|
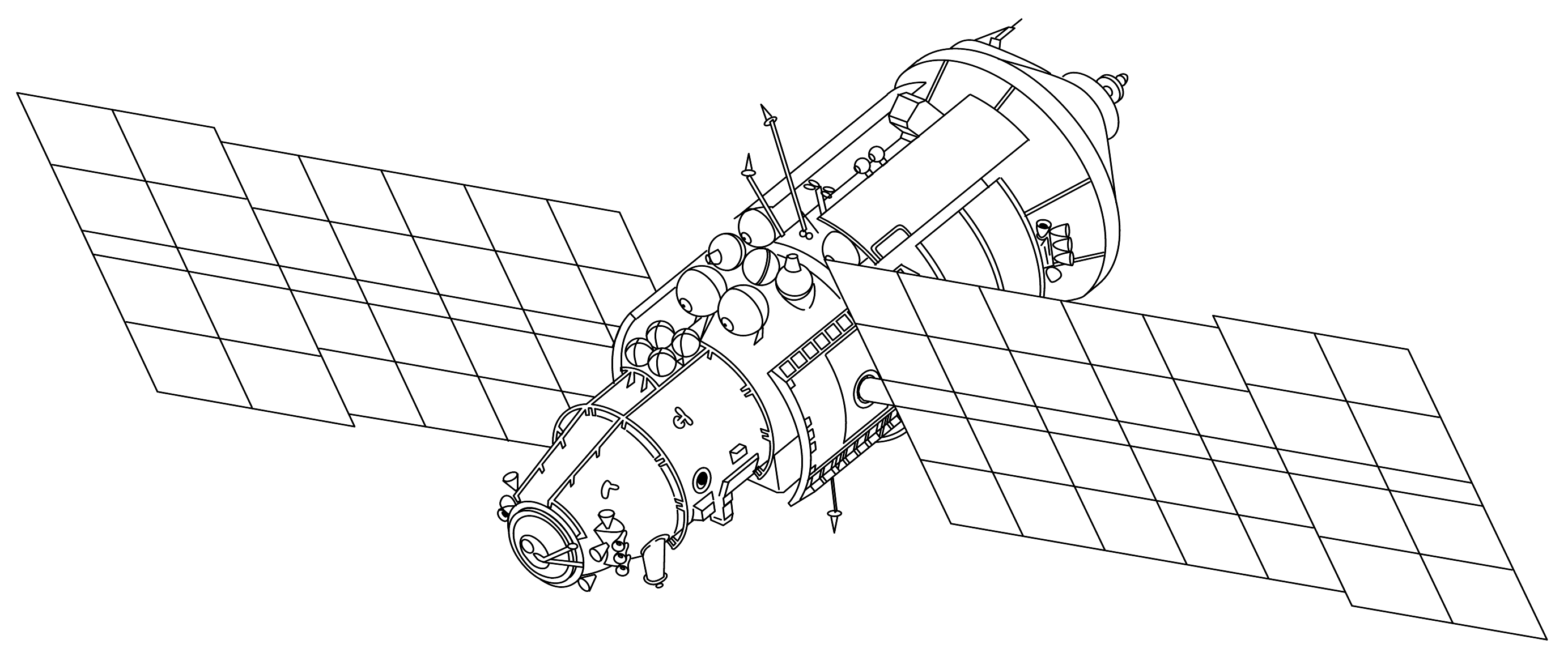
Lyappa Arm
The Lyappa (or Ljappa) arm, officially Automatic system of re-docking (russian: –Р–≤—В–Њ–Љ–∞—В–Є—З–µ—Б–Ї–∞—П —Б–Є—Б—В–µ–Љ–∞ –њ–µ—А–µ—Б—В—Л–Ї–Њ–≤–Ї–Є (–Р–°–Я—А), translit=Avtomaticheskaya sistema perestykovki (ASPr)), was a robotic arm used during the assembly of the Soviet/Russian space station '' Mir''. Each of the '' Kvant-2'', '' Kristall'', '' Spektr'' and '' Priroda'' modules was equipped with one of these arms, which, after the module had docked to the Mir Core Module's forward (or axial) port, grappled one of two fixtures positioned on the core module's hub module. The module's main docking probe was then retracted, and the arm raised the module so that it could be pivoted 90 degrees for docking to one of the four radial docking ports. Likewise the Prichal module will host the grapple fixtures for the redocking of future modules docked to it from one port to another using the Lyappa Arm attached to those modules, if needed. Both the Wentian and Mengtian modules of the pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mir Arm2
''Mir'' (russian: –Ь–Є—А, ; ) was a space station that operated in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001, operated by the Soviet Union and later by Russia. ''Mir'' was the first modular space station and was assembled in orbit from 1986 to 1996. It had a greater mass than any previous spacecraft. At the time it was the largest artificial satellite in orbit, succeeded by the International Space Station (ISS) after ''Mir'''s orbital decay, orbit decayed. The station served as a microgravity research laboratory in which crews conducted experiments in biology, human biology, physics, astronomy, meteorology, and spacecraft systems with a goal of developing technologies required for permanent occupation of Outer space, space. ''Mir'' was the first continuously inhabited long-term research station in orbit and held the record for the longest continuous human presence in space at 3,644 days, until it was surpassed by the ISS on 23 October 2010. It holds the record for the longes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Station
A space station is a spacecraft capable of supporting a human crew in orbit for an extended period of time, and is therefore a type of space habitat. It lacks major propulsion or landing systems. An orbital station or an orbital space station is an artificial satellite (i.e. a type of orbital spaceflight). Stations must have docking ports to allow other spacecraft to dock to transfer crew and supplies. The purpose of maintaining an orbital outpost varies depending on the program. Space stations have most often been launched for scientific purposes, but military launches have also occurred. Space stations have harboured so far the only long-duration direct human presence in space. After the first station Salyut 1 (1971) and its tragic Soyuz 11 crew, space stations have been operated consecutively since Skylab (1973), having allowed a progression of long-duration direct human presence in space. Stations have been occupied by consecutive crews since 1987 with the Salyut succe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kvant-2
Kvant-2 (russian: –Ъ–≤–∞–љ—В-2; English: Quantum-II/2) (77KSD, TsM-D, 11F77D) was the third module and second major addition to the Mir space station. Its primary purpose was to deliver new science experiments, better life support systems, and an airlock to Mir. It was launched on November 26, 1989 on a Proton rocket. It docked to Mir on December 6. Its control system was designed by the NPO "Electropribor" (Kharkiv, Ukraine). Description Kvant-2 was the first Mir module based on the TKS spacecraft (77k module). Kvant-2 was divided into three compartments. They were the EVA airlock, the instrument/cargo compartment, and the instrument/experiment compartment. The instrument/cargo compartment could be sealed off and act as an extension or a back-up to the airlock. Before Kvant-2 docked to the station, EVAs had to be carried by depressurizing the docking node on the Core Module. Kvant-2 also carried the Soviet version of the Manned Maneuvering Unit for the Orlan space suit. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kristall
The Kristall (russian: –Ъ—А–Є—Б—В–∞–ї–ї, , Crystal) (77KST, TsM-T, 11F77T) module was the fourth module and the third major addition to '' Mir''. As with previous modules, its configuration was based on the 77K (TKS) module, and was originally named "Kvant 3". It was launched on May 31, 1990 on Proton-K. It docked to Mir autonomously on June 10, 1990. Description Kristall had several materials processing furnaces. They were called Krater 5, Optizon 1, Zona 2, and Zona 3. It also had a biotechnology experiment called the Aniur electrophoresis unit. These experiments were capable of generating 100 kg of raw materials for use on Earth. Located in the docking node was the Priroda 5 camera which was used for Earth resources experiments. Kristall also had several astronomy and astrophysics experiments which were designed to augment experiments that were already located in Kvant-1. Kristall's solar panels were also different from others on Mir. They were designed to be "collapsibl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spektr
Spektr (russian: –°–њ–µ–Ї—В—А; en, Spectrum) (TKM-O, 77KSO, 11F77O) was the fifth module of the Mir Space Station. The module was designed for remote observation of Earth's environment containing atmospheric and surface research equipment. Spektr also had four solar arrays which generated about half of the station's electrical power. Development The Spektr module was originally developed as part of a top-secret military program code-named " Oktant". It was planned to carry experiments with space-borne surveillance and test antimissile defense. The surveillance instruments were mounted on the exterior of the module opposite the docking port. Also in this location were two launchers for artificial targets. The heart of the Spektr payload was an experimental optical telescope code-named "PionвАЭ (Peony). Instrument list: * 286K binocular radiometer * Astra 2 вАУ monitored atmospheric trace constituents, Mir environment * Balkan 1 lidar вАУ measures upper cloud altitude. Use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priroda
The Priroda (russian: –Я—А–Є—А–Њ–і–∞; en, Nature) (TsM-I, 77KSI, 11F77I) module was the seventh and final module of the Mir Space Station. Its primary purpose was to conduct Earth resource experiments through remote sensing and to develop and verify remote sensing methods. The control system of Priroda was developed by the Khartron (Kharkov, Ukraine). Description Priroda was originally designed to carry a deployable solar array. However, due to delays, and the fact that solar arrays were planned for other parts of Mir, a solar array was not included in the launch configuration. Instead, during free flight, Priroda was powered by two redundant sets of batteries totaling 168. Priroda had an unpressurized instrument compartment and a habitable instrument/payload compartment. The unpressurized compartment contained propulsion system components, EVA handrails, and scientific equipment. The instrument/payload compartment was divided into two sections: an outer instrument section a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mir Core Module
''Mir'' (russian: –Ь–Є—А lit. ''Peace'' or ''World''), DOS-7, was the first module of the Soviet/Russian '' Mir'' space station complex, in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001. Generally referred to as either the core module or base block, the module was launched on 20 February 1986 on a Proton-K rocket from LC-200/39 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome. The spacecraft was generally similar in design to the two previous Soviet orbital stations, Salyut 6 and Salyut 7, however possessed a revolutionary addition in the form of a multiple docking node at the forward end of the module. This, in addition to the docking port at the rear of the spacecraft, allowed five additional modules ( ''Kvant''-1 (1987), ''Kvant''-2 (1989), ''Kristall'' (1990), '' Spektr'' (1995) and '' Priroda'' (1996)) to be docked directly to DOS-7, greatly expanding the station's capabilities. Designed as a 'habitat' or 'living' module, DOS-7 possessed less scientific apparatus than its predecessors (lacking, for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prichal (ISS Module)
''Prichal'' nodal module also known as Uzlovoy Module or UM (russian: –£–Ј–ї–Њ–≤–Њ–є –Ь–Њ–і—Г–ї—М "–Я—А–Є—З–∞–ї", ''Nodal Module Berth'') is a Russian spacecraft which is part of the International Space Station (ISS). It was approved in 2011 and was launched on 24 November 2021, at 13:06:35 UTC, atop Progress M-UM, with operations beginning in 2022. Originally, the nodal module was intended to serve as the only permanent element of the future Orbital Piloted Assembly and Experiment Complex (OPSEK), but those plans were scrapped in 2017. Description ''Prichal'' is a nodal module that has a pressurized spherical ball-shaped design with six hybrid docking ports. It also has functional components located outside and inside it. The interior of the module is divided into two zones: habitable and instrument with on-board systems. The zenith port out of the six ports is active SSVP-M to allow docking with the space station, while the four ports are passive hybrids of SSVP-M ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotation Arm On Wentian
Rotation, or spin, is the circular movement of an object around a '' central axis''. A two-dimensional rotating object has only one possible central axis and can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise direction. A three-dimensional object has an infinite number of possible central axes and rotational directions. If the rotation axis passes internally through the body's own center of mass, then the body is said to be ''autorotating'' or ''spinning'', and the surface intersection of the axis can be called a '' pole''. A rotation around a completely external axis, e.g. the planet Earth around the Sun, is called ''revolving'' or ''orbiting'', typically when it is produced by gravity, and the ends of the rotation axis can be called the ''orbital poles''. Mathematics Mathematically, a rotation is a rigid body movement which, unlike a translation, keeps a point fixed. This definition applies to rotations within both two and three dimensions (in a plane and in space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tianhe Core Module
''Tianhe'' (), officially the ''Tianhe'' core module (), is the first module to launch of the Tiangong space station. It was launched into orbit on 29 April 2021, as the first launch of the final phase of Tiangong program, part of the China Manned Space Program (Project 921). ''Tianhe'' follows the earlier projects Salyut, Skylab, Mir, International Space Station, Tiangong-1 and Tiangong-2 space stations. It is the first module of a third-generation Chinese modular space station. Other examples of modular station projects include the Soviet/Russian Mir and the International Space Station. Operations will be controlled from the Beijing Aerospace Flight Control Center. In 2018, a fullscale mockup of ''Tianhe'' was publicly presented at China International Aviation & Aerospace Exhibition in Zhuhai. In October 2020, China selected 18 new astronauts ahead of the space station construction to participate in the country's space station project. Functions and systems The core m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Syromyatnikov
Vladimir Sergeevich Syromyatnikov (January 7, 1933 - September 19, 2006) was a Soviet and Russian space scientist best known for designing docking mechanisms for crewed spacecraft; it was his Androgynous Peripheral Attach System which, in the 1970s, linked the Soviet and American space capsules in the Apollo-Soyuz test flight. Syromyatnikov also helped design and develop Vostok, the world's first crewed spacecraft, which launched Yuri Gagarin into space in 1961. In the 1990s, he updated the design of his docking mechanism for the meeting of the Mir space station and the ''Atlantis'' Space Shuttle. Syromyatnikov's designs are still used by spacecraft visiting the International Space Station The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA .... See also * Apollo-Soyuz Test Project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |