|
LBO Valuation Model
The LBO (or leveraged buyout) valuation model estimates the current value of a business to a "financial buyer", based on the business's forecast financial performance. An already-completed five-year financial forecast and two assumptions are all that are necessary to create a first draft of a comprehensive LBO valuation of the business. From a processing standpoint, the model makes a copy of the already completed five-year forecast and uses that copy (and any changes made to it) for projecting future operating results. As such, the original forecast is preserved. The model analyzes the value of a business from the point of view of a "financial buyer" who owns no other businesses in that industry and, therefore, expects all of its investment return to result solely from the future operations of the business. The LBO valuation model assumes that the buyer has investigated a business and operating plan and believes the business will achieve the financial results that have been for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leveraged Buyout
A leveraged buyout (LBO) is one company's acquisition of another company using a significant amount of borrowed money (leverage) to meet the cost of acquisition. The assets of the company being acquired are often used as collateral for the loans, along with the assets of the acquiring company. The use of debt, which normally has a lower cost of capital than equity, serves to reduce the overall cost of financing the acquisition. The cost of debt is lower because interest payments often reduce corporate income tax liability, whereas dividend payments normally do not. This reduced cost of financing allows greater gains to accrue to the equity, and, as a result, the debt serves as a lever to increase the returns to the equity. The term LBO is usually employed when a financial sponsor acquires a company. However, many corporate transactions are partially funded by bank debt, thus effectively also representing an LBO. LBOs can have many different forms such as management buyout (MBO), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business
Business is the practice of making one's living or making money by producing or Trade, buying and selling Product (business), products (such as goods and Service (economics), services). It is also "any activity or enterprise entered into for profit." Having a business name does not separate the business entity from the owner, which means that the owner of the business is responsible and liable for debts incurred by the business. If the business acquires debts, the creditors can go after the owner's personal possessions. A business structure does not allow for corporate tax rates. The proprietor is personally taxed on all income from the business. The term is also often used colloquially (but not by lawyers or by public officials) to refer to a company, such as a corporation or cooperative. Corporations, in contrast with Sole proprietorship, sole proprietors and partnerships, are a separate legal entity and provide limited liability for their owners/members, as well as being su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buyer
Procurement is the method of discovering and agreeing to terms and purchasing goods, services, or other works from an external source, often with the use of a tendering or competitive bidding process. When a government agency buys goods or services through this practice, it is referred to as public procurement. Procurement as an organizational process is intended to ensure that the buyer receives goods, services, or works at the best possible price when aspects such as quality, quantity, time, and location are compared. Corporations and public bodies often define processes intended to promote fair and open competition for their business while minimizing risks such as exposure to fraud and collusion. Almost all purchasing decisions include factors such as delivery and handling, marginal benefit, and fluctuations in the prices of goods. Organisations which have adopted a corporate social responsibility perspective are also likely to require their purchasing activity to take wide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Forecast
A financial forecast is an estimate of future financial outcomes for a company or project, usually applied in budgeting, capital budgeting and / or valuation; see . Depending on context the term may also refer to listed company (quarterly) earnings guidance. For a country or economy, see Economic forecast. Typically, using historical internal accounting and sales data, in addition to external industry data and economic indicators, a financial forecast will be the analyst's modeled prediction of company outcomes in financial terms over a given time period. (For fundamental analysis, analysts often also use stock market information, such as the 52-week high of stock prices to augment their analysis of stock prices. ) For the components / steps of business modeling here, see . Arguably, the key aspect of preparing a financial forecast is predicting revenue; future costs, fixed and variable, as well as capital, can then be estimated as a function of sales via "common-si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operating Profit
In accounting and finance, earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) is a measure of a firm's profit that includes all incomes and expenses (operating and non-operating) except interest expenses and income tax expenses. Operating income and operating profit are sometimes used as a synonym for EBIT when a firm does not have non-operating income and non-operating expenses. Formula *EBIT = (net income) + interest + taxes = EBITDA – (depreciation and amortization expenses) *operating income = ( gross income) – OPEX = EBIT – (non-operating profit) + (non-operating expenses) where *EBITDA = earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization *OPEX = operating expense Overview A professional investor contemplating a change to the capital structure of a firm (e.g., through a leveraged buyout) first evaluates a firm's fundamental earnings potential (reflected by earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization (EBITDA) and EBIT), and then determines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
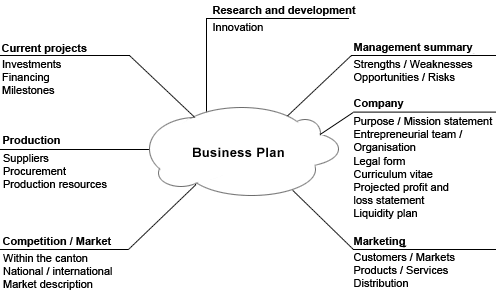
Business Plan
A business plan is a formal written document containing the goals of a business, the methods for attaining those goals, and the time-frame for the achievement of the goals. It also describes the nature of the business, background information on the organization, the organization's financial projections, and the strategies it intends to implement to achieve the stated targets. In its entirety, this document serves as a road-map (a plan) that provides direction to the business. Written business plans are often required to obtain a bank loan or other kind of financing. Templates and guides, such as the ones offered in the United States by the Small Business Administration can be used to facilitate producing a business plan. Audience Business plans may be internally or externally focused. Externally-focused plans draft goals that are important to outside stakeholders, particularly financial stakeholders. These plans typically have detailed information about the organization or the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asset
In financial accountancy, financial accounting, an asset is any resource owned or controlled by a business or an economic entity. It is anything (tangible or intangible) that can be used to produce positive economic value. Assets represent value of ownership that can be converted into cash (although cash itself is also considered an asset). The balance sheet of a firm records the monetaryThere are different methods of assessing the monetary value of the assets recorded on the Balance Sheet. In some cases, the ''Historical Cost'' is used; such that the value of the asset when it was bought in the past is used as the monetary value. In other instances, the present fair market value of the asset is used to determine the value shown on the balance sheet. value of the assets owned by that firm. It covers money and other valuables belonging to an individual or to a business. Assets can be grouped into two major classes: Tangible property, tangible assets and intangible assets. Tangible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liability (financial Accounting)
In financial accounting, a liability is defined as the future sacrifices of economic benefits that the entity is ''obliged'' to make to other entities as a result of past transactions or other ''past'' events, the settlement of which may result in the transfer or use of assets, provision of services or other yielding of economic benefits in the future. Characteristics A liability is defined by the following characteristics: * Any type of borrowing from persons or banks for improving a business or personal income that is payable during short or long time; * A duty or responsibility to others that entails settlement by future transfer or use of assets, provision of services, or other transaction yielding an economic benefit, at a specified or determinable date, on occurrence of a specified event, or on demand; * A duty or responsibility that obligates the entity to another, leaving it little or no discretion to avoid settlement; and, * A transaction or event obligating the entity t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seller
Sales are activities related to selling or the number of goods sold in a given targeted time period. The delivery of a service for a cost is also considered a sale. The seller, or the provider of the Goods and services, goods or services, completes a sale in response to an takeover, acquisition, appropriation (economics), appropriation, purchase order, requisition, or a direct interaction with the ''buyer'' at the point of sale. There is a passing of title (property or ownership) of the Commodity, item, and the settlement of a price, in which agreement is reached on a price for which transfer of ownership of the item will occur. The ''seller'', not the Purchasing, purchaser, typically executes the sale and it may be completed prior to the obligation of payment. In the case of indirect interaction, a person who sells goods or service on behalf of the owner is known as a salesman or saleswoman or salesperson, but this often refers to someone selling goods in a store/shop, in wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |