|
LSWR Class N15
The LSWR N15 class was a British 2–cylinder 4-6-0 express passenger steam locomotive designed by Robert W. Urie. The class has a complex build history spanning three sub-classes and eight years of construction from 1918 to 1927. The first batch of the class was constructed for the London and South Western Railway (LSWR), where they hauled heavy express trains to the south coast ports and further west to Exeter. After the Lord Nelsons, they were the second biggest 4-6-0 passenger locomotives on the Southern Railway. They could reach speeds of up to 90 mph (145 km/h). Following the grouping of railway companies in 1923, the LSWR became part of the Southern Railway (SR) and its publicity department gave the N15 locomotives names associated with Arthurian legend; the class hence becoming known as King Arthurs.Nock (''British Steam Locomotives'': 1983), p. 172 The Chief Mechanical Engineer (CME) of the newly formed company, Richard Maunsell, modified the Urie locomot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Urie
Robert Wallace Urie (22 October 1854 – 6 January 1937) was a Scotland, Scottish locomotive engineer who was the last chief mechanical engineer of the London and South Western Railway. Career After serving an apprenticeship with and working for various private locomotive manufacturers he joined the Caledonian Railway in 1890, and became chief draughtsman, and later Works Manager at St. Rollox railway works under Dugald Drummond. In 1897 he moved with Drummond to join the London and South Western Railway (LSWR) as works manager at Nine Elms in London. He transferred to the new works at Eastleigh Works, Eastleigh in 1909. Following the death of Dugald Drummond in 1912, Urie became chief mechanical engineer until his own retirement at the grouping of 1923. Locomotive designs Robert Urie made a significant contribution to the development of more powerful express passenger and goods locomotives for use on the London and South Western Railway main line, with simple yet robust design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SR Lord Nelson Class
The SR class LN or ''Lord Nelson'' class is a type of 4-cylinder 4-6-0 steam locomotive designed for the Southern Railway by Richard Maunsell in 1926. They were intended for Continental boat trains between London (Victoria) and Dover harbour, but were also later used for express passenger work to the South-West of England. Sixteen of them were constructed, representing the most powerful (although not the most successful) Southern 4-6-0 design. They were all named after famous admirals. The class continued to operate with British Railways until withdrawn during 1961 and 1962. Only one example of the class – the first engine, ''Lord Nelson'' itself – has been saved from scrapping. This has been seen running on mainline tours and preserved railways throughout Britain. Background Although the improved ”King Arthur” class 4-6-0 locomotives were capable of the heaviest express passenger work between London and South West England, there was a growth in demand for Continenta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixed-traffic Locomotive
A locomotive or engine is a rail transport vehicle that provides the motive power for a train. If a locomotive is capable of carrying a payload, it is usually rather referred to as a multiple unit, motor coach, railcar or power car; the use of these self-propelled vehicles is increasingly common for passenger trains, but rare for freight (see CargoSprinter). Traditionally, locomotives pulled trains from the front. However, push-pull operation has become common, where the train may have a locomotive (or locomotives) at the front, at the rear, or at each end. Most recently railroads have begun adopting DPU or distributed power. The front may have one or two locomotives followed by a mid-train locomotive that is controlled remotely from the lead unit. __TOC__ Etymology The word ''locomotive'' originates from the Latin 'from a place', ablative of 'place', and the Medieval Latin 'causing motion', and is a shortened form of the term ''locomotive engine'', which was first us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LSWR Class H15
The LSWR/SR H15 class was a class of 2-cylinder 4-6-0 steam locomotives designed by Robert Urie for mixed-traffic duties on the LSWR. Further batches were constructed by Richard Maunsell for the SR. They were given the nickname of "Junior King Arthur" due to the size of their driving wheels, the S15 and their N15 cousins had driving wheels which had a diameter of 5 foot and 7 inches and 6 foot and 7 inches respectively. Construction history The H15 class represented Robert Urie's first design for the LSWR. It was created in response to a desperate lack of adequate locomotives in service on the LSWR that could be utilised for heavy freight duties. Reliability was also an issue, with ageing locomotive designs taking their toll on the LSWR's resources. The resultant design was an outside 2-cylinder locomotive fitted with outside Walschaerts valve gear for ease of maintenance, with all the working parts relatively accessible when compared to previous designs operating on the LSWR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railtour
A railtour is a special train which is run in order to allow people to experience rail travel which is not normally available using timetabled passenger services. The 'unusual' aspect may be the route of the train, the destination, the occasion, specific sections of railway track (for example, freight-only lines), the locomotive hauling the train, the rolling stock (passenger carriages), or any combination of these. Organisers may own or hire locomotives or rolling stock, or tours may be organised by railway management or other bodies outside the railway fraternity. Perhaps the most famous railtour in England was the ''Fifteen Guinea Special'', the last steam hauled main line train run by British Rail. Railtours are often identifiable through the use of a train headboard, often identifying the name of the specific tour or the tour operator. On TOPS, railtours are always given a 1Zxx headcode. Types of Railtour Destination tours A 'destination' railtour is often associated with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Collection
The UK National Collection is a collection of around 280 historic rolling stock, rail vehicles (predominantly of British origin). The majority of the collection is kept at four national museums: * National Railway Museum, York * National Railway Museum Shildon, Locomotion, Shildon * Science Museum, London, Science Museum, Kensington, London * Science and Industry Museum, Manchester Other items are on short or long-term loans to museums and heritage railways such as the Museum of the Great Western Railway at Swindon and the Head of Steam museum at Darlington. __TOC__ Steam locomotives Standard gauge designs up to 1869 These locomotives are all gauge unless noted otherwise. Standard gauge designs 1870 to 1899 These locomotives are all gauge. Standard gauge designs 1900 to 1922 These locomotives are all gauge unless noted otherwise. Standard gauge designs 1923 to 1947 These locomotives are all gauge unless noted otherwise. Standard gauge designs from 1948 onwards The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
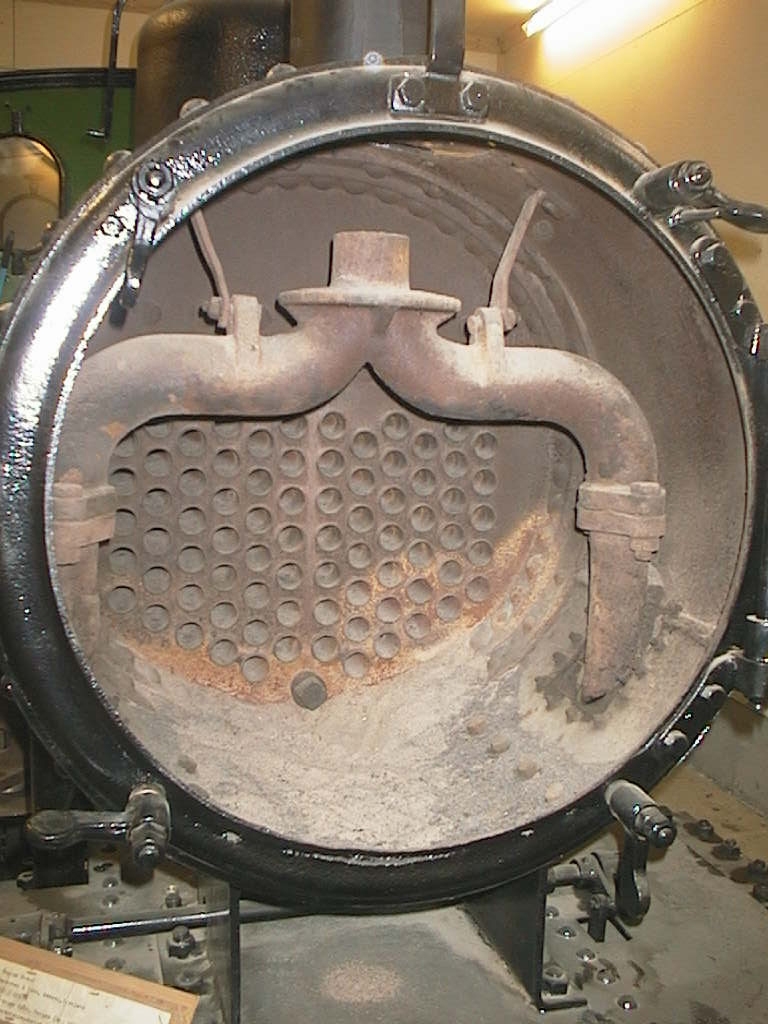
Steam Locomotive Exhaust System
The steam locomotive exhaust system consists of those parts of a steam locomotive which together discharge exhaust steam from the cylinders in order to increase the draught through the fire. It usually consists of the blastpipe (or first stage nozzle), smokebox, and chimney, although later designs also include second and third stage nozzles. History The primacy of discovery of the effect of directing the exhaust steam up the chimney as a means of providing draft through the fire is the matter of some controversy, Ahrons (1927) devoting significant attention to this matter. The exhaust from the cylinders on the first steam locomotive – built by Richard Trevithick – was directed up the chimney, and he noted its effect on increasing the draft through the fire at the time. At Wylam, Timothy Hackworth also employed a blastpipe on his earliest locomotives, but it is not clear whether this was an independent discovery or a copy of Trevithick's design. Shortly after Hackworth, Geor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smoke Deflectors
Smoke deflectors, sometimes called "blinkers" in the UK because of their strong resemblance to the blinkers used on horses, and "elephant ears" in US railway slang, are vertical plates attached to each side of the smokebox at the front of a steam locomotive. They are designed to lift smoke away from the locomotive at speed so that the driver has better visibility. On the South Australian Railways they are called "valances". Overview Smoke deflectors became increasingly common on later steam locomotives because the velocity of smoke exiting the chimney had been reduced as the result of efficiency gains obtained by improved smokebox design, such as the Kylchap exhaust and Giesl ejector. Styles Various styles of smoke deflectors have been used by different railway operators. However, many are essentially a variation of one of two designs of ''Windleitbleche'' (wind deflecting plates) developed by the Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft The ''Deutsche Reichsbahn'', also known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastleigh Railway Works
Eastleigh Works is a locomotive, carriage and wagon building and repair facility in the town of Eastleigh, in the county of Hampshire in England. History LSWR The London and South Western Railway (LSWR) opened a carriage and wagon works at Eastleigh in 1891. In 1903, the Chief Mechanical Engineer, Dugald Drummond, oversaw the construction of a large motive power depot in the town; replacing the existing maintenance and repair shops at Northam, Southampton. In January 1910, locomotive building was likewise transferred to the new workshops at Eastleigh from Nine Elms in London. Among the locomotives produced by the LSWR under Drummond at Eastleigh, were the S14 0-4-0 and M7 0-4-4 tank engines, the P14 and T14 4-6-0, and D15 4-4-0, classes. Following the appointment of Robert Urie as Chief Mechanical Engineer in 1912, the works were responsible for the construction of the H15, S15, and N15 (King Arthur) 4-6-0 classes, and the G16 4-8-0, and H16 4-6-0 tank engines. Sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
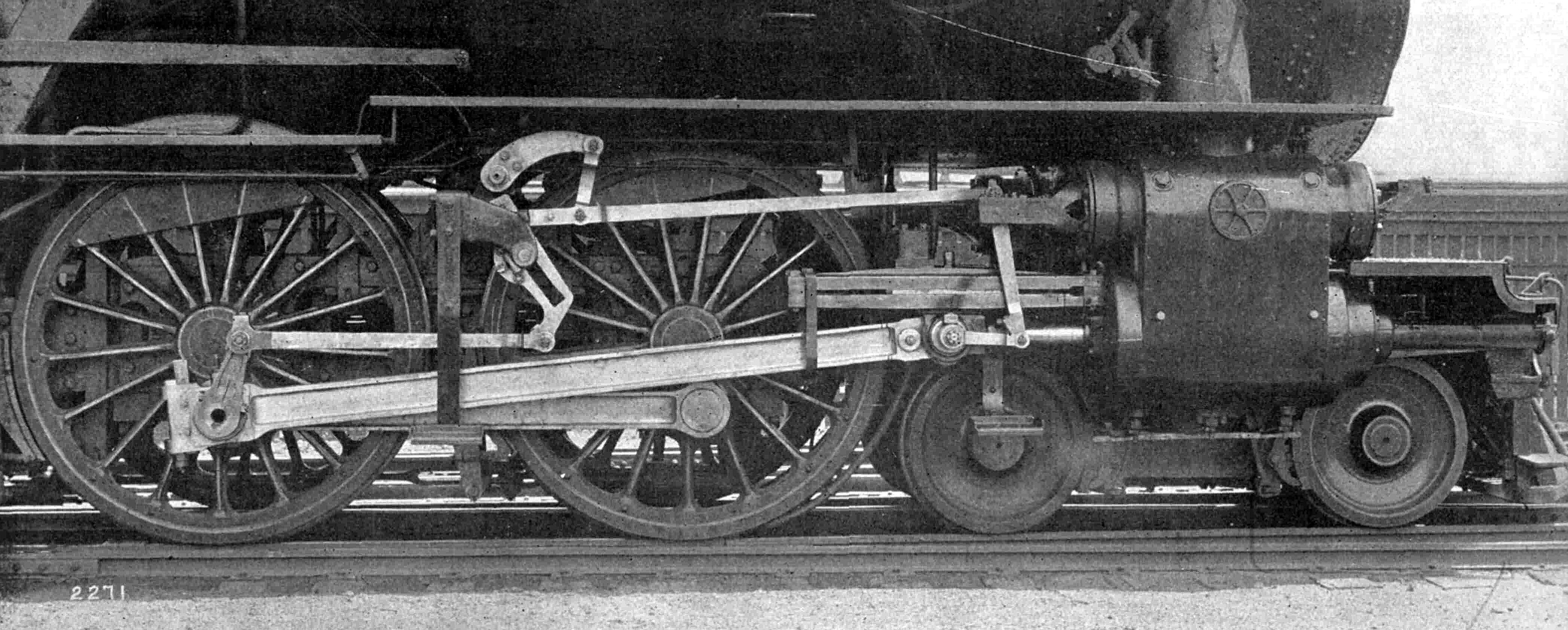
Valve Gear
The valve gear of a steam engine is the mechanism that operates the inlet and exhaust valves to admit steam into the cylinder and allow exhaust steam to escape, respectively, at the correct points in the cycle. It can also serve as a reversing gear. It is sometimes referred to as the "motion". Purpose In the simple case, this can be a relatively simple task as in the internal combustion engine in which the valves always open and close at the same points. This is not the ideal arrangement for a steam engine, though, because greatest power is achieved by keeping the inlet valve open throughout the power stroke (thus having full boiler pressure, minus transmission losses, against the piston throughout the stroke) while peak efficiency is achieved by only having the inlet valve open for a short time and then letting the steam expand in the cylinder (expansive working). The point at which steam stops being admitted to the cylinder is known as the '' cutoff'', and the optimal positio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Circuit
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the locomotive's boiler to the point where it becomes gaseous and its volume increases 1,700 times. Functionally, it is a steam engine on wheels. In most locomotives, the steam is admitted alternately to each end of its cylinders, in which pistons are mechanically connected to the locomotive's main wheels. Fuel and water supplies are usually carried with the locomotive, either on the locomotive itself or in a tender coupled to it. Variations in this general design include electrically-powered boilers, turbines in place of pistons, and using steam generated externally. Steam locomotives were first developed in the United Kingdom during the early 19th century and used for railway transport until the middle of the 20th century. Richard Trevithick bui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Clayton (engineer)
James Clayton MBE (17 November 1872 – 12 October 1946) was an English mechanical engineer who worked extensively on railway locomotives. Clayton was born in Stockport, Cheshire and attended the Technical School in Manchester and thereafter served an apprenticeship at Beyer Peacock, becoming a draughtsman in their drawing office. After six years in that post he took a position with the South Eastern and Chatham Railway (SECR). In 1904, he left for a year's work with the Motor Manufacturing Company, an automobile manufacturer in Coventry, as their chief draughtsman and assistant works manager. Following this, he was hired by Cecil Paget, Chief Superintendent of the Midland Railway, to work on his high pressure multi-cylinder locomotive. During his time with the Midland, he spent two years in charge of the casualty and investigation section, and was appointed Assistant Chief Locomotive Draughtsman in 1907. In 1914, he rejoined the SECR and was soon Chief Locomotive Draugh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |