|
LLHol Family
The Putative ''Lactococcus lactis'' Holin (LLHol) FamilyTC# 1.E.44 consists of just a few proteins from ''Lactococcus lactis'' species and their phage. These proteins are small, between 61 and 78 amino acyl residues (aas) in length, and exhibit one or two transmembrane segments (TMSs). As of March 2016, LLHol proteins remain functionally uncharacterized. They are not demonstrably homologous to members of other holin families and thus do not belong to one of the seven holin superfamilies. A representative list of proteins belonging to the LLHol family can be found in thTransporter Classification Database See also * Holin * Lysin Lysins, also known as endolysins or murein hydrolases, are hydrolytic enzymes produced by bacteriophages in order to cleave the host's cell wall during the final stage of the lytic cycle. Lysins are highly evolved enzymes that are able to targ ... * Transporter Classification Database Further reading * Reddy, Bhaskara L.; Saier Jr., Milton H. (20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactococcus Lactis
''Lactococcus lactis'' is a Gram-positive bacterium used extensively in the production of buttermilk and cheese, but has also become famous as the first genetically modified organism to be used alive for the treatment of human disease. ''L. lactis'' cells are cocci that group in pairs and short chains, and, depending on growth conditions, appear ovoid with a typical length of 0.5 - 1.5 µm. ''L. lactis'' does not produce spores ( nonsporulating) and are not motile ( nonmotile). They have a homofermentative metabolism, meaning they produce lactic acid from sugars. They've also been reported to produce exclusive L-(+)-lactic acid. However, reported D-(−)-lactic acid can be produced when cultured at low pH. The capability to produce lactic acid is one of the reasons why ''L. lactis'' is one of the most important microorganisms in the dairy industry. Based on its history in food fermentation, ''L. lactis'' has generally recognized as safe (GRAS) status, with few case reports ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteriophage
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a ''phage'' (), is a duplodnaviria virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν ('), meaning "to devour". Bacteriophages are composed of proteins that encapsulate a DNA or RNA genome, and may have structures that are either simple or elaborate. Their genomes may encode as few as four genes (e.g. MS2) and as many as hundreds of genes. Phages replicate within the bacterium following the injection of their genome into its cytoplasm. Bacteriophages are among the most common and diverse entities in the biosphere. Bacteriophages are ubiquitous viruses, found wherever bacteria exist. It is estimated there are more than 1031 bacteriophages on the planet, more than every other organism on Earth, including bacteria, combined. Viruses are the most abundant biological entity in the water column of the world's oceans, and the second largest component of biom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
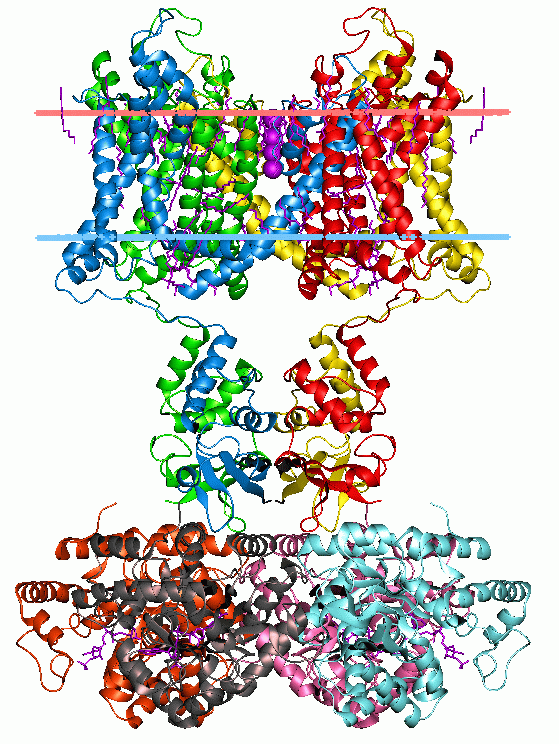
Holin
Holins are a diverse group of small proteins produced by dsDNA bacteriophages in order to trigger and control the degradation of the host's cell wall at the end of the lytic cycle. Holins form pores in the host's cell membrane, allowing lysins to reach and degrade peptidoglycan, a component of bacterial cell walls. Holins have been shown to regulate the timing of lysis with great precision. Over 50 unrelated gene families encode holins, making them the most diverse group of proteins with common function. Together with lysins, holins are being studied for their potential use as antibacterial agents. While canonical holins act by forming large pores, pinholins such as the S protein of lambdoid phage 21 act by forming heptameric channels that depolarize the bacterial membrane. They are associated with SAR endolysins, which remain inactive in the periplasm prior to the depolarization of the membrane. Viruses that infect eukaryotic cells may use similar channel-forming proteins called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysin
Lysins, also known as endolysins or murein hydrolases, are hydrolytic enzymes produced by bacteriophages in order to cleave the host's cell wall during the final stage of the lytic cycle. Lysins are highly evolved enzymes that are able to target one of the five bonds in peptidoglycan (murein), the main component of bacterial cell walls, which allows the release of progeny virions from the lysed cell. Cell-wall-containing Archaea are also lysed by specialized pseudomurein-cleaving lysins, while most archaeal viruses employ alternative mechanisms. Similarly, not all bacteriophages synthesize lysins: some small single-stranded DNA and RNA phages produce membrane proteins that activate the host's autolytic mechanisms such as autolysins. Lysins are being used as antibacterial agents due to their high effectiveness and specificity in comparison with antibiotics, which are susceptible to bacterial resistance. Structure Double-stranded DNA phage lysins tend to lie within the 25 to 40 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Families
A protein family is a group of evolutionarily related proteins. In many cases, a protein family has a corresponding gene family, in which each gene encodes a corresponding protein with a 1:1 relationship. The term "protein family" should not be confused with family as it is used in taxonomy. Proteins in a family descend from a common ancestor and typically have similar three-dimensional structures, functions, and significant sequence similarity. The most important of these is sequence similarity (usually amino-acid sequence), since it is the strictest indicator of homology and therefore the clearest indicator of common ancestry. A fairly well developed framework exists for evaluating the significance of similarity between a group of sequences using sequence alignment methods. Proteins that do not share a common ancestor are very unlikely to show statistically significant sequence similarity, making sequence alignment a powerful tool for identifying the members of protein familie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Membrane Proteins
Membrane proteins are common proteins that are part of, or interact with, biological membranes. Membrane proteins fall into several broad categories depending on their location. Integral membrane proteins are a permanent part of a cell membrane and can either penetrate the membrane (transmembrane) or associate with one or the other side of a membrane ( integral monotopic). Peripheral membrane proteins are transiently associated with the cell membrane. Membrane proteins are common, and medically important—about a third of all human proteins are membrane proteins, and these are targets for more than half of all drugs. Nonetheless, compared to other classes of proteins, determining membrane protein structures remains a challenge in large part due to the difficulty in establishing experimental conditions that can preserve the correct conformation of the protein in isolation from its native environment. Function Membrane proteins perform a variety of functions vital to the surv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmembrane Proteins
A transmembrane protein (TP) is a type of integral membrane protein that spans the entirety of the cell membrane. Many transmembrane proteins function as gateways to permit the transport of specific substances across the membrane. They frequently undergo significant conformational changes to move a substance through the membrane. They are usually highly hydrophobic and aggregate and precipitate in water. They require detergents or nonpolar solvents for extraction, although some of them (beta-barrels) can be also extracted using denaturing agents. The peptide sequence that spans the membrane, or the transmembrane segment, is largely hydrophobic and can be visualized using the hydropathy plot. Depending on the number of transmembrane segments, transmembrane proteins can be classified as single-span (or bitopic) or multi-span (polytopic). Some other integral membrane proteins are called monotopic, meaning that they are also permanently attached to the membrane, but do not pass t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmembrane Transporters
A transmembrane protein (TP) is a type of integral membrane protein that spans the entirety of the cell membrane. Many transmembrane proteins function as gateways to permit the transport of specific substances across the membrane. They frequently undergo significant conformational changes to move a substance through the membrane. They are usually highly hydrophobic and aggregate and precipitate in water. They require detergents or nonpolar solvents for extraction, although some of them (beta-barrels) can be also extracted using denaturing agents. The peptide sequence that spans the membrane, or the transmembrane segment, is largely hydrophobic and can be visualized using the hydropathy plot. Depending on the number of transmembrane segments, transmembrane proteins can be classified as single-span (or bitopic) or multi-span (polytopic). Some other integral membrane proteins are called monotopic, meaning that they are also permanently attached to the membrane, but do not pass t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transport Proteins
A transport protein (variously referred to as a transmembrane pump, transporter, escort protein, acid transport protein, cation transport protein, or anion transport protein) is a protein that serves the function of moving other materials within an organism. Transport proteins are vital to the growth and life of all living things. There are several different kinds of transport proteins. Carrier proteins are proteins involved in the movement of ions, small molecules, or macromolecules, such as another protein, across a biological membrane. Carrier proteins are integral membrane proteins; that is, they exist within and span the membrane across which they transport substances. The proteins may assist in the movement of substances by facilitated diffusion (i.e., passive transport) or active transport. These mechanisms of movement are known as carrier-mediated transport. Each carrier protein is designed to recognize only one substance or one group of very similar substances. Research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integral Membrane Proteins
An integral, or intrinsic, membrane protein (IMP) is a type of membrane protein that is permanently attached to the biological membrane. All ''transmembrane proteins'' are IMPs, but not all IMPs are transmembrane proteins. IMPs comprise a significant fraction of the proteins encoded in an organism's genome. Proteins that cross the membrane are surrounded by annular lipids, which are defined as lipids that are in direct contact with a membrane protein. Such proteins can only be separated from the membranes by using detergents, nonpolar solvents, or sometimes denaturing agents. Structure Three-dimensional structures of ~160 different integral membrane proteins have been determined at atomic resolution by X-ray crystallography or nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. They are challenging subjects for study owing to the difficulties associated with extraction and crystallization. In addition, structures of many water-soluble protein domains of IMPs are available in the Prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |