|
Lynn And Fakenham Railway
The Eastern and Midlands Railway was formed in 1881 by the amalgamation of several small railways in the Isle of Ely, Cambridgeshire, Lincolnshire and Norfolk, England, including the Yarmouth and North Norfolk Railway, the Lynn and Fakenham Railway and the Yarmouth Union Railway. Many of these lines were built by contractors Wilkinson and Jarvis. In 1893 the Eastern and Midlands Railway became part of the Midland and Great Northern Joint Railway. Constituents The constituents of the Eastern and Midlands Railway were: * Peterborough, Wisbech and Sutton Bridge Railway, opened 1866 * Midland & Eastern Railway (incorporating Lynn and Sutton Bridge Railway, Norwich & Spalding Railway and Spalding & Bourne Railway) * Lynn & Fakenham Railway * Yarmouth & North Norfolk (Light) Railway (incorporating Great Yarmouth & Stalham Light Railway) * Yarmouth Union Railway ;Spelling variations The spellings of some place names have changed since the 19th century (e.g. Wisbeach/Wisbech and Bourn/Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Of England
The East of England is one of the nine official regions of England. This region was created in 1994 and was adopted for statistics purposes from 1999. It includes the ceremonial counties of Bedfordshire, Cambridgeshire, Essex, Hertfordshire, Norfolk and Suffolk. Essex has the highest population in the region. The population of the East of England region in 2018 was 6.24 million. Bedford, Luton, Basildon, Peterborough, Southend-on-Sea, Norwich, Ipswich, Colchester, Chelmsford and Cambridge are the region's most populous settlements. The southern part of the region lies in the London commuter belt. Geography The East of England region has the lowest elevation range in the UK. Twenty percent of the region is below mean sea level, most of this in North Cambridgeshire, Norfolk and on the Essex Coast. Most of the remaining area is of low elevation, with extensive glacial deposits. The Fens, a large area of reclaimed marshland, are mostly in North Cambridgeshire. The Fens includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
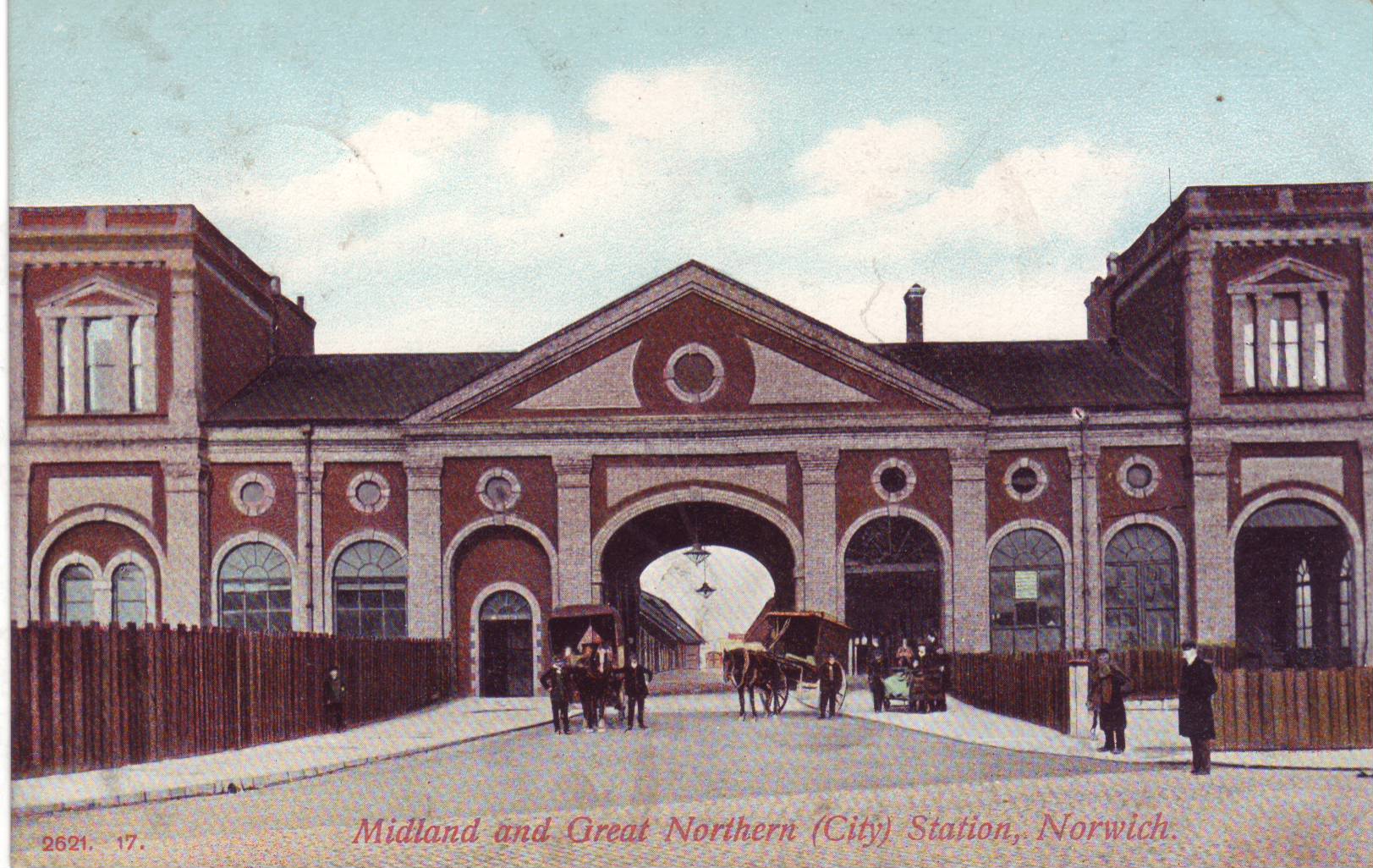
Norwich City Railway Station
Norwich City railway station was located in Norwich, Norfolk, England and was closed in 1969. History The station was opened in 1882 by the Lynn and Fakenham Railway, and later became the southern terminus of the Midland and Great Northern Joint Railway (MG&N) line from Melton Constable. The station became well-used, with services to Cromer and through-carriages to a range of destinations including Peterborough and Leicester. The station was badly bombed in the Baedeker raids of 1942 when the main building was largely destroyed. The station was further damaged when a badly damaged USAF B24 Liberator bomber was deliberately crashed there to avoid greater loss of life. Thereafter, the station operated from "temporary" buildings constructed on the site. It was closed to passengers on 2 March 1959 along with most of the Midland & Great Northern system, although the station remained in use for goods traffic until 1969. Location The old Norwich City station stood where a rounda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornwall Minerals Railway
The Cornwall Minerals Railway owned and operated a network of of standard gauge railway lines in central Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It started by taking over an obsolescent horse-operated tramway in 1862, and it improved and extended it, connecting Newquay and Par Harbours, and Fowey. Having expended considerable capital, it was hurt by a collapse in mineral extraction due to a slump in prices. Despite its title, it operated a passenger service between Newquay and Fowey. After a period in bankruptcy it returned to normal financial arrangements and acquired the moribund Lostwithiel and Fowey line. In 1896 it sold its line to the Great Western Railway. Its main passenger line from Par to Newquay is still in use as the Atlantic Coast Line, and also carries some mineral traffic, but the Par to Fowey line has been converted to a private road. Before the CMR Treffry Joseph Austen (1782 - 1850) of Fowey inherited considerable lands and mineral resources in central Cornw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharp Stewart
Sharp, Stewart and Company was a steam locomotive manufacturer, initially located in Manchester, England. The company was formed in 1843 upon the demise of Sharp, Roberts & Co.. It moved to Glasgow, Scotland, in 1888, eventually amalgamating with two other Glaswegian locomotive manufacturers to form the North British Locomotive Company. Early days Iron merchant Thomas Sharp and mechanical engineer Richard Roberts first formed a partnership, Sharp, Roberts & Co. (about which, see also company section in article on Roberts), to manufacture textile machinery and machine tools. They opened the Atlas Works in Manchester in 1828. They had built a few stationary steam engines, and in 1833 built a locomotive, ''Experiment'' for the Liverpool and Manchester Railway. It was a four-wheeled 2-2-0 with vertical cylinders over the leading wheels. After a number of modifications, three similar locomotives (Britannia, Manchester, and ''Hibernia'') were built in 1834 for the Dublin and Kingst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beyer Peacock
Beyer, Peacock and Company was an English railway locomotive manufacturer with a factory in Openshaw, Manchester. Founded by Charles Beyer, Richard Peacock and Henry Robertson, it traded from 1854 until 1966. The company exported locomotives, and machine tools to service them, throughout the world. Founders German-born Charles Beyer had undertaken engineering training related to cotton milling in Dresden before moving to England in 1831 aged 21. He secured employment as a draughtsman at Sharp, Roberts and Company's Atlas works in central Manchester, which manufactured cotton mill machinery and had just started building locomotives for the Liverpool and Manchester Railway. There he was mentored by head engineer and prolific inventor of cotton mill machinery, Richard Roberts. By the time he resigned 22 years later he was well established as the company's head engineer; he had been involved in producing more than 600 locomotives. Richard Peacock had been chief engineer of the Man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hudswell Clarke
Hudswell, Clarke and Company Limited was an engineering and locomotive building company in Jack Lane, Hunslet, Leeds, West Yorkshire, England. History The company was founded as Hudswell and Clarke in 1860. In 1870 the name was changed to Hudswell, Clarke and Rodgers. There was another change in 1881 to Hudswell, Clarke and Company. The firm became a limited company in 1899. In 1862, soon after the company had been formed, they were given the initial design work on William Hamond Bartholomew's compartment boats for the Aire and Calder Navigation. The choice of the company may have been influenced by the fact that Bartholomew, the chief engineer for the Navigation, and William Clayton, one of the founders of Hudswell and Clarke, both lived on Spencer Place in Leeds. They produced at least one of the prototype Tom Pudding compartments, but did not get the main contract for their production once the design work had been done. As steam locomotive builders, like many of the sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
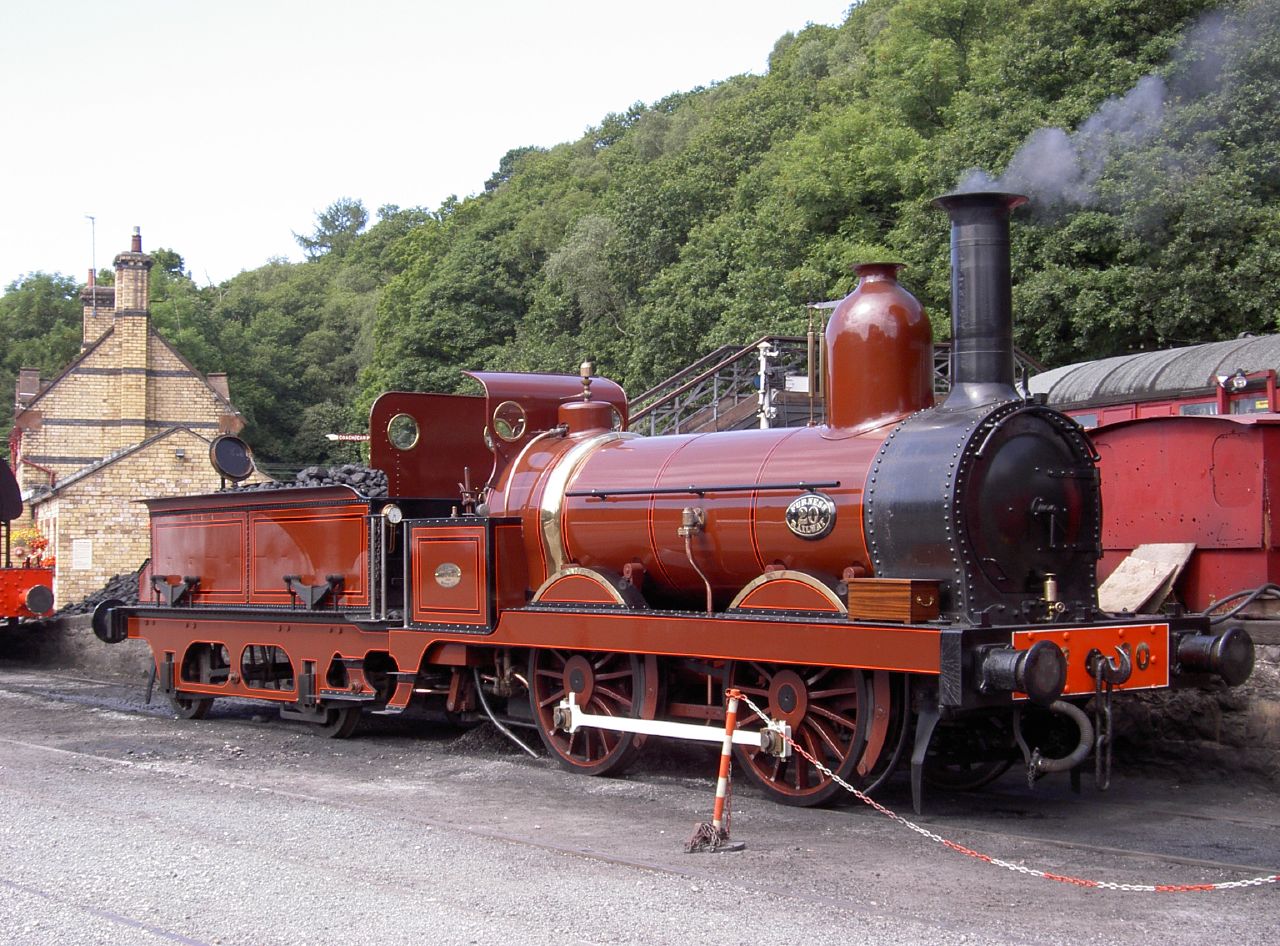
4-4-0
4-4-0 is a locomotive type with a classification that uses the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement and represents the arrangement: four leading wheels on two axles (usually in a leading bogie), four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles, and a lack of trailing wheels. Due to the large number of the type that were produced and used in the United States, the 4-4-0 is most commonly known as the American type, but the type subsequently also became popular in the United Kingdom, where large numbers were produced.White, John H., Jr. (1968). ''A history of the American locomotive; its development: 1830-1880''. New York: Dover Publications, pp. 46-. Almost every major railroad that operated in North America in the first half of the 19th century owned and operated locomotives of this type. The first use of the name ''American'' to describe locomotives of this wheel arrangement was made by ''Railroad Gazette'' in April 1872. Prior to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locomotive
A locomotive or engine is a rail transport vehicle that provides the Power (physics), motive power for a train. If a locomotive is capable of carrying a payload, it is usually rather referred to as a multiple unit, Motor coach (rail), motor coach, railcar or power car; the use of these self-propelled vehicles is increasingly common for passenger trains, but rare for freight (see CargoSprinter). Traditionally, locomotives pulled trains from the front. However, Push-pull train, push-pull operation has become common, where the train may have a locomotive (or locomotives) at the front, at the rear, or at each end. Most recently railroads have begun adopting DPU or distributed power. The front may have one or two locomotives followed by a mid-train locomotive that is controlled remotely from the lead unit. __TOC__ Etymology The word ''locomotive'' originates from the Latin language, Latin 'from a place', Ablative case, ablative of 'place', and the Medieval Latin 'causing mot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
0-6-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles and no trailing wheels. This was the most common wheel arrangement used on both tender and tank locomotives in versions with both inside and outside cylinders. In the United Kingdom, the Whyte notation of wheel arrangement was also often used for the classification of electric and diesel-electric locomotives with side-rod coupled driving wheels. Under the UIC classification, popular in Europe, this wheel arrangement is written as C if the wheels are coupled with rods or gears, or Co if they are independently driven, the latter usually being electric and diesel-electric locomotives. Overview History The 0-6-0 configuration was the most widely used wheel arrangement for both tender and tank steam locomotives. The type was also widely used for diesel switchers (shunters). Because they lack leading a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Peckett And Sons Railway Locomotives
List of Peckett and Sons railway locomotives, plus those from Fox Walker, both built at the Atlas Engine Works, Bristol. Despite hard work and poor maintenance, the engines were long-lasting, and many Peckett locomotives survive working on today's heritage railways. The oldest surviving Fox Walker locomotive is ''Karlskoga'', an 0-6-0ST of 1873 which was returned to steam at Nora, Sweden in 1982. References * * * * Notes External links Data and photographs*{{cite web, url=http://www.preservedshunters.co.uk/psh_list_ind_steam.php , title=List of Peckett & Sons locomotives, publisher=Preserved Hubters, archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080201050153/http://www.preservedshunters.co.uk/psh_list_ind_steam.php, archive-date=1 February 2008, access-date=17 October 2015 Locomotives * Peckett Peckett and Sons was a locomotive manufacturer at the Atlas Locomotive Works on Deep Pit Road between Fishponds and St. George, Bristol, England. Fox, Walker and Company The c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locomotive Superintendent
Chief mechanical engineer and locomotive superintendent are titles applied by British, Australian, and New Zealand railway companies to the person ultimately responsible to the board of the company for the building and maintaining of the locomotives and rolling stock. In Britain, the post of ''locomotive superintendent'' was introduced in the late 1830s, and ''chief mechanical engineer'' in 1886. Emerging professional roles In the early Victorian era, projected canal or railway schemes were prepared by groups of promoters who hired specialists such as civil engineers, surveyors, architects or contractors to survey a route; and this resulted in the issue of a prospectus setting out their proposals. Provided that adequate capital could be raised from potential investors, agreements obtained from the landowners along the proposed route and, in Britain, an Act of Parliament obtained (different terminology is used in other countries), then construction might begin either by a new compa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Marriott (engineer)
William Marriott (1857 – 17 November 1943) was the engineer, locomotive superintendent and traffic manager of the Midland & Great Northern Joint Railway (M&GN) Marriott was born at Basel, Switzerland where his father was a professor of English at the University of Basel. He was orphaned in 1868 and was brought to live in Bideford, receiving an education in England and on the continent. He served an apprenticeship with Ransomes & Rapier Ltd in Ipswich from 1875 to 1879 and as a draughtsman in 1880. He left Ransomes in 1881 to become an assistant engineer with Wilkinson & Jarvis Ltd completing a six-week unpaid trial period on the Yarmouth & North Norfolk Railway at Yarmouth. He was offered a permanent post which he accepted, and in 1883 he became the civil engineer and in 1884 the locomotive superintendent of the Eastern & Midlands Railway. This company was the amalgamation of all the Wilkinson & Jarvis lines in Norfolk, including both the Yarmouth & North Norfolk Railway a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


.jpg)
