|
LCROSS
The Lunar Crater Observation and Sensing Satellite (LCROSS) was a robotic spacecraft operated by NASA. The mission was conceived as a low-cost means of determining the nature of hydrogen detected at the polar regions of the Moon. Launched immediately after discovery of lunar water by Chandrayaan-1, the main LCROSS mission objective was to further explore the presence of water in the form of ice in a permanently shadowed crater near a lunar polar region. It was successful in confirming water in the southern lunar crater Cabeus. It was launched together with the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) on June 18, 2009, as part of the shared Lunar Precursor Robotic Program, the first American mission to the Moon in over ten years. LCROSS was designed to collect and relay data from the impact and debris plume resulting from the launch vehicle's spent Centaur upper stage (and data-collecting Shepherding Spacecraft) striking the crater Cabeus near the south pole of the Moon. Centaur had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LCROSS Centaur Impact Flash
The Lunar Crater Observation and Sensing Satellite (LCROSS) was a robotic spacecraft operated by NASA. The mission was conceived as a low-cost means of determining the nature of hydrogen detected at the polar regions of the Moon. Launched immediately after discovery of lunar water by Chandrayaan-1, the main LCROSS mission objective was to further explore the presence of water in the form of ice in a permanently shadowed crater near a lunar polar region. It was successful in confirming water in the southern lunar crater Cabeus. It was launched together with the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) on June 18, 2009, as part of the shared Lunar Precursor Robotic Program, the first American mission to the Moon in over ten years. LCROSS was designed to collect and relay data from the impact and debris plume resulting from the launch vehicle's spent Centaur upper stage (and data-collecting Shepherding Spacecraft) striking the crater Cabeus near the south pole of the Moon. Centaur had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
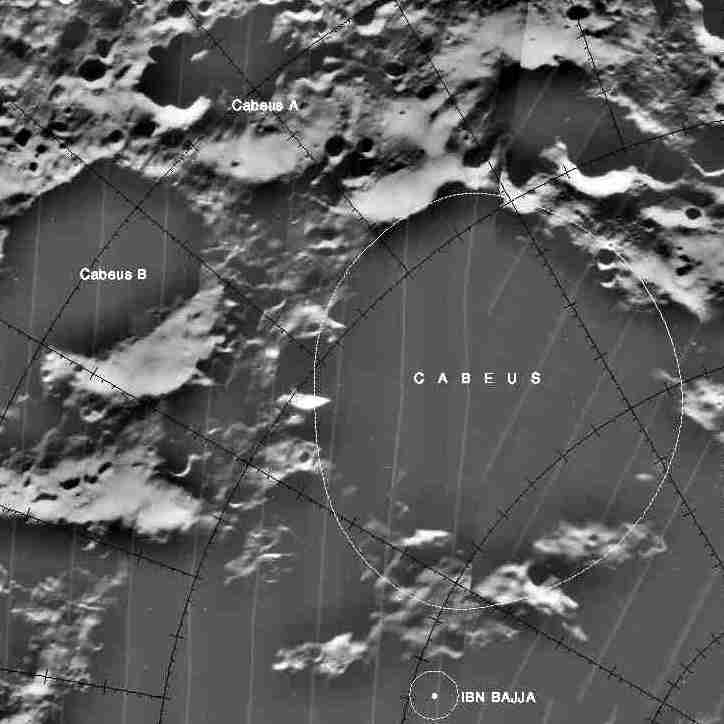
Cabeus (crater)
Cabeus is a lunar impact crater that is located about from the south pole of the Moon. At this location the crater is seen obliquely from Earth, and it is almost perpetually in deep shadow due to lack of sunlight. Hence, not much detail can be seen of this crater, even from orbit. Through a telescope, this crater appears near the southern limb of the Moon, to the west of the crater Malapert and to the south-southwest of Newton. Description The crater name ''Cabeus'' first appeared in the 1651 work ''Almagestum Novum'' by Giovanni Riccioli, who named it after Niccolò Cabeo. However, the position of the Cabeus crater was in the location later assigned to Newton crater.Whitaker (1999:61, 211) The official name and location for this crater was adopted by the IAU Commission 17, as established in the 1935 work ''Named Lunar Formations'' by Mary A. Blagg and Karl Müller. This crater is a worn formation that has been eroded by subsequent impacts. The rim is eroded and uneve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter
The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) is a NASA robotic spacecraft currently orbiting the Moon in an eccentric polar mapping orbit. Data collected by LRO have been described as essential for planning NASA's future human and robotic missions to the Moon. Its detailed mapping program is identifying safe landing sites, locating potential resources on the Moon, characterizing the radiation environment, and demonstrating new technologies. Launched on June 18, 2009, in conjunction with the Lunar Crater Observation and Sensing Satellite (LCROSS), as the vanguard of NASA's Lunar Precursor Robotic Program, LRO was the first United States mission to the Moon in over ten years. LRO and LCROSS were launched as part of the United States's Vision for Space Exploration program. The probe has made a 3-D map of the Moon's surface at 100-meter resolution and 98.2% coverage (excluding polar areas in deep shadow), including 0.5-meter resolution images of Apollo landing sites. The first images f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Water
Lunar water is water that is present on the Moon. Diffuse water molecules can persist at the Moon's sunlit surface, as discovered by NASA's SOFIA observatory in 2020. Gradually water vapor is decomposed by sunlight, leaving hydrogen and oxygen lost to outer space. Scientists have found water ice in the cold, permanently shadowed craters at the Moon's poles. Water molecules are also present in the extremely thin lunar atmosphere. Water (H2O), and the chemically related hydroxyl group (-OH), exist in forms chemically bound as hydrates and hydroxides to lunar minerals (rather than free water), and evidence strongly suggests that this is the case in low concentrations as for much of the Moon's surface. In fact, of surface matter, adsorbed water is calculated to exist at trace concentrations of 10 to 1000 parts per million. Inconclusive evidence of free water ice at the lunar poles had accumulated during the second half of the 20th century from a variety of observations suggestin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Precursor Robotic Program
The Lunar Precursor Robotic Program (LPRP) is a NASA program that uses robotic spacecraft to prepare for future manned missions to the Moon. The program gathers data such as lunar radiation, surface imaging, areas of scientific interest, temperature and lighting conditions, and potential resource identification. Two LPRP missions, the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) and the Lunar Crater Observation and Sensing Satellite (LCROSS), were launched in June 2009. The lift-off above Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on June 18, 2009, was successful. The uncrewed Atlas V rocket launched the two space probes towards the Moon, where they will provide a 3D map and search for water in conjunction with the Hubble Space Telescope. The launch date, originally planned for October 2008, was moved to June 17, 2009, due to a postponement of the June 13, 2009 launch of the Space Shuttle ''Endeavour'' because a hydrogen fuel leak. This lunar program marked the first United States miss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of Australia). The Moon is a planetary-mass object with a differentiated rocky body, making it a satellite planet under the geophysical definitions of the term and larger than all known dwarf planets of the Solar System. It lacks any significant atmosphere, hydrosphere, or magnetic field. Its surface gravity is about one-sixth of Earth's at , with Jupiter's moon Io being the only satellite in the Solar System known to have a higher surface gravity and density. The Moon orbits Earth at an average distance of , or about 30 times Earth's diameter. Its gravitational influence is the main driver of Earth's tides and very slowly lengthens Earth's day. The Moon's orbit around Earth has a sidereal period of 27.3 days. During each synodic period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
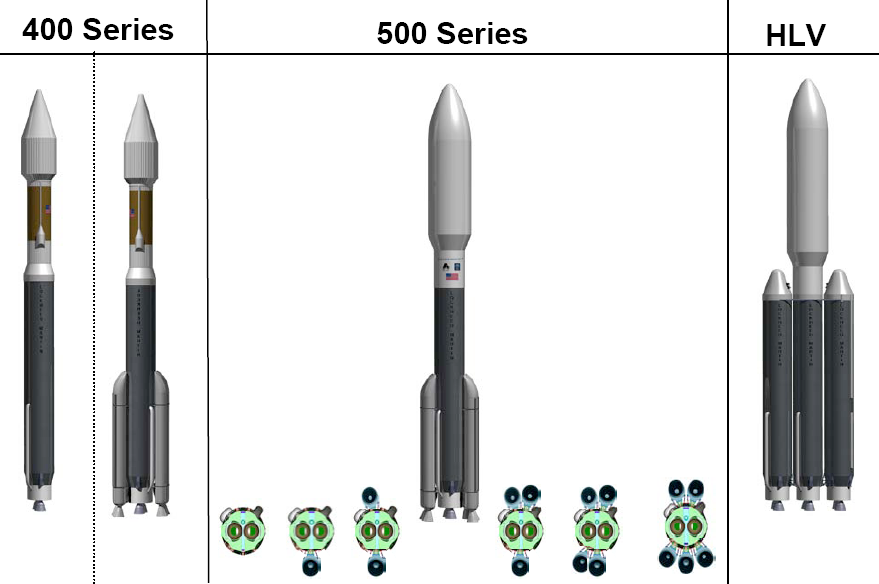
Atlas V
Atlas V is an expendable launch system and the fifth major version in the Atlas (rocket family), Atlas launch vehicle family. It was originally designed by Lockheed Martin, now being operated by United Launch Alliance (ULA), a joint venture between Lockheed Martin and Boeing. Atlas V is also a major NASA launch vehicle. It is America's longest-serving active rocket. In August 2021, ULA announced that Atlas V would be retired, and all 29 remaining launches had been sold. , 19 launches remain. Each Atlas V launch vehicle consists of two main stages. The first stage (rocketry), first stage is powered by a Russian RD-180 engine manufactured by NPO Energomash, Energomash and burning kerosene and liquid oxygen. The Centaur (rocket stage), Centaur upper stage is powered by one or two American RL10 engine(s) manufactured by Aerojet Rocketdyne and burns liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen. The Star 48 upper stage was used on the ''New Horizons'' mission as a third stage. strap-on booster, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Launch Alliance
United Launch Alliance (ULA), legally United Launch Alliance, LLC, is an American spacecraft launch service provider that manufactures and operates a number of rocket vehicles that are capable of launching spacecraft into orbits around Earth, and to other bodies in the Solar System and beyond. The company, which is a joint venture between Lockheed Martin Space and Boeing Defense, Space & Security, was formed in December 2006. Launch customers of the United Launch Alliance include the Department of Defense (DoD), NASA, and other organizations. ULA provides launch services using expendable launch systems Delta IV Heavy and Atlas V, and until 2018 the medium-lift Delta II. The Atlas, Delta IV Heavy and the recently retired Delta IV launch systems have launched payloads including weather, telecommunications, and national security satellites, scientific probes and orbiters. ULA also launches commercial satellites. , the company is developing the Vulcan Centaur, a successor to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandrayaan-1
Chandrayaan-1 (, ) was the first Indian lunar probe under the Chandrayaan program. It was launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation in October 2008, and operated until August 2009. The mission included a lunar orbiter and an impactor. India launched the spacecraft using a PSLV-XL rocket on 22 October 2008 at 00:52 UTC from Satish Dhawan Space Centre, at Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh. The mission was a major boost to India's space program, as India researched and developed indigenous technology to explore the Moon. The vehicle was inserted into lunar orbit on 8 November 2008. On 14 November 2008, the Moon Impact Probe separated from the Chandrayaan orbiter at 14:36 UTC and struck the south pole in a controlled manner, making India the fourth country to place its flag insignia on the Moon. The probe hit near the crater Shackleton at 15:01 UTC The location of impact was named Jawahar Point. The estimated cost for the project was . It was intended to survey th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ames Research Center
The Ames Research Center (ARC), also known as NASA Ames, is a major NASA research center at Moffett Federal Airfield in California's Silicon Valley. It was founded in 1939 as the second National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) laboratory. That agency was dissolved and its assets and personnel transferred to the newly created National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) on October 1, 1958. NASA Ames is named in honor of Joseph Sweetman Ames, a physicist and one of the founding members of NACA. At last estimate NASA Ames had over US$3 billion in capital equipment, 2,300 research personnel and a US$860 million annual budget. Ames was founded to conduct wind-tunnel research on the aerodynamics of propeller-driven aircraft; however, its role has expanded to encompass spaceflight and information technology. Ames plays a role in many NASA missions. It provides leadership in astrobiology; small satellites; robotic lunar exploration; the search for habitable planets; s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta II
Delta II was an expendable launch system, originally designed and built by McDonnell Douglas. Delta II was part of the Delta rocket family and entered service in 1989. Delta II vehicles included the Delta 6000, and the two later Delta 7000 variants ("Light" and "Heavy"). The rocket flew its final mission ICESat-2 on 15 September 2018, earning the launch vehicle a streak of 100 successful missions in a row, with the last failure being GPS IIR-1 in 1997. History In the early 1980s, all United States expendable launch vehicles were planned to be phased out in favor of the Space Shuttle, which would be responsible for all government and commercial launches. Production of Delta, Atlas-Centaur, and Titan 34D had ended. The ''Challenger'' disaster of 1986 and the subsequent halt of Shuttle operations changed this policy, and President Ronald Reagan announced in December 1986 that the Space Shuttle would no longer launch commercial payloads, and NASA would seek to purchase launches ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
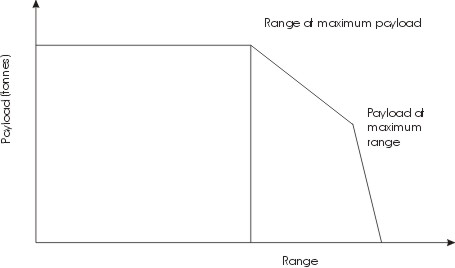
Payload (air And Space Craft)
Payload is the object or the entity which is being carried by an aircraft or launch vehicle. Sometimes payload also refers to the carrying capacity of an aircraft or launch vehicle, usually measured in terms of weight. Depending on the nature of the flight or mission, the payload of a vehicle may include cargo, passengers, flight crew, munitions, scientific instruments or experiments, or other equipment. Extra fuel, when optionally carried, is also considered part of the payload. In a commercial context (i.e., an airline or air freight carrier), payload may refer only to revenue-generating cargo or paying passengers. A payload of ordnance carried by a combat aircraft is sometimes alternatively referred to as the aircraft's warload. For a rocket, the payload can be a satellite, space probe, or spacecraft carrying humans, animals, or cargo. For a ballistic missile, the payload is one or more warheads and related systems; their total weight is referred to as the throw-weight. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_launches_with_LRO_and_LCROSS.jpg)