, publishes books and journals, and offers certification programs for personal trainers and exercise physiologists. History The American College of Sports Medicine was founded in 1954 as the "Federation of Sports Medicine" in New York City at the Hotel Statler on April 22, as part of the afternoon program of the American Association for Health, Physical Education, and Recreation (AAHPER). The following year, the American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM) was officially incorporated, and 11 individuals were designated as founders. This group was composed of seven men and one woman with careers in physical education, as well as three physicians. The physical educators were Clifford Brownell, Ph.D. Ernst Jok, M.D., Peter Karpovich, M.D., Leonard Larson, Ph.D. Grover Mueller, M.S., Neils Neils ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |