|
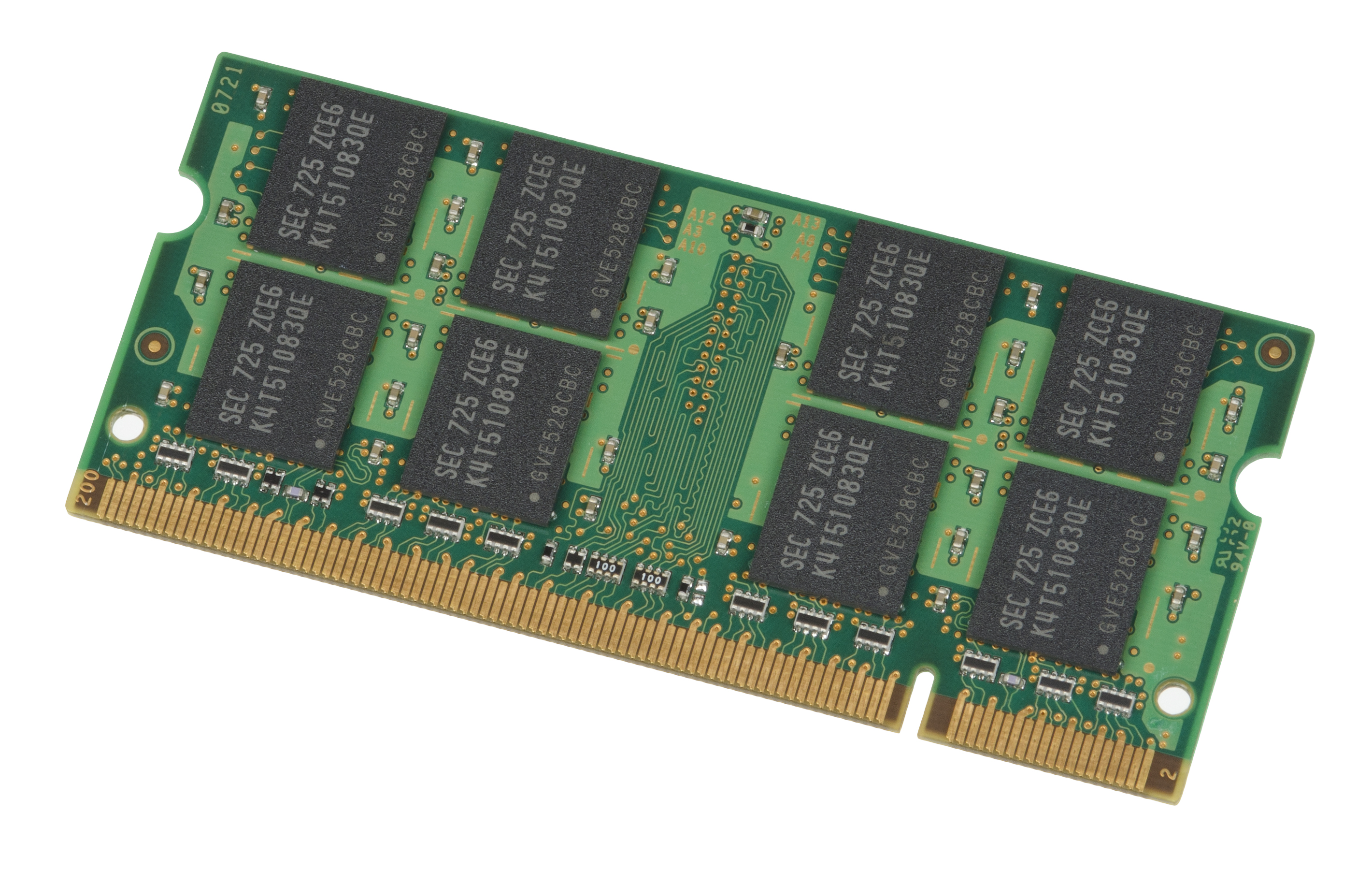
LPDDR4
Low-Power Double Data Rate (LPDDR), also known as LPDDR SDRAM, is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory that consumes less power and is targeted for mobile computers and devices such as mobile phones. Older variants are also known as Mobile DDR, and abbreviated as mDDR. Modern LPDDR SDRAM is distinct from DDR SDRAM, with various differences that make the technology more appropriate for the mobile application. LPDDR technology standards are developed independently of DDR standards, with LPDDR4X and even LPDDR5 for example being implemented prior to DDR5 SDRAM and offering far higher data rates than DDR4 SDRAM. Bus width In contrast with standard SDRAM, used in stationary devices and laptops and usually connected over a 64-bit wide memory bus, LPDDR also permits 16- or 32-bit wide channels. The "E" versions mark enhanced versions of the specifications. They formalize overclocking the memory array up to 266 MHz for a 33% performance boost. Memory modules impleme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
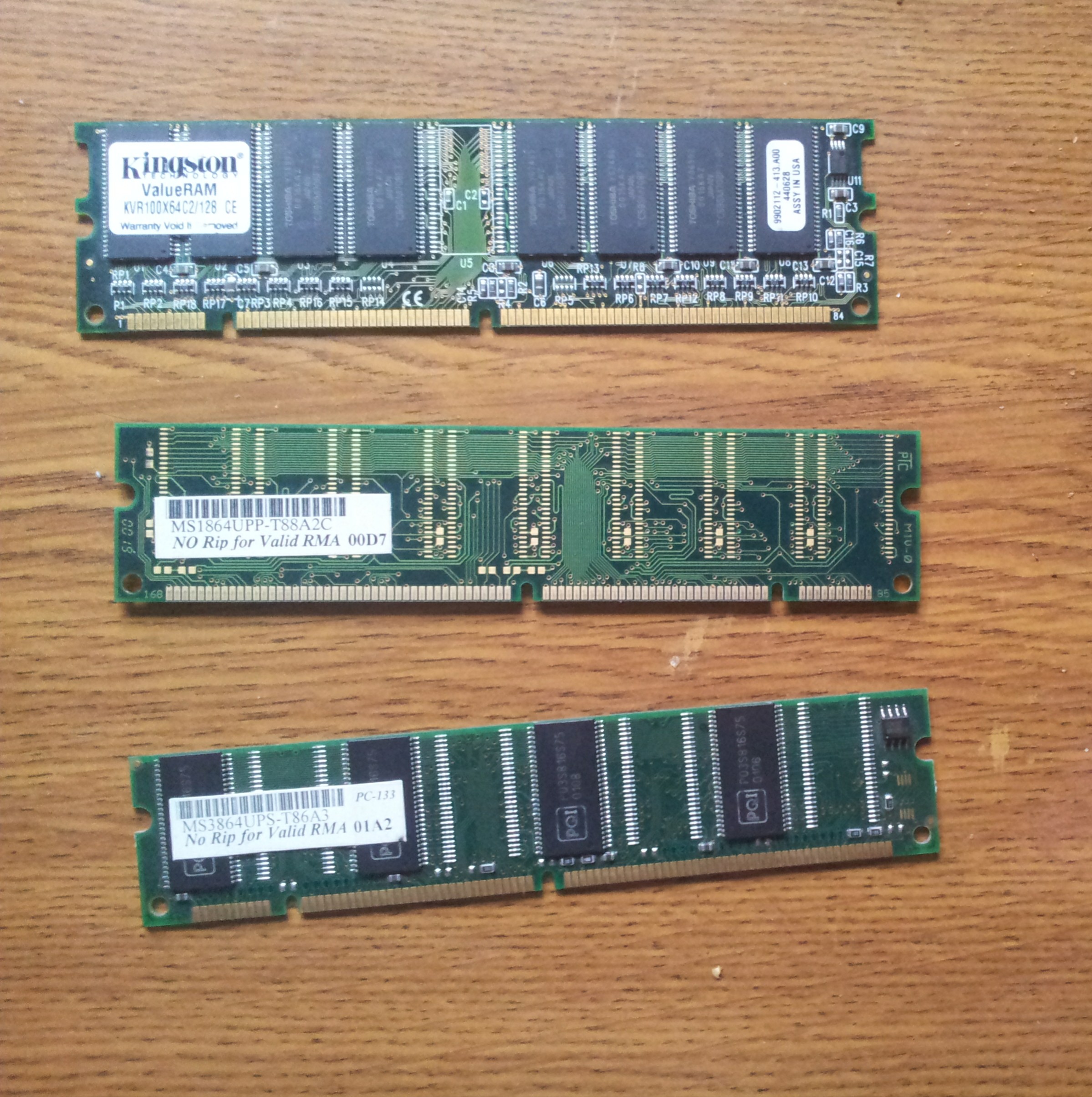
Synchronous Dynamic Random-access Memory
Synchronous dynamic random-access memory (synchronous dynamic RAM or SDRAM) is any DRAM where the operation of its external pin interface is coordinated by an externally supplied clock signal. DRAM integrated circuits (ICs) produced from the early 1970s to early 1990s used an ''asynchronous'' interface, in which input control signals have a direct effect on internal functions only delayed by the trip across its semiconductor pathways. SDRAM has a ''synchronous'' interface, whereby changes on control inputs are recognised after a rising edge of its clock input. In SDRAM families standardized by JEDEC, the clock signal controls the stepping of an internal finite-state machine that responds to incoming commands. These commands can be pipelined to improve performance, with previously started operations completing while new commands are received. The memory is divided into several equally sized but independent sections called ''banks'', allowing the device to operate on a memory a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SDRAM
Synchronous dynamic random-access memory (synchronous dynamic RAM or SDRAM) is any DRAM where the operation of its external pin interface is coordinated by an externally supplied clock signal. DRAM integrated circuits (ICs) produced from the early 1970s to early 1990s used an ''asynchronous'' interface, in which input control signals have a direct effect on internal functions only delayed by the trip across its semiconductor pathways. SDRAM has a ''synchronous'' interface, whereby changes on control inputs are recognised after a rising edge of its clock input. In SDRAM families standardized by JEDEC, the clock signal controls the stepping of an internal finite-state machine that responds to incoming commands. These commands can be pipelined to improve performance, with previously started operations completing while new commands are received. The memory is divided into several equally sized but independent sections called ''banks'', allowing the device to operate on a memory a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DDR5 SDRAM
Double Data Rate 5 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR5 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory. Compared to its predecessor DDR4 SDRAM, DDR5 was planned to reduce power consumption, while doubling bandwidth. The standard, originally targeted for 2018, was released on July 14, 2020. A new feature called Decision Feedback Equalization (DFE) enables I/O speed scalability for higher bandwidth and performance improvement. DDR5 supports more bandwidth than its predecessor, DDR4, with 4.8 gigabits per second possible, but not shipping at launch. DDR5 has about the same latency as DDR4 and DDR3. DDR5 octuples the maximum DIMM capacity from 64 GB to 512 GB. DDR5 also has higher frequencies than DDR4. Rambus announced a working DDR5 DIMM in September 2017. On November 15, 2018, SK Hynix announced completion of its first DDR5 RAM chip; it runs at 5200 MT/s at 1.1 V. In February 2019, SK Hynix announced a 6400 MT/s chip, the highest speed specified by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samsung Electronics
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. (, sometimes shortened to SEC and stylized as SΛMSUNG) is a South Korean multinational corporation, multinational electronics corporation headquartered in Yeongtong-gu, Suwon, South Korea. It is the pinnacle of the Samsung chaebol, accounting for 70% of the group's revenue in 2012. Samsung Electronics has played a key role in the group's corporate governance due to circular ownership. Samsung Electronics has Assembly line, assembly plants and sales networks in 74 countries and employs around 290,000 people. It is majority-owned by foreign investors. Samsung Electronics is the world's List of largest technology companies by revenue, second-largest technology company by revenue, and its market capitalization stood at US$520.65 billion, the 12th largest in the world. Samsung is a major manufacturer of Electronic component, Electronic Components such as lithium-ion batteries, semiconductors, image sensors, camera modules, and Display device, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NAND Flash
Flash memory is an Integrated circuit, electronic Non-volatile memory, non-volatile computer memory storage medium that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. The two main types of flash memory, NOR flash and NAND flash, are named for the NOR gate, NOR and NAND gate, NAND logic gates. Both use the same cell design, consisting of floating gate MOSFETs. They differ at the circuit level depending on whether the state of the bit line or word lines is pulled high or low: in NAND flash, the relationship between the bit line and the word lines resembles a NAND gate; in NOR flash, it resembles a NOR gate. Flash memory, a type of floating-gate memory, was invented at Toshiba in 1980 and is based on EEPROM technology. Toshiba began marketing flash memory in 1987. EPROMs had to be erased completely before they could be rewritten. NAND flash memory, however, may be erased, written, and read in blocks (or pages), which generally are much smaller than the entire device. NOR flash memo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Data Rate
In computing, a computer bus operating with double data rate (DDR) transfers data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal. This is also known as double pumped, dual-pumped, and double transition. The term toggle mode is used in the context of NAND flash memory. Overview The simplest way to design a clocked electronic circuit is to make it perform one transfer per full cycle (rise and fall) of a clock signal. This, however, requires that the clock signal changes twice per transfer, while the data lines change at most once per transfer. When operating at a high bandwidth, signal integrity limitations constrain the clock frequency. By using both edges of the clock, the data signals operate with the same limiting frequency, thereby doubling the data transmission rate. This technique has been used for microprocessor front-side busses, Ultra-3 SCSI, expansion buses ( AGP, PCI-X), graphics memory (GDDR), main memory (both RDRAM and DDR1 through DDR5), and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
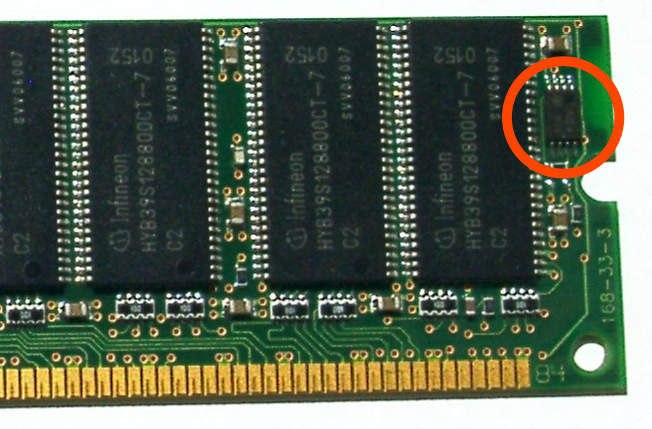
Serial Presence Detect
In computing, serial presence detect (SPD) is a standardized way to automatically access information about a memory module. Earlier 72-pin SIMMs included five pins that provided five bits of ''parallel presence detect'' (PPD) data, but the 168-pin DIMM standard changed to a serial presence detect to encode much more information. When an ordinary modern computer is turned on, it starts by doing a power-on self-test (POST). Since about the mid-1990s, this process includes automatically configuring the hardware currently present. SPD is a memory hardware feature that makes it possible for the computer to know what memory is present, and what memory timings to use to access the memory. Some computers adapt to hardware changes completely automatically. In most cases, there is a special optional procedure for accessing BIOS parameters, to view and potentially make changes in settings. It may be possible to control how the computer uses the memory SPD data—to choose settings, sel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gigabit
The bit is the most basic unit of information in computing and digital communications. The name is a portmanteau of binary digit. The bit represents a logical state with one of two possible values. These values are most commonly represented as either , but other representations such as ''true''/''false'', ''yes''/''no'', ''on''/''off'', or ''+''/''−'' are also commonly used. The relation between these values and the physical states of the underlying storage or device is a matter of convention, and different assignments may be used even within the same device or program. It may be physically implemented with a two-state device. The symbol for the binary digit is either "bit" per recommendation by the IEC 80000-13:2008 standard, or the lowercase character "b", as recommended by the IEEE 1541-2002 standard. A contiguous group of binary digits is commonly called a ''bit string'', a bit vector, or a single-dimensional (or multi-dimensional) ''bit array''. A group of eight b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IPhone 5S
The iPhone 5S (stylized and marketed as iPhone 5s) is a smartphone that was designed and marketed by Apple Inc. It is the seventh generation of the iPhone, succeeding the iPhone 5, and unveiled in September 2013, alongside the iPhone 5C. The iPhone 5S maintains almost the same external design as its predecessor, the iPhone 5, although the 5S received a new white/gold color scheme in addition to white/silver and space gray/black. The 5S has vastly upgraded internal hardware, however. It introduced the A7 64-bit dual-core system-on-chip, the first 64-bit processor to be used on a smartphone, accompanied by the M7 "motion co-processor". A redesigned home button with Touch ID, a fingerprint recognition system which can be used to unlock the phone and authenticate App Store and iTunes Store purchases, was also introduced. The camera was also updated with a larger aperture and a dual-LED flash optimized for different color temperatures. Earphones known as EarPods were included w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DDR2 SDRAM
Double Data Rate 2 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR2 SDRAM) is a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) interface. It superseded the original DDR SDRAM specification, and was itself superseded by DDR3 SDRAM (launched in 2007). DDR2 DIMMs are neither forward compatible with DDR3 nor backward compatible with DDR. In addition to double pumping the data bus as in DDR SDRAM (transferring data on the rising and falling edges of the bus clock signal), DDR2 allows higher bus speed and requires lower power by running the internal clock at half the speed of the data bus. The two factors combine to produce a total of four data transfers per internal clock cycle. Since the DDR2 internal clock runs at half the DDR external clock rate, DDR2 memory operating at the same external data bus clock rate as DDR results in DDR2 being able to provide the same bandwidth but with better latency. Alternatively, DDR2 memory operating at twice the external data ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nexus 10
The Nexus 10 is a tablet computer co-developed by Google and Samsung Electronics that runs the Android operating system. It is the second tablet in the Google Nexus series, a family of Android consumer devices marketed by Google and built by an OEM partner. Following the success of the 7-inch Nexus 7, the first Google Nexus tablet, the Nexus 10 was released with a 10.1-inch, 2560×1600 pixel display, which was the world's highest resolution tablet display at the time of its release. The Nexus 10 was announced on October 29, 2012, and became available on November 13, 2012. The device is available in two storage sizes, 16 GB for US$399 and 32 GB for US$499. Along with the Nexus 4 mobile phone, the Nexus 10 launched Android 4.2 ("Jelly Bean"), which offered several new features, such as: 360° panoramic photo stitching called "Photo Sphere"; a quick settings menu; widgets on the lock screen; gesture typing; an updated version of Google Now; and multiple user accounts for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |