|
LIMK1
LIM domain kinase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''LIMK1'' gene. Function There are approximately 40 known eukaryotic LIM proteins, so named for the LIM domains they contain. LIM domains are highly conserved cysteine-rich structures containing 2 zinc fingers. Although zinc fingers usually function by binding to DNA or RNA, the LIM motif probably mediates protein-protein interactions. LIM kinase-1 and LIM kinase-2 belong to a small subfamily with a unique combination of 2 N-terminal LIM motifs, a central PDZ domain, and a C-terminal protein kinase domain. LIMK1 is likely to be a component of an intracellular signaling pathway and may be involved in brain development. Clinical significance LIMK1 hemizygosity is implicated in the impaired visuospatial constructive cognition of Williams syndrome. Interactions LIMK1 has been shown to interact with: * CFL1, * CDKN1C, * NRG1, * PAK1, * PAK4, and * YWHAZ 14-3-3 protein zeta/delta (14-3-3ζ) is a protein that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
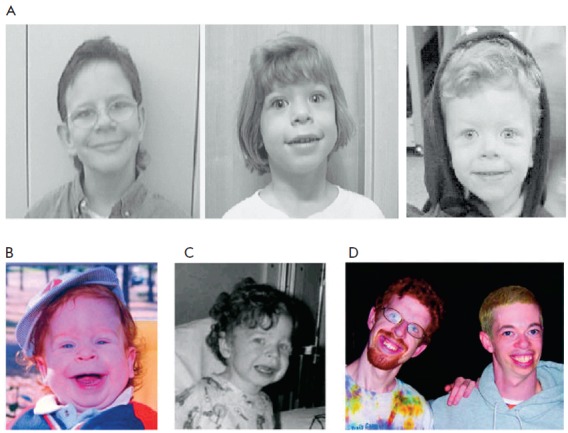
Williams Syndrome
Williams syndrome (WS) is a genetic disorder that affects many parts of the body. Facial features frequently include a broad forehead, underdeveloped chin, short nose, and full cheeks. Mild to moderate intellectual disability is observed in people with WS, with particular challenges with visual spatial tasks such as drawing. Verbal skills are relatively unaffected. Many people with WS have an outgoing personality, an openness to engaging with other people, and a happy disposition. Medical issues with teeth, heart problems (especially supravalvular aortic stenosis), and periods of high blood calcium are common. Williams syndrome is caused by a genetic abnormality, specifically a deletion of about 27 genes from the long arm of one of the two chromosome 7s. Typically, this occurs as a random event during the formation of the egg or sperm from which a person develops. In a small number of cases, it is inherited from an affected parent in an autosomal dominant manner. The different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PAK4
Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PAK4'' gene. PAK4 is one of six members of the PAK family of serine/threonine kinases which are divided into group I (PAK1, PAK2 and PAK3) and group II (PAK4, PAK6 and PAK5/7). PAK4 localizes in sub-cellular domains of the cytoplasm and nucleus. PAK4 regulates cytoskeleton remodeling, phenotypic signaling and gene expression, and affects directional motility, invasion, metastasis, and growth. Similar to PAK1, PAK4-signaling-dependent cellular functions also regulate both physiologic and disease processes such as cancer, as PAK4 is overexpressed and/or hyperstimulated in human cancer, at-large. Discovery PAK4, the founding member of Group II PAK member, was cloned and identified by Minden A. and colleagues in 1998 using a PCR-based strategy from a cDNA library prepared from Jurkett cells. Gene and spliced variants The group II PAKs have less coding exons compared with group I PAKs, highlights ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cofilin 1
Cofilin 1 (non-muscle; n-cofilin), also known as CFL1, is a human gene, part of the ADF/cofilin family. Cofilin is a widely distributed intracellular actin-modulating protein that binds and depolymerizes filamentous F-actin and inhibits the polymerization of monomeric G-actin in a pH-dependent manner. It is involved in the translocation of actin-cofilin complex from cytoplasm to nucleus. One group reports that reelin signaling leads to serine3- phosphorylation of cofilin-1, and this interaction may play a role in the reelin-related regulation of neuronal migration. Interactions Cofilin 1 has been shown to interact with HSPH1 and LIMK1 LIM domain kinase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''LIMK1'' gene. Function There are approximately 40 known eukaryotic LIM proteins, so named for the LIM domains they contain. LIM domains are highly conserved cysteine-rich struc .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PAK1
Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PAK1'' gene. PAK1 is one of six members of the PAK family of serine/threonine kinases which are broadly divided into group I (PAK1, PAK2 and PAK3) and group II (PAK4, PAK6 and PAK5/7). The PAKs are evolutionarily conserved. PAK1 localizes in distinct sub-cellular domains in the cytoplasm and nucleus. PAK1 regulates cytoskeleton remodeling, phenotypic signaling and gene expression, and affects a wide variety of cellular processes such as directional motility, invasion, metastasis, growth, cell cycle progression, angiogenesis. PAK1-signaling dependent cellular functions regulate both physiologic and disease processes, including cancer, as PAK1 is widely overexpressed and hyperstimulated in human cancer, at-large. Discovery PAK1 was first discovered as an effector of the Rho GTPases in rat brain by Manser and colleagues in 1994. The human PAK1 was identified as a GTP-dependent interacting partner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuregulin 1
Neuregulin 1, or NRG1, is a gene of the epidermal growth factor family that in humans is encoded by the ''NRG1'' gene. NRG1 is one of four proteins in the neuregulin family that act on the EGFR family of receptors. Neuregulin 1 is produced in numerous isoforms by alternative splicing, which allows it to perform a wide variety of functions. It is essential for the normal development of the nervous system and the heart. Structure Neuregulin 1 (NRG1) was originally identified as a 44-kD glycoprotein that interacts with the NEU/ERBB2 receptor tyrosine kinase to increase its phosphorylation on tyrosine residues. It is known that an extraordinary variety of different isoforms are produced from the NRG1 gene by alternative splicing. These isoforms include heregulins (HRGs), glial growth factors (GGFs) and sensory and motor neuron-derived factor (SMDF). They are tissue-specific and differ significantly in their structure. The HRG isoforms all contain immunoglobulin (Ig) and epiderm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclin-dependent Kinase Inhibitor 1C
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1C (p57, Kip2), also known as CDKN1C, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''CDKN1C'' imprinted gene. Function Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1C is a tight-binding inhibitor of several G1 cyclin/Cdk complexes and a negative regulator of cell proliferation. Mutations of CDKN1C are implicated in sporadic cancers and Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome suggesting that it is a tumor suppressor candidate. CDKN1C is a tumor suppressor human gene on chromosome 11 (11p15) and belongs to the ''cip/kip'' gene family. It encodes a cell cycle inhibitor that binds to G1 cyclin-CDK complexes. Thus p57KIP2 causes arrest of the cell cycle in G1 phase. CDKN1C was found to lead to cancer cell dormancy; its gene expression is regulated through the activity of glucocorticoid receptors (GRs) through chromatin remodelling mediated by SWI/SNF. Clinical significance A mutation of this gene may lead to loss of control over the cell cycle leading to uncont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PDZ Domain
The PDZ domain is a common structural domain of 80-90 amino-acids found in the signaling proteins of bacteria, yeast, plants, viruses and animals. Proteins containing PDZ domains play a key role in anchoring receptor proteins in the membrane to cytoskeletal components. Proteins with these domains help hold together and organize signaling complexes at cellular membranes. These domains play a key role in the formation and function of signal transduction complexes. PDZ domains also play a highly significant role in the anchoring of cell surface receptors (such as Cftr and FZD7) to the actin cytoskeleton via mediators like NHERF and ezrin. ''PDZ'' is an initialism combining the first letters of the first three proteins discovered to share the domain — post synaptic density protein (PSD95), Drosophila disc large tumor suppressor (Dlg1), and zonula occludens-1 protein (zo-1). PDZ domains have previously been referred to as DHR (Dlg homologous region) or GLGF (glycine-leucine-glycin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemizygosity
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism. Most eukaryotes have two matching sets of chromosomes; that is, they are diploid. Diploid organisms have the same loci on each of their two sets of homologous chromosomes except that the sequences at these loci may differ between the two chromosomes in a matching pair and that a few chromosomes may be mismatched as part of a chromosomal sex-determination system. If both alleles of a diploid organism are the same, the organism is homozygous at that locus. If they are different, the organism is heterozygous at that locus. If one allele is missing, it is hemizygous, and, if both alleles are missing, it is nullizygous. The DNA sequence of a gene often varies from one individual to another. These gene variants are called alleles. While some gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-terminal
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from N-terminus to C-terminus. The convention for writing peptide sequences is to put the C-terminal end on the right and write the sequence from N- to C-terminus. Chemistry Each amino acid has a carboxyl group and an amine group. Amino acids link to one another to form a chain by a dehydration reaction which joins the amine group of one amino acid to the carboxyl group of the next. Thus polypeptide chains have an end with an unbound carboxyl group, the C-terminus, and an end with an unbound amine group, the N-terminus. Proteins are naturally synthesized starting from the N-terminus and ending at the C-terminus. Function C-terminal retention signals While the N-terminus of a protein often cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |