|
LGBT Rights In Georgia (country)
While rights have advanced significantly since the start of the 21st century, lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) people in Georgia still face some legal challenges that non-LGBT people do not experience. Georgia is one of only a few countries in the former Soviet space (others being the Baltic states, Moldova, and Ukraine) that directly prohibits discrimination against all LGBT people in legislation, labor-related or otherwise. Since 2012, Georgian law has considered crimes committed on the grounds of one's sexual orientation or gender identity an aggravating factor in prosecution.ILGA-EuropePresident of Georgia signs anti-discrimination amendment 20 April 2012 Despite this, homosexuality is still considered a major deviation from the highly traditional Orthodox Christian values prevalent in the country, where public discussions of sexuality in general tend to be viewed in a highly negative light. Consequently, homosexuals are often targets of abuse and physical vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgian Orthodox Church
The Apostolic Autocephalous Orthodox Church of Georgia ( ka, საქართველოს სამოციქულო ავტოკეფალური მართლმადიდებელი ეკლესია, tr), commonly known as the Georgian Orthodox Church or the Orthodox Church of Georgia, is an autocephalous Eastern Orthodox church in full communion with the other churches of Eastern Orthodoxy. It is Georgia's dominant religious institution, and a majority of Georgian people are members. The Orthodox Church of Georgia is one of the oldest churches in the world. It asserts apostolic foundation, and that its historical roots can be traced to the early and late Christianization of Iberia and Colchis by Andrew the Apostle in the 1st century AD and by Saint Nino in the 4th century AD, respectively. As in similar autocephalous Eastern Orthodox Christian churches, the church's highest governing body is the holy synod of bishops. The church is headed by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
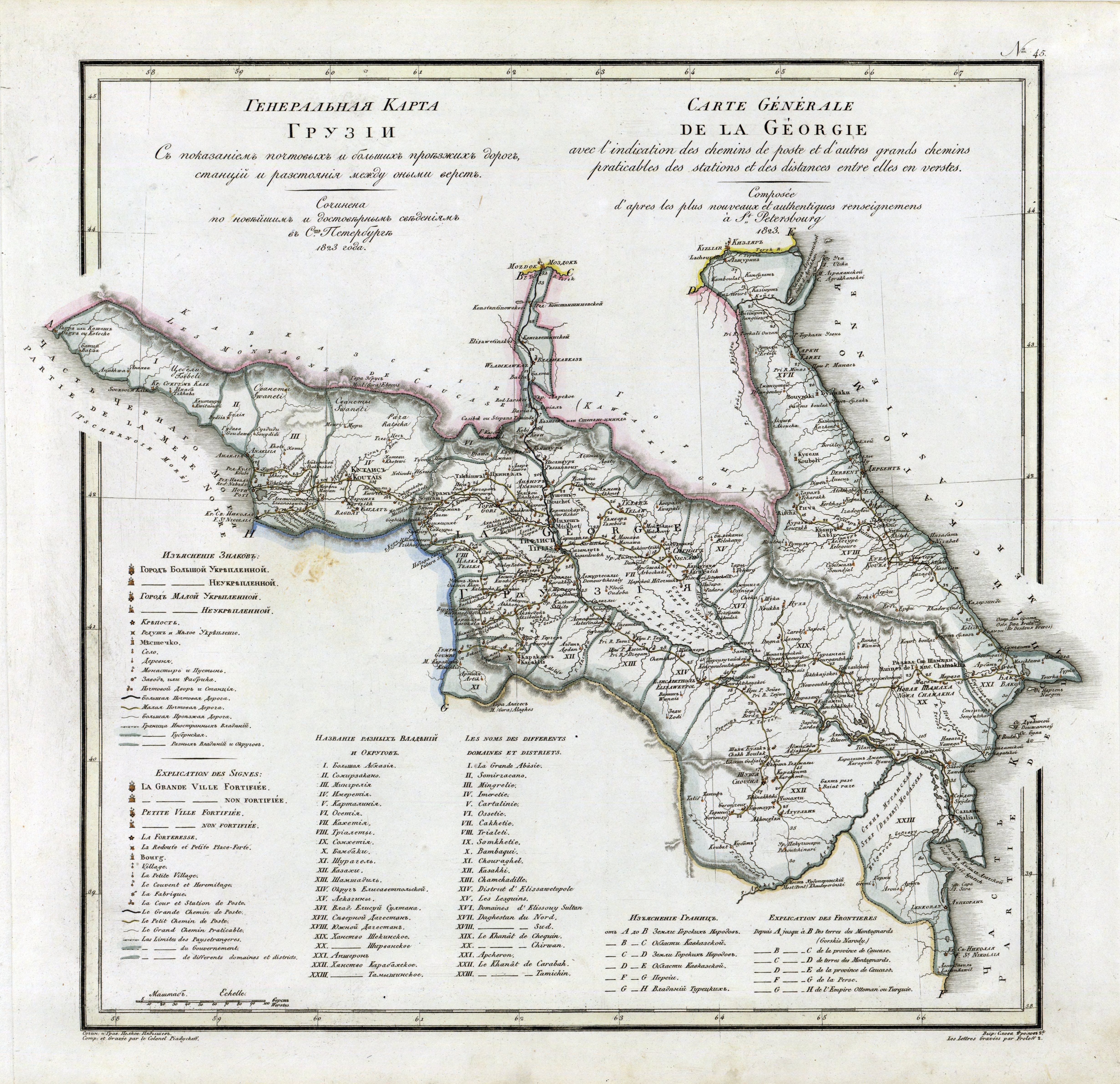
Georgia Within The Russian Empire
The country of Georgia became part of the Russian Empire in the 19th century. Throughout the early modern period, the Muslim Ottoman and Persian empires had fought over various fragmented Georgian kingdoms and principalities; by the 18th century, Russia emerged as the new imperial power in the region. Since Russia was an Orthodox Christian state like Georgia, the Georgians increasingly sought Russian help. In 1783, Heraclius II of the eastern Georgian kingdom of Kartli-Kakheti forged an alliance with the Russian Empire, whereby the kingdom became a Russian protectorate and abjured any dependence on its suzerain Persia. The Russo-Georgian alliance, however, backfired as Russia was unwilling to fulfill the terms of the treaty, proceeding to annex the troubled kingdom in 1801, and reducing it to the status of a guberniya, Russian region (Georgia Governorate). In 1810, the western Georgian kingdom of Kingdom of Imereti, Imereti was annexed as well. Russian rule over Georgia was ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodomy
Sodomy () or buggery (British English) is generally anal or oral sex between people, or sexual activity between a person and a non-human animal ( bestiality), but it may also mean any non- procreative sexual activity. Originally, the term ''sodomy'', which is derived from the story of Sodom and Gomorrah in the Book of Genesis, was commonly restricted to anal sex. Sodomy laws in many countries criminalized the behavior. In the Western world, many of these laws have been overturned or are routinely not enforced. A person who practices sodomy is sometimes referred to as a sodomite. Terminology The term is derived from the Ecclesiastical Latin or "sin of Sodom", which in turn comes from the Ancient Greek word (Sódoma). Genesis (chapters 18–20) tells how God wished to destroy the "sinful" cities of Sodom and Gomorrah. Two angels are invited by Lot to take refuge with his family for the night. The men of Sodom surround Lot's house and demand that he bring the messengers o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David IV Of Georgia
David IV, also known as David the Builder ( ka, დავით აღმაშენებელი, ') (1073–1125), of the Bagrationi dynasty, was the 5th king of United Georgia from 1089 until his death in 1125. Popularly considered to be the greatest and most successful Georgian ruler in history and an original architect of the Georgian Golden Age, he succeeded in driving the Seljuk Turks out of the country, winning the Battle of Didgori in 1121. His reforms of the army and administration enabled him to reunite the country and bring most of the lands of the Caucasus under Georgia's control. A friend of the church and a notable promoter of Christian culture, he was canonized by the Georgian Orthodox Church. Sobriquet and regnal ordinal The epithet ''aghmashenebeli'' (), which is translated as "the Builder" (in the sense of "built completely"), "the Rebuilder", or "the Restorer", first appears as the sobriquet of David in the charter issued in the name of "King of Kings Bagr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Ruisi-Urbnisi
Council of Ruisi-Urbnisi ( ka, რუის-ურბნისის საეკლესიო კრება) was a synod convened at Ruisi and Urbnisi by the Georgian monarch David IV in 1103, that limited the church’s authority, expelled rebellious clergy, and expanded the royal administration into the clerical sphere. Overview Throughout the 10th-11th centuries the Georgian Orthodox Church came into possession of vast land holdings, turning it into “ state within a state” and clashing with the royal authority. In 1089, David IV became the King of Georgia and began to actively reform the country. In 1103 he convened the "''Ruis-Urbnisi Church Council"'' at which he purged the clerical hierarchy of his opponents. The aim was the subjection of the church to state power, which was necessary for David given his plans of centralization and the reordering of church affairs. He gave unprecedented power to his friend and advisor George of Chqondidi. The office of the powerful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bagrationi Dynasty
The Bagrationi dynasty (; ) is a royal dynasty which reigned in Georgia from the Middle Ages until the early 19th century, being among the oldest extant Christian ruling dynasties in the world. In modern usage, the name of the dynasty is sometimes Hellenized and referred to as the Georgian Bagratids, also known in English as the Bagrations. The origins of the dynasty are disputed. The early Georgian Bagratids gained the Principality of Iberia through dynastic marriage after succeeding the Chosroid dynasty at the end of the 8th century. In 888 Adarnase IV of Iberia restored the Georgian monarchy; various native polities then united into the Kingdom of Georgia, which prospered from the 11th to the 13th century. This period of time, particularly the reigns of David IV the Builder (1089–1125) and of his great-granddaughter Tamar the Great (1184–1213) inaugurated the Georgian Golden Age in the history of Georgia. Montgomery-Massingberd, Hugh. " Burke's Royal Families of the Worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
11th Century
The 11th century is the period from 1001 ( MI) through 1100 ( MC) in accordance with the Julian calendar, and the 1st century of the 2nd millennium. In the history of Europe, this period is considered the early part of the High Middle Ages. There was, after a brief ascendancy, a sudden decline of Byzantine power and a rise of Norman domination over much of Europe, along with the prominent role in Europe of notably influential popes. Christendom experienced a formal schism in this century which had been developing over previous centuries between the Latin West and Byzantine East, causing a split in its two largest denominations to this day: Roman Catholicism and Eastern Orthodoxy. In Song dynasty China and the classical Islamic world, this century marked the high point for both classical Chinese civilization, science and technology, and classical Islamic science, philosophy, technology and literature. Rival political factions at the Song dynasty court created strife amongst th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pride Parade
A pride parade (also known as pride march, pride event, or pride festival) is an outdoor event celebrating lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer culture, queer (LGBTQ) social and self-acceptance, achievements, LGBT rights by country or territory, legal rights, and gay pride, pride. The events sometimes also serve as demonstrations for legal rights such as same-sex marriage. Pride events occur in many urban areas in the United States, Canada, Brazil, Mexico, the United Kingdom, Japan, South Korea and Australia. Most occur annually while some take place every June to commemorate the 1969 Stonewall riots in New York City LGBT Pride March, New York City, a pivotal moment in modern LGBT social movements, LGBTQ social movements. The parades seek to create community and honor the history of the movement. In 1970, pride and protest marches were held in Chicago, Los Angeles, New York City, and San Francisco around the first anniversary of Stonewall. The events became annual and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2021 Attack On Tbilisi Pride
The 2021 attack on Tbilisi Pride was a violent counter-demonstration by far-right protesters against an attempt to hold a pride parade by pro-LGBT organizers of the NGO Tbilisi Pride in Tbilisi, Georgia. Anti-LGBT protesters frustrated attempts to hold a parade, attacked dozens of journalists who were covering the events and NGO offices, which resulted in the canceling of the Pride demonstration after four location changes from the initial procession at Rustaveli Avenue. The protest held in support of Tbilisi Pride by a number of media outlets and political parties on the second day was also met by violent counter-protests. Background On 16 May 2021, a day ahead of International Day Against Homophobia, Transphobia and Biphobia, 15 political parties, including the United National Movement, the largest opposition party, signed the agreement "to fight to eliminate discrimination and violence against LGBTQ citizens with all mechanisms at their disposal" with Tbilisi Pride. The Tb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rustaveli Avenue
Rustaveli Avenue ( ka, რუსთაველის გამზირი, ''Rust'avelis Gamziri''), formerly known as ''Golovin Street'', is the central avenue in Tbilisi named after the medieval Georgian poet, Shota Rustaveli. The avenue starts at Freedom Square and extends for about 1.5 km in length, before it turns into an extension of Kostava Street. Rustaveli is often considered the main thoroughfare of Tbilisi due to the numerous governmental, public, cultural, and business buildings that are located along or near the avenue. The Parliament of Georgia building, the Georgian National Opera Theater, the Rustaveli State Academic Theater, the Georgian Academy of Sciences, Kashveti Church, the Georgian Museum of Fine Arts, Simon Janashia Museum of Georgia (part of the Georgian National Museum), and Biltmore Hotel Tbilisi among others, are all located on Rustaveli. In 1989, tens of thousands of Georgians gathered before the House of Government on Rustaveli Avenue. An at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Internal Affairs Of Georgia
The Ministry of Internal Affairs of Georgia ( ka, საქართველოს შინაგან საქმეთა სამინისტრო), abbreviated MIA (''შსს''), is the highest state law enforcement agency of Georgia, the head of which (Minister) is a member of the Government. The Ministry is accountable to the Government and fulfills the tasks imposed on it by the Prime Minister. Vakhtang Gomelauri is the current Minister of Internal Affairs. The Ministry's main office is in Tbilisi. History After gaining independence on May 26, 1918 on the National Council meeting the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Georgia was formed. Its main tasks included fighting counter-revolutionary rallies and Bolshevik propaganda, combating embezzlement of public funds, etc. On February 25, 1921, with the help of Russia, the Georgian Bolsheviks overthrew the legitimate Menshevik government of Georgia. Since this day, the independent Ministry of Internal Affairs w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
