|
LBV 1806−20
LBV 1806−20 is a candidate luminous blue variable (LBV) and likely binary star located around from the Sun, towards the center of the Milky Way. It has an estimated mass of around 36 solar masses and an estimated variable luminosity of around two million times that of the Sun. It is highly luminous but is invisible from the Solar System at visual wavelengths because less than one billionth of its visible light reaches us. When first discovered, LBV 1806−20 was considered both the most luminous and most massive star known, which challenged scientific understanding of the formation of massive stars. Recent estimates place it somewhat nearer to Earth, which when combined with its binary nature mean that it is now well within the expected range of parameters for extremely luminous stars in the galaxy. It is estimated at 2 million times as luminous as the sun which makes it one of the most luminous stars in the galaxy. Location LBV 1806−20 lies at the core of radio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1806-20 Cluster
Eighteen or 18 may refer to: * 18 (number), the natural number following 17 and preceding 19 * one of the years 18 BC, AD 18, 1918, 2018 Film, television and entertainment * ''18'' (film), a 1993 Taiwanese experimental film based on the short story ''God's Dice'' * ''Eighteen'' (film), a 2005 Canadian dramatic feature film * 18 (British Board of Film Classification), a film rating in the United Kingdom, also used in Ireland by the Irish Film Classification Office * 18 (''Dragon Ball''), a character in the ''Dragon Ball'' franchise * "Eighteen", a 2006 episode of the animated television series ''12 oz. Mouse'' Music Albums * ''18'' (Moby album), 2002 * ''18'' (Nana Kitade album), 2005 * '' 18...'', 2009 debut album by G.E.M. Songs * "18" (5 Seconds of Summer song), from their 2014 eponymous debut album * "18" (One Direction song), from their 2014 studio album ''Four'' * "18", by Anarbor from their 2013 studio album ''Burnout'' * "I'm Eighteen", by Alice Cooper commonly re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H II Region
An H II region or HII region is a region of interstellar atomic hydrogen that is ionized. It is typically in a molecular cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place, with a size ranging from one to hundreds of light years, and density from a few to about a million particles per cubic centimetre. The Orion Nebula, now known to be an H II region, was observed in 1610 by Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Peiresc by telescope, the first such object discovered. The regions may be of any shape because the distribution of the stars and gas inside them is irregular. Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, The short-lived blue stars created in these regions emit copious amounts of ultraviolet light that ionize the surrounding gas. H II regions—sometimes several hundred light-years across—are often associated with giant molecular clouds. They often appear clumpy and filamentary, sometimes showing intricate shapes such as the Horsehead Nebula. H II regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelvin
The kelvin, symbol K, is the primary unit of temperature in the International System of Units (SI), used alongside its prefixed forms and the degree Celsius. It is named after the Belfast-born and University of Glasgow-based engineer and physicist William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin (1824–1907). The Kelvin scale is an absolute thermodynamic temperature scale, meaning it uses absolute zero as its null (zero) point. Historically, the Kelvin scale was developed by shifting the starting point of the much-older Celsius scale down from the melting point of water to absolute zero, and its increments still closely approximate the historic definition of a degree Celsius, but since 2019 the scale has been defined by fixing the Boltzmann constant to be exactly . Hence, one kelvin is equal to a change in the thermodynamic temperature that results in a change of thermal energy by . The temperature in degree Celsius is now defined as the temperature in kelvins minus 273.15, meaning t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Effective Temperature
The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total amount of electromagnetic radiation. Effective temperature is often used as an estimate of a body's surface temperature when the body's emissivity curve (as a function of wavelength) is not known. When the star's or planet's net emissivity in the relevant wavelength band is less than unity (less than that of a black body), the actual temperature of the body will be higher than the effective temperature. The net emissivity may be low due to surface or atmospheric properties, including greenhouse effect. Star The effective temperature of a star is the temperature of a black body with the same luminosity per ''surface area'' () as the star and is defined according to the Stefan–Boltzmann law . Notice that the total (bolometric) luminosity of a star is then , where is the stellar radius. The definition of the stellar radius is obviously not straightf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stefan–Boltzmann Law
The Stefan–Boltzmann law describes the power radiated from a black body in terms of its temperature. Specifically, the Stefan–Boltzmann law states that the total energy radiated per unit surface area of a black body across all wavelengths per unit time j^ (also known as the black-body ''radiant emittance'') is directly proportional to the fourth power of the black body's thermodynamic temperature ''T'': : j^ = \sigma T^. The constant of proportionality ''σ'', called the Stefan–Boltzmann constant, is derived from other known physical constants. Since 2019, the value of the constant is : \sigma=\frac = 5.670374419\times 10^\, \mathrm, where ''k'' is the Boltzmann constant, ''h'' is Planck's constant, and ''c'' is the speed of light in a vacuum. The radiance from a specified angle of view (watts per square metre per steradian) is given by : L = \frac\pi = \frac\sigma\pi T^. A body that does not absorb all incident radiation (sometimes known as a grey body) emits ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around 1 millimeter (300 GHz) to the nominal red edge of the visible spectrum, around 700 nanometers (430 THz). Longer IR wavelengths (30 μm-100 μm) are sometimes included as part of the terahertz radiation range. Almost all black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is at infrared wavelengths. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, IR propagates energy and momentum, exerts radiation pressure, and has properties corresponding to both those of a wave and of a particle, the photon. It was long known that fires emit invisible heat; in 1681 the pioneering experimenter Edme Mariotte showed that glass, though transparent to sunlight, obstructed radiant heat. In 1800 the astronomer Sir William Herschel discovered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactic Center
The Galactic Center or Galactic Centre is the rotational center, the barycenter, of the Milky Way galaxy. Its central massive object is a supermassive black hole of about 4 million solar masses, which is called Sagittarius A*, a compact radio source which is almost exactly at the galactic rotational center. The Galactic Center is approximately away from Earth in the direction of the constellations Sagittarius, Ophiuchus, and Scorpius, where the Milky Way appears brightest, visually close to the Butterfly Cluster (M6) or the star Shaula, south to the Pipe Nebula. There are around 10 million stars within one parsec of the Galactic Center, dominated by red giants, with a significant population of massive supergiants and Wolf–Rayet stars from star formation in the region around 1 million years ago. The core stars are a small part within the much wider galactic bulge. Discovery Because of interstellar dust along the line of sight, the Galactic Center cannot be studied at v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P Cygni Profile
P Cygni (34 Cygni) is a variable star in the constellation Cygnus. The designation "P" was originally assigned by Johann Bayer in ''Uranometria'' as a nova. Located about 5,300 light-years (1,560 parsecs) from Earth, it is a hypergiant luminous blue variable (LBV) star of spectral type B1-2 Ia-0ep that is one of the most luminous stars in the Milky Way. Visibility The star is located about 5,000 to 6,000 light-years (1,500–1,800 parsecs) from Earth. Despite this vast distance, it is visible to the naked eye in suitable dark sky locations. It was unknown until the end of the 16th century, when it suddenly brightened to 3rd magnitude. It was first observed on 18 August (Gregorian) 1600 by Willem Janszoon Blaeu, a Dutch astronomer, mathematician and globe-maker. Bayer's atlas of 1603 assigned it the miscellaneous label P and the name has stuck ever since. After six years the star faded slowly, dropping below naked-eye visibility in 1626. It brightened again in 1655, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling and melting point are the lowest among all the elements. It is the second lightest and second most abundant element in the observable universe (hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant). It is present at about 24% of the total elemental mass, which is more than 12 times the mass of all the heavier elements combined. Its abundance is similar to this in both the Sun and in Jupiter, due to the very high nuclear binding energy (per nucleon) of helium-4, with respect to the next three elements after helium. This helium-4 binding energy also accounts for why it is a product of both nuclear fusion and radioactive decay. The most common isotope of helium in the universe is helium-4, the vast majority of which was formed during t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Hydrogen is the most abundant chemical substance in the universe, constituting roughly 75% of all normal matter.However, most of the universe's mass is not in the form of baryons or chemical elements. See dark matter and dark energy. Stars such as the Sun are mainly composed of hydrogen in the plasma state. Most of the hydrogen on Earth exists in molecular forms such as water and organic compounds. For the most common isotope of hydrogen (symbol 1H) each atom has one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. In the early universe, the formation of protons, the nuclei of hydrogen, occurred during the first second after the Big Bang. The emergence of neutral hydrogen atoms throughout the universe occurred about 370,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
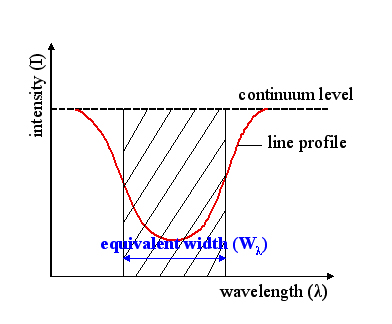
Equivalent Width
The equivalent width of a spectral line is a measure of the area of the line on a plot of intensity versus wavelength in relation to underlying continuum level. It is found by forming a rectangle with a height equal to that of continuum emission, and finding the width such that the area of the rectangle is equal to the area in the spectral line. It is a measure of the strength of spectral features that is primarily used in astronomy. Definition Formally, the equivalent width is given by the equation W_\lambda = \int d\lambda = \int (1 - F_s / F_c) d\lambda. Here, F_c(\lambda) represents the underlying continuum intensity, while F_s(\lambda) represents the intensity of the actual spectrum (the line and continuum). Then W_\lambda represents the width of a hypothetical line which drops to an intensity of zero and has the "same integrated flux deficit from the continuum as the true one." This equation can be applied to either emission or absorption, but when applied to emission, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SGR 1806−20
SGR 1806−20 is a magnetar, a type of neutron star with a very powerful magnetic field, that was discovered in 1979 and identified as a soft gamma repeater. SGR 1806−20 is located about 13 kiloparsecs (42,000 light-years) from Earth on the far side of the Milky Way in the constellation of Sagittarius. It has a diameter of no more than and rotates on its axis every 7.5 seconds ( rotation speed at the surface). , SGR 1806-20 is the most highly magnetized object ever observed, with a magnetic field over 1015 gauss (G) (1011 tesla) in intensity (compared to the Sun's 1–5 G and Earth's 0.25–0.65 G). Explosion Fifty thousand years after a starquake occurred on the surface of SGR 1806-20, the radiation from the resultant explosion reached Earth on December 27, 2004 ( GRB 041227). In terms of gamma rays, the burst had an absolute magnitude around −29. It was the brightest event known to have been sighted on this planet from an origin outside the Solar System, unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |