|
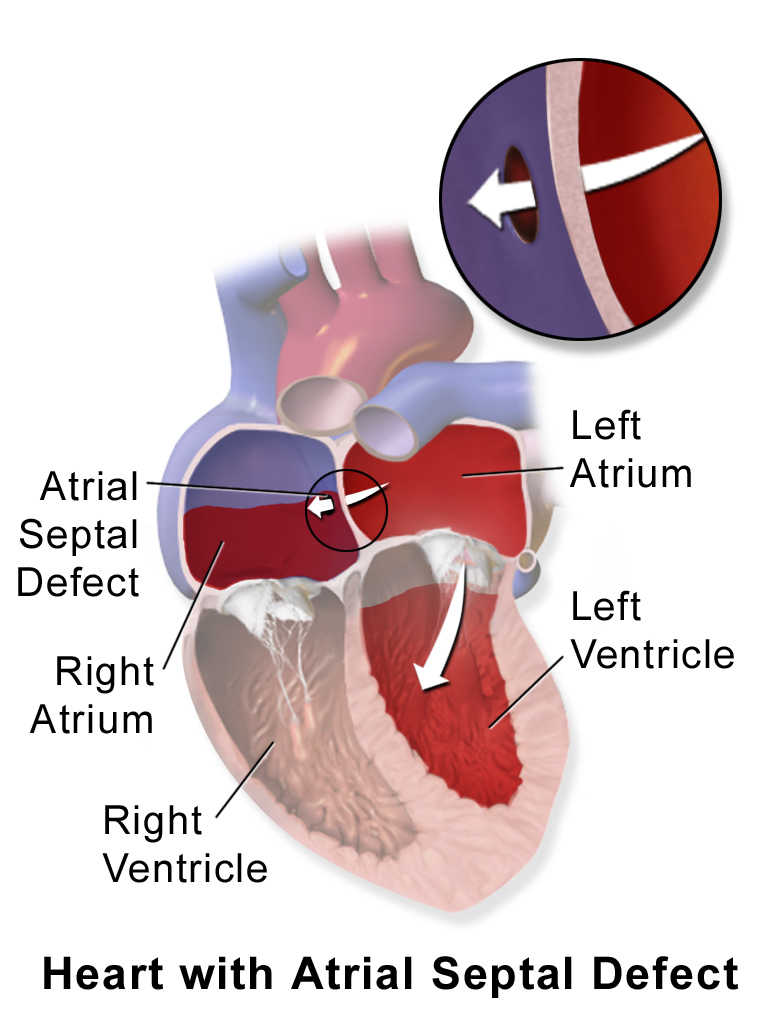
Lutembacher's Syndrome
Lutembacher's syndrome is a very rare form of congenital heart disease that affects one of the chambers of the heart (commonly the atrium) as well as a valve (commonly the mitral valve). It is commonly known as both congenital atrial septal defect (ASD) and acquired mitral stenosis (MS). Congenital (at birth) atrial septal defect refers to a hole being in the septum or wall that separates the two atria; this condition is usually seen in fetuses and infants. Mitral stenosis refers to mitral valve leaflets (or valve flaps) sticking to each other making the opening for blood to pass from the atrium to the ventricles very small. With the valve being so small, blood has difficulty passing from the left atrium into the left ventricle. Septal defects that may occur with Lutembacher's syndrome include: Ostium primum atrial septal defect or ostium secundum which is more prevalent. Lutembacher's syndrome affects females more often than males. It can affect children or adults; the person ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
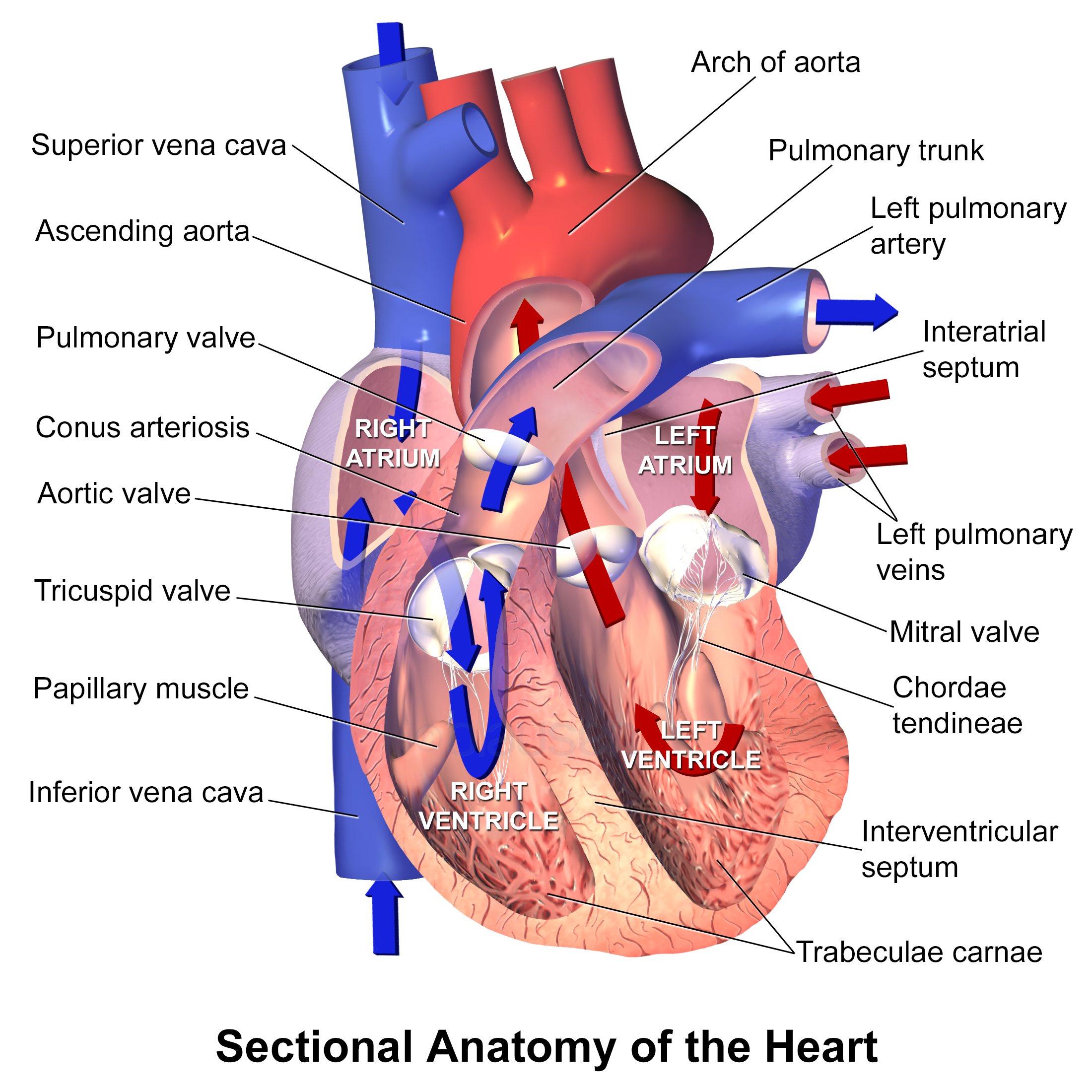
Congenital Heart Disease
A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly, congenital cardiovascular malformation, and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. A congenital heart defect is classed as a cardiovascular disease. Signs and symptoms depend on the specific type of defect. Symptoms can vary from none to life-threatening. When present, symptoms are variable and may include rapid breathing, bluish skin (cyanosis), poor weight gain, and feeling tired. CHD does not cause chest pain. Most congenital heart defects are not associated with other diseases. A complication of CHD is heart failure. Congenital heart defects are the most common birth defect. In 2015, they were present in 48.9 million people globally. They affect between 4 and 75 per 1,000 live births, depending upon how they are diagnosed. In about 6 to 19 per 1,000 they cause a moderate to severe degree of problems. Congenital heart defects are th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventricular Septal Defect
A ventricular septal defect (VSD) is a defect in the ventricular septum, the wall dividing the left and right ventricles of the heart. It's a common heart problem present at birth ( congenital heart defect). The extent of the opening may vary from pin size to complete absence of the ventricular septum, creating one common ventricle. The ventricular septum consists of an inferior muscular and superior membranous portion and is extensively innervated with conducting cardiomyocytes. The membranous portion, which is close to the atrioventricular node, is most commonly affected in adults and older children in the United States. It is also the type that will most commonly require surgical intervention, comprising over 80% of cases. Membranous ventricular septal defects are more common than muscular ventricular septal defects, and are the most common congenital cardiac anomaly. Signs and symptoms Ventricular septal defect is usually symptomless at birth. It usually manifests a fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Heart Defects
A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly, congenital cardiovascular malformation, and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. A congenital heart defect is classed as a cardiovascular disease. Signs and symptoms depend on the specific type of defect. Symptoms can vary from none to life-threatening. When present, symptoms are variable and may include rapid breathing, bluish skin (cyanosis), poor weight gain, and feeling tired. CHD does not cause chest pain. Most congenital heart defects are not associated with other diseases. A complication of CHD is heart failure. Congenital heart defects are the most common birth defect. In 2015, they were present in 48.9 million people globally. They affect between 4 and 75 per 1,000 live births, depending upon how they are diagnosed. In about 6 to 19 per 1,000 they cause a moderate to severe degree of problems. Congenital heart defects are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EUROCAT (medicine)
EUROCAT is a network of population-based congenital anomaly registries across Europe for the monitoring, surveillance and research of congenital anomalies. It was founded in 1979. As of January 2023, the network has 43 member registries from 23 countries covering more than 25% of European births per year. The detailed registry descriptions can be found on the EUROCAT website Objectives EUROCAT's objectives are to: * Provide essential epidemiologic information on congenital anomalies in Europe. * Facilitate the early warning of teratogenic exposures. * Evaluate the effectiveness of primary prevention. * Assess the impact of developments in prenatal screening. * Act as an information and resource center regarding clusters or exposures or risk factors for concern. * Provide a ready collaborative network and infrastructure for research related to the causes and prevention of congenital anomalies and the treatment and care of affected children. * Act as a catalyst for the sett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitral Valvuloplasty
Mitral stenosis is a valvular heart disease characterized by the narrowing of the opening of the mitral valve of the heart. It is almost always caused by rheumatic valvular heart disease. Normally, the mitral valve is about 5 cm2 during diastole. Any decrease in area below 2 cm2 causes mitral stenosis. Early diagnosis of mitral stenosis in pregnancy is very important as the heart cannot tolerate increased cardiac output demand as in the case of exercise and pregnancy. Atrial fibrillation is a common complication of resulting left atrial enlargement, which can lead to systemic thromboembolic complications such as stroke. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms of mitral stenosis include the following: * Heart failure symptoms, such as dyspnea on exertion, orthopnea and paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea (PND) * Palpitations * Chest pain * Hemoptysis * Thromboembolism in later stages when the left atrial volume is increased (i.e., dilation). The latter leads to increase risk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventricular Septal Defect
A ventricular septal defect (VSD) is a defect in the ventricular septum, the wall dividing the left and right ventricles of the heart. It's a common heart problem present at birth ( congenital heart defect). The extent of the opening may vary from pin size to complete absence of the ventricular septum, creating one common ventricle. The ventricular septum consists of an inferior muscular and superior membranous portion and is extensively innervated with conducting cardiomyocytes. The membranous portion, which is close to the atrioventricular node, is most commonly affected in adults and older children in the United States. It is also the type that will most commonly require surgical intervention, comprising over 80% of cases. Membranous ventricular septal defects are more common than muscular ventricular septal defects, and are the most common congenital cardiac anomaly. Signs and symptoms Ventricular septal defect is usually symptomless at birth. It usually manifests a fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitral Regurgitation
Mitral regurgitation (MR), also known as mitral insufficiency or mitral incompetence, is a form of valvular heart disease in which the mitral valve is insufficient and does not close properly when the heart pumps out blood. Section: Valvular Heart Disease Rupture or dysfunction of the papillary muscle are also common causes in acute cases, dysfunction, which can include mitral valve prolapse.VOC=VITIUM ORGANICUM CORDIS, a compendium of the Department of Cardiology at Uppsala Academic Hospital. By Per Kvidal September 1999, with revision by Erik Björklund May 2008 Pathophysiology The pathophysiology of MR can be broken into three phases of the disease process: the acute phase, the chronic compensated phase, and the chronic decompensated phase. Acute phase Acute MR (as may occur due to the sudden rupture of the chordae tendinae or papillary muscle) causes a sudden volume overload of both the left atrium and the left ventricle. The left ventricle develops volume overload because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blausen 0648 MitralValveStenosis
Blausen Medical Communications, Inc. (BMC) is the creator and owner of a library of two- and three-dimensional medical and scientific images and animations, a developer of information technology allowing access to that content, and a business focused on licensing and distributing the content. It was founded by Bruce Blausen in Houston, Texas, in 1991, and is privately held. Background Blausen Medical Communications is a privately held company founded by Bruce Blausen in Houston, Texas in 1991. BMC created and owns a library of medical and scientific images and animations, and has developed information technology tools allowing access to the library; as well, it licenses and otherwise works to distribute the content. As of this date, BMC's animation library comprised approximately 1,500 animations and over 27,000 two- and three-dimensional images designed for point-of-care patient education, which could be accessed by consumers or professional caregivers (primarily via hospital o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septum Primum
During heart development of a human embryo, the single primitive atrium becomes divided into right and left by a , the septum primum. The septum primum () grows downward into the single atrium. Development The gap below it is known as the ostium primum (), and becomes increasingly small. The septum primum eventually fuses with the endocardial cushion, closing the ostium primum off completely. Meanwhile, perforations appear in the superior part of the septum primum, forming the ostium secundum (). The septum primum will eventually form part of the fossa ovalis. Blood flow Hemodynamics American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, or haemodynamics are the Fluid dynamics, dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostasis, homeostatic mechanisms of autoregulation, just as hydrau ... between atria will continue through the foramen ovale (heart). Clinical significance Failure of the septum primum to fuse with the endocardial cushion ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ebstein's Anomaly
Ebstein's anomaly is a congenital heart defect in which the septal and posterior leaflets of the tricuspid valve are displaced downwards towards the apex of the right ventricle of the heart. Ebstein's anomaly has great anatomical heterogeneity that generates a wide spectrum of clinical features at presentation and is complicated by the fact that the lesion is often accompanied by other congenital cardiac lesions. It is classified as a critical congenital heart defect accounting for less than 1% of all congenital heart defects presenting in around 1 per 200,000 live births. Ebstein's anomaly usually presents with a systolic murmur (sometimes diastolic) and frequently with a gallop rhythm. Signs and symptoms The annulus of the valve is still in the normal position. The valve leaflets, however, are to a varying degree, attached to the walls and septum of the right ventricle. A subsequent "atrialization" of a portion of the morphologic right ventricle (which is then contiguous with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitral Regurgitation
Mitral regurgitation (MR), also known as mitral insufficiency or mitral incompetence, is a form of valvular heart disease in which the mitral valve is insufficient and does not close properly when the heart pumps out blood. Section: Valvular Heart Disease Rupture or dysfunction of the papillary muscle are also common causes in acute cases, dysfunction, which can include mitral valve prolapse.VOC=VITIUM ORGANICUM CORDIS, a compendium of the Department of Cardiology at Uppsala Academic Hospital. By Per Kvidal September 1999, with revision by Erik Björklund May 2008 Pathophysiology The pathophysiology of MR can be broken into three phases of the disease process: the acute phase, the chronic compensated phase, and the chronic decompensated phase. Acute phase Acute MR (as may occur due to the sudden rupture of the chordae tendinae or papillary muscle) causes a sudden volume overload of both the left atrium and the left ventricle. The left ventricle develops volume overload because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |