|
LARS2
Probable leucyl-tRNA synthetase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''LARS2'' gene. This gene encodes a class 1 aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, mitochondrial leucyl-tRNA synthetase. Each of the twenty aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases catalyzes the aminoacylation of a specific tRNA or tRNA isoaccepting family with the cognate amino acid. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * Biology of bipolar disorder {{gene-3-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' Chemical specificity, specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
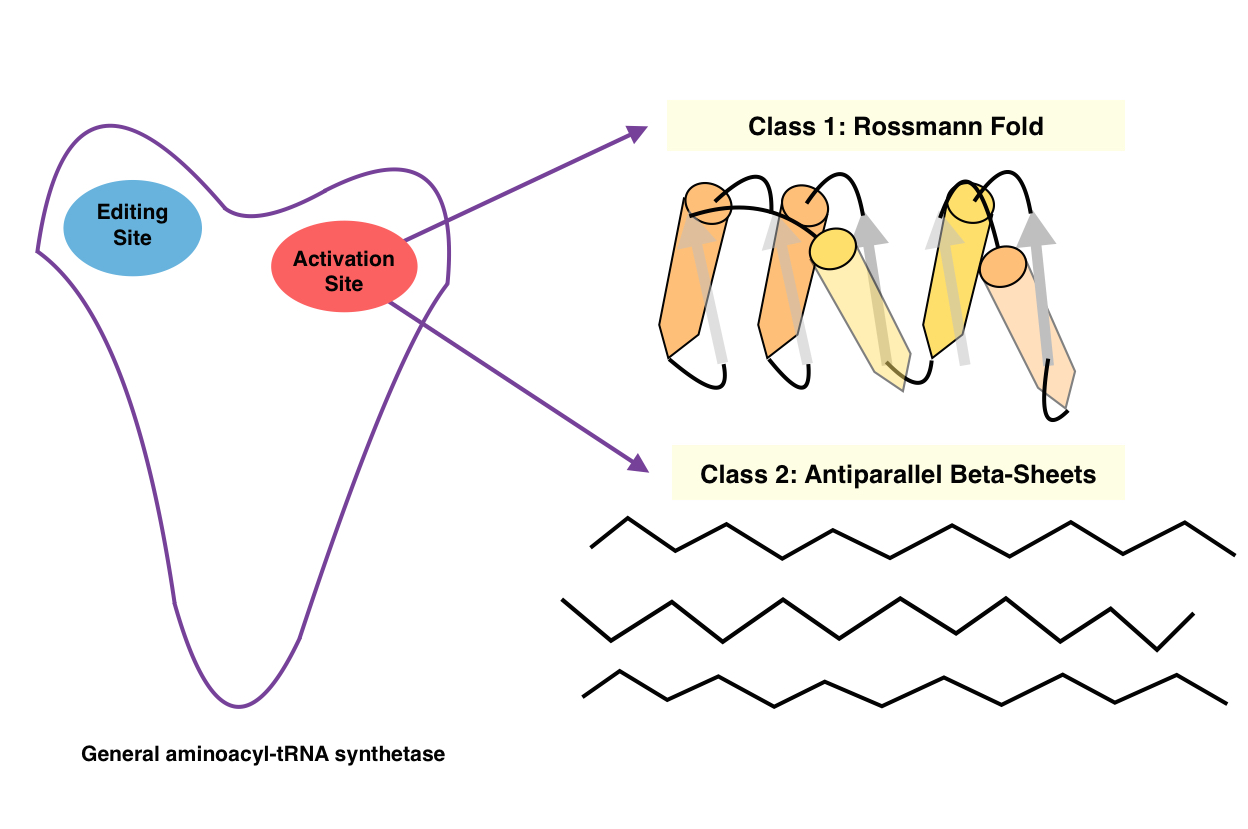
Aminoacyl TRNA Synthetases, Class I
The aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases catalyse the attachment of an amino acid to its cognate transfer RNA molecule in a highly specific two-step reaction. These proteins differ widely in size and oligomeric state, and have limited sequence homology. The 20 aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are divided into two classes, I and II. Class I aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases contain a characteristic Rossmann fold The Rossmann fold is a tertiary fold found in proteins that bind nucleotides, such as enzyme cofactors FAD, NAD+, and NADP+. This fold is composed of alternating beta strands and alpha helical segments where the beta strands are hydrogen bonde ... catalytic domain and are mostly monomeric. Class II aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases share an anti-parallel beta-sheet fold flanked by alpha-helices, and are mostly dimeric or multimeric, containing at least three conserved regions. However, tRNA binding involves an alpha-helical structure that is conserved between class I and class II synthetases. In re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetase
An aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (aaRS or ARS), also called tRNA-ligase, is an enzyme that attaches the appropriate amino acid onto its corresponding tRNA. It does so by catalyzing the transesterification of a specific cognate amino acid or its precursor to one of all its compatible cognate tRNAs to form an aminoacyl-tRNA. In humans, the 20 different types of aa-tRNA are made by the 20 different aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, one for each amino acid of the genetic code. This is sometimes called "charging" or "loading" the tRNA with an amino acid. Once the tRNA is charged, a ribosome can transfer the amino acid from the tRNA onto a growing peptide, according to the genetic code. Aminoacyl tRNA therefore plays an important role in RNA translation, the expression of genes to create proteins. Mechanism The synthetase first binds ATP and the corresponding amino acid (or its precursor) to form an aminoacyl-adenylate, releasing inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi). The adenylate-aaRS co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |