|
Lutjanus Viridis
The blue-and-gold snapper (''Lutjanus viridis'') is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a snapper belonging to the family Lutjanidae. It is native to the eastern Pacific Ocean where it is important to local subsistence fisheries. Taxonomy The blue and gold snapper was first formally described in 1846 as ''Diacope viridis'' by the French zoologist Achille Valenciennes with the type locality given as the Galápagos Islands. The specific name ''viridis'' means "green", Valenciennes described and illustrated this species with a greenish body marked with darker green stripes along the flanks although it is actually bright yellow with bluish-white, black-edged stripes. Description Blue-and-gold snapper has an oblong body. The pointed snout has front and rear nostrils which are simple holes. It has a relatively large mouth which has protractile jaws. The teeth are conical to canine like in shape, with the front teeth typically enlarged so that they resemble fangs. The vomer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achille Valenciennes
Achille Valenciennes (9 August 1794 – 13 April 1865) was a French zoologist. Valenciennes was born in Paris, and studied under Georges Cuvier. His study of parasitic worms in humans made an important contribution to the study of parasitology. He also carried out diverse systematic classifications, linking fossil and current species. He worked with Cuvier on the 22-volume "'' Histoire Naturelle des Poissons''" (Natural History of Fish) (1828–1848), carrying on alone after Cuvier died in 1832. In 1832, he succeeded Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville (1777–1850) as chair of ''Histoire naturelle des mollusques, des vers et des zoophytes'' at the Muséum national d'histoire naturelle. Early in his career, he was given the task of classifying animals described by Alexander von Humboldt (1769–1859) during his travels in the American tropics (1799 to 1803), and a lasting friendship was established between the two men. He is the binomial authority for many species of fish, such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pectoral Fin
Fins are distinctive anatomical features composed of bony spines or rays protruding from the body of a fish. They are covered with skin and joined together either in a webbed fashion, as seen in most bony fish, or similar to a flipper, as seen in sharks. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the spine and are supported only by muscles. Their principal function is to help the fish swim. Fins located in different places on the fish serve different purposes such as moving forward, turning, keeping an upright position or stopping. Most fish use fins when swimming, flying fish use pectoral fins for gliding, and frogfish use them for crawling. Fins can also be used for other purposes; male sharks and mosquitofish use a modified fin to deliver sperm, thresher sharks use their caudal fin to stun prey, reef stonefish have spines in their dorsal fins that inject venom, anglerfish use the first spine of their dorsal fin like a fishing rod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopedia Of Life
The ''Encyclopedia of Life'' (''EOL'') is a free, online encyclopedia intended to document all of the 1.9 million living species known to science. It is compiled from existing trusted databases curated by experts and with the assistance of non-experts throughout the world. It aims to build one "infinitely expandable" page for each species, including video, sound, images, graphics, as well as text. In addition, the Encyclopedia incorporates content from the Biodiversity Heritage Library, which digitizes millions of pages of printed literature from the world's major natural history libraries. The project was initially backed by a US$50 million funding commitment, led by the MacArthur Foundation and the Sloan Foundation, who provided US$20 million and US$5 million, respectively. The additional US$25 million came from five cornerstone institutions—the Field Museum, Harvard University, the Marine Biological Laboratory, the Missouri Botanical Garden, and the Smithsonian Institutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madreporite
The madreporite is a light colored calcareous opening used to filter water into the water vascular system of echinoderms. It acts like a pressure-equalizing valve. It is visible as a small red or yellow button-like structure, looking like a small wart, on the aboral surface of the central disk of a sea star or sea urchin or the oral surface of Ophiuroidea. Close up, it is visibly structured, resembling a "madrepore" (stone coral, Scleractinia) colony. From this, it derives its name. The water vascular system of the sea star consists of a series of seawater-filled ducts that function in locomotion and feeding and respiration. Its main parts are the madreporite, the stone canal, the ring canal, the radial canals, the lateral canals, and the tube feet. The sieve-like madreporite allows entry of seawater into the stone canal, which connects to the ring canal around the mouth. Five or more radial canals extend from the ring canal, one in each arm above the ambulacral groove. From th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
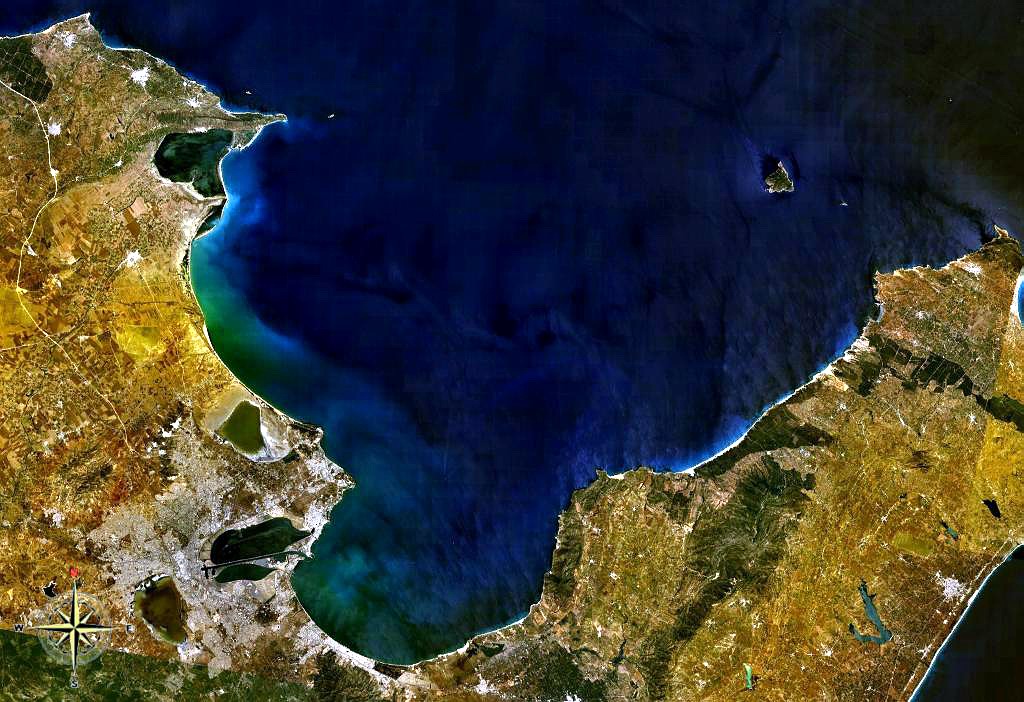
Gulf Of Chriqui
A gulf is a large inlet from the ocean into the landmass, typically with a narrower opening than a bay, but that is not observable in all geographic areas so named. The term gulf was traditionally used for large highly-indented navigable bodies of salt water that are enclosed by the coastline. Many gulfs are major shipping areas, such as the Persian Gulf, Gulf of Mexico, Gulf of Finland, and Gulf of Aden The Gulf of Aden ( ar, خليج عدن, so, Gacanka Cadmeed 𐒅𐒖𐒐𐒕𐒌 𐒋𐒖𐒆𐒗𐒒) is a deepwater gulf of the Indian Ocean between Yemen to the north, the Arabian Sea to the east, Djibouti to the west, and the Guardafui Channe .... See also * References External links * {{Authority control Bodies of water Coastal and oceanic landforms Coastal geography Oceanographical terminology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malpelo Island
Malpelo is a small oceanic island in the eastern Pacific Ocean, located about west of the Colombian mainland with a military post manned by the Colombian Armed Forces. It consists of a sheer and barren rock with three high peaks, the highest being ''Cerro de la Mona'' with a height of . The island is about in length from northeast to southwest, and in width. Geography Malpelo is the only island that rises above the surface from the Malpelo Ridge, which is a solitary volcanic submarine ridge that extends in a northeast-southwest direction with a length of and a width of . This island is surrounded by a number of offshore rocks. Off the northeast corner are the ''Tres Mosqueteros''. Off the southwest corner are ''Salomón'', ''Saúl'', ''La Gringa'', and ''Escuba''. All the rocks are surrounded by deep water, and most of the face of the main island is very steep. Soundings between are obtainable within a few kilometres of the shore and the currents are strong and changeable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cocos Island
Cocos Island ( es, Isla del Coco) is an island in the Pacific Ocean administered by Costa Rica, approximately southwest of the Costa Rican mainland. It constitutes the 11th of the 13 districts of Puntarenas Canton of the Province of Puntarenas. With an area of approximately , the island is more or less rectangular in shape. It is the southernmost point of geopolitical North America if non-continental islands are included. The entirety of Cocos Island has been designated a Costa Rican National Park since 1978, and has no permanent inhabitants other than Costa Rican park rangers. Surrounded by deep waters with counter-currents, Cocos Island is admired by scuba divers for its populations of hammerhead sharks, rays, dolphins and other large marine species. The wet climate and oceanic qualities give Cocos an ecological character that is not shared with either the Galápagos Archipelago or any of the other islands (for example, Malpelo, Gorgona or Coiba) in the eastern Pacific O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clipperton Island
Clipperton Island ( or ; ) is an uninhabited, coral atoll in the eastern Pacific Ocean. It is from Paris, France, from Papeete, Tahiti, and from Mexico. It is an Overseas France, overseas state private property of France under direct authority of the Minister of the Overseas (France), Minister of the Overseas. In the past, Clipperton Island was the subject of a sovereignty dispute in particular between France and Mexico, which was finally settled through arbitration in 1931; the ''Clipperton Island Case'' remains widely studied in international law textbooks. Geography The atoll is south-west of Mexico, west of Nicaragua, west of Costa Rica and north-west of the Galápagos Islands, Ecuador, at . Clipperton is about south-east of Socorro Island in the Revillagigedo Islands, Revillagigedo Archipelago, which is the nearest land, while the nearest French-owned island is Hiva Oa. Some consider it to be one of the eastern-most points of Oceania, rather than an outlying isla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revillagigedo Islands
The Revillagigedo Islands ( es, Islas Revillagigedo, ) or Revillagigedo Archipelago are a group of four volcanic islands in the Pacific Ocean, known for their unique ecosystem. They lie approximately from Socorro Island south and southwest of Cabo San Lucas, the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula, and west of Manzanillo, Colima, Manzanillo. Historically linked to the Mexican state of Colima, to which they were granted in 1861 to establish a penal colony, the islands are under Mexican federal property and jurisdiction. In July 2016, the Revillagigedo Archipelago was inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, and in November 2017 they were declared to be a marine reserve and a List of national parks of Mexico, national park of Mexico. Some of the volcanoes are active, with the last eruption of Volcán Bárcena in 1953, and Socorro (volcano), Socorro in 1993. Travelling to the islands from their nearest land point takes approximately 26 to 30 hours, as they are typicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baja California
Baja California (; 'Lower California'), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Baja California), is a state in Mexico. It is the northernmost and westernmost of the 32 federal entities of Mexico. Before becoming a state in 1952, the area was known as the North Territory of Baja California (). It has an area of (3.57% of the land mass of Mexico) and comprises the northern half of the Baja California Peninsula, north of the 28th parallel, plus oceanic Guadalupe Island. The mainland portion of the state is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean; on the east by Sonora, the U.S. state of Arizona, and the Gulf of California; on the north by the U.S. state of California; and on the south by Baja California Sur. The state has an estimated population of 3,769,020 as of 2020, significantly higher than the sparsely populated Baja California Sur to the south, and similar to San Diego County, California, to its north. Over 75% of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
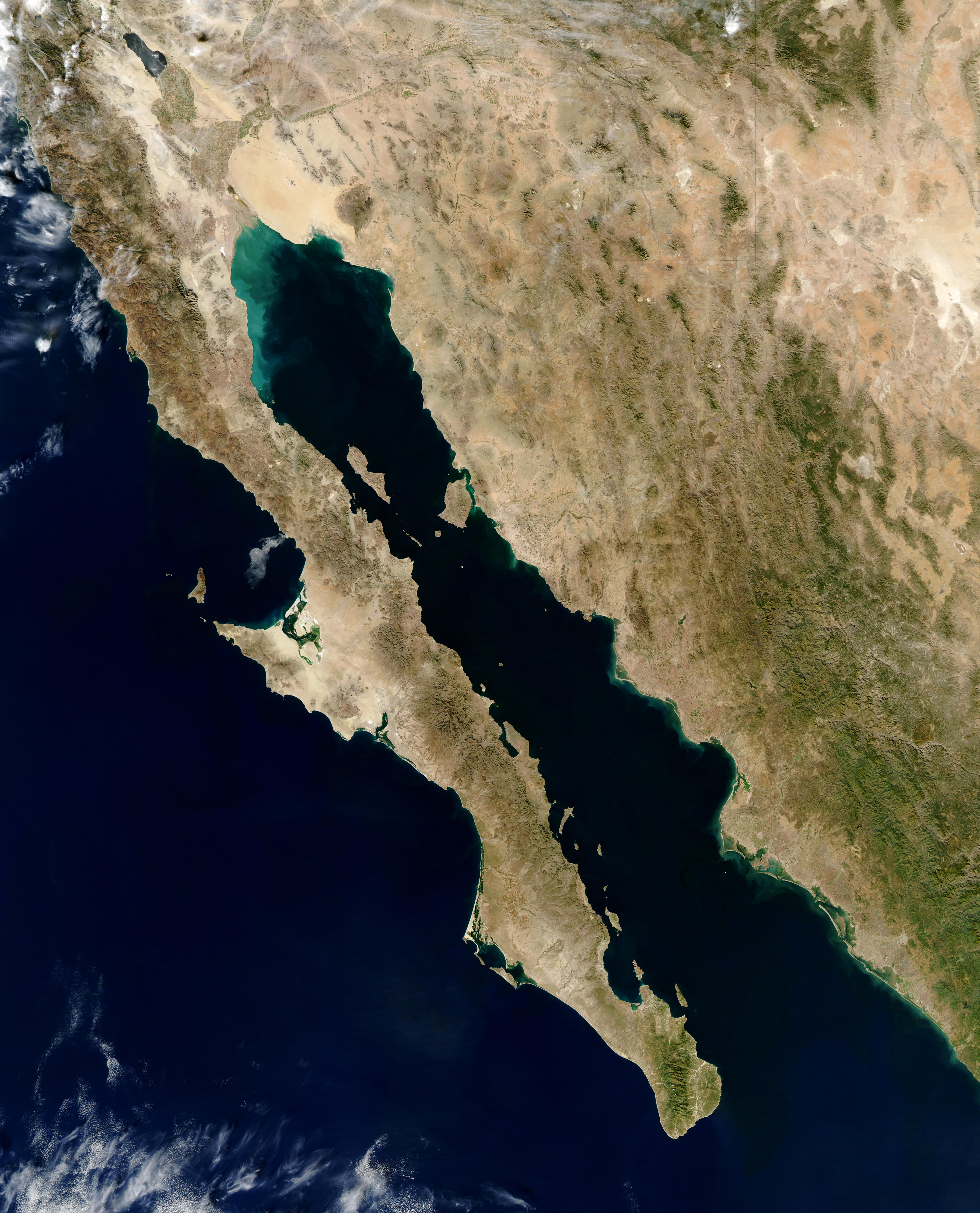
Gulf Of California
The Gulf of California ( es, Golfo de California), also known as the Sea of Cortés (''Mar de Cortés'') or Sea of Cortez, or less commonly as the Vermilion Sea (''Mar Bermejo''), is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean that separates the Baja California Peninsula from the Mexico, Mexican mainland. It is bordered by the states of Baja California, Baja California Sur, Sonora, and Sinaloa with a coastline of approximately . Rivers that flow into the Gulf of California include the Colorado River, Colorado, Fuerte River, Fuerte, Mayo River (Mexico), Mayo, Sinaloa River, Sinaloa, Sonora River, Sonora, and the Yaqui River, Yaqui. The surface of the gulf is about . Maximum depths exceed because of the complex geology, linked to plate tectonics. The gulf is thought to be one of the most diverse seas on Earth and is home to more than 5,000 species of micro-invertebrates. Parts of the Gulf of California are a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Geography History The marine expeditions of Fortún ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Length
Fish measurement is the measuring of individual fish and various parts of their anatomies. These data are used in many areas of ichthyology, including taxonomy and fisheries biology. Overall length * Standard length (SL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the posterior end of the last vertebra or to the posterior end of the midlateral portion of the hypural plate. Simply put, this measurement excludes the length of the caudal (tail) fin. * Total length (TL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the tip of the longer lobe of the caudal fin, usually measured with the lobes compressed along the midline. It is a straight-line measure, not measured over the curve of the body. Standard length measurements are used with Teleostei (most bony fish), while total length measurements are used with Myxini (hagfish), Petromyzontiformes (lampreys), and (usually) Elasmobranchii (sharks and rays), as well as some other fishes. Total length me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)