|
Lundberg Lag
The Lundberg lag, named after the Swedish economist Erik Lundberg Erik Filip Lundberg (13 August 1907 – 14 September 1987) was a Swedish economist, born in Stockholm. He was a professor of political economics at Stockholm University and a member of the Stockholm School of economic thought. He was president ..., stresses the lag between changes in the demand and response in output. This is one lag which points out that business cycles do not follow a completely random fashion but can be explained with a few different important regularities. See also * Robertson lag Notes and references Business cycle {{macroeconomics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erik Lundberg
Erik Filip Lundberg (13 August 1907 – 14 September 1987) was a Swedish economist, born in Stockholm. He was a professor of political economics at Stockholm University and a member of the Stockholm School of economic thought. He was president of the International Economic Association from 1968 to 1971. From 1969 to 1979, he was a member of the committee that selects the laureates for the Sveriges Riksbank Prize in Economic Sciences, the Economics Prize Committee, and served as the committee's chairman from 1975 to 1979. Erik Lundberg was the son of mathematician Ph.D. Filip Lundberg (1876-1965) and Astrid Bergstedt. 1931-33 he studied in the United States as Rockefeller Scholar, after his associate degree at Stockholm University, and when he returned to Sweden, he received post at the Riksbank's economic secretariat. In 1934 he was economic planning committee financial advisor in Iceland. He took his doctorate in 1937 with Studies in the theory of economic expansion, and rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
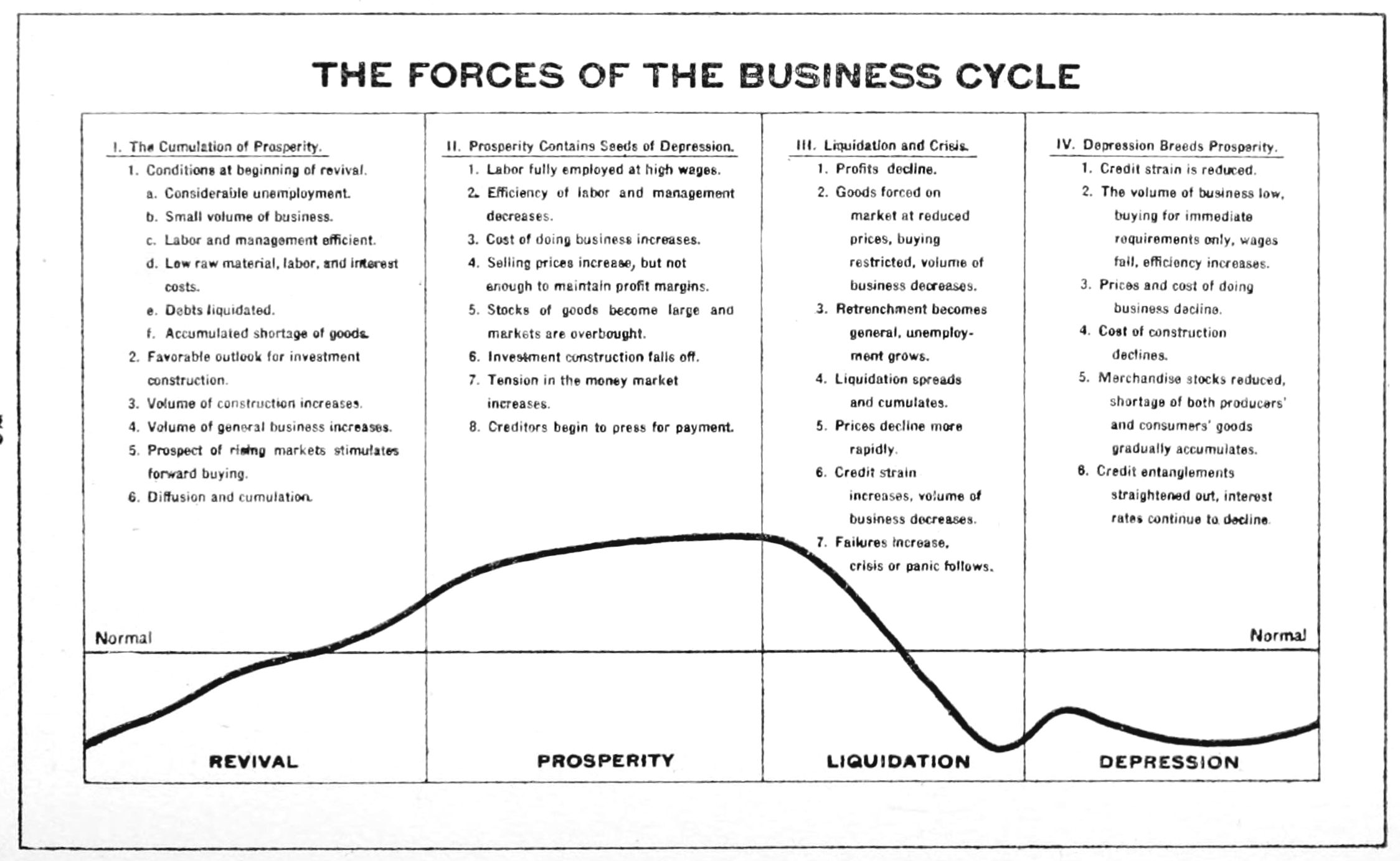
Business Cycles
Business cycles are intervals of expansion followed by recession in economic activity. These changes have implications for the welfare of the broad population as well as for private institutions. Typically business cycles are measured by examining trends in a broad economic indicator such as Real Gross Domestic Production. Business cycle fluctuations are usually characterized by general upswings and downturns in a span of macroeconomic variables. The individual episodes of expansion/recession occur with changing duration and intensity over time. Typically their periodicity has a wide range from around 2 to 10 years (the technical phrase "stochastic cycle" is often used in statistics to describe this kind of process.) As in arvey, Trimbur, and van Dijk, 2007, ''Journal of Econometrics'' such flexible knowledge about the frequency of business cycles can actually be included in their mathematical study, using a Bayesian statistical paradigm. There are numerous sources of business ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robertson Lag
The Robertson Lag is an example of the systematic delay which the economy suffers from when conditions change and is named after the famous economist Dennis Robertson. This lag describes how a consumers change in income and wealth, a change in its consumption function, leads to a delayed change in its consumption.Burda, Wyplosz (2005): Macroeconomics: A European Text, Fourth Edition, Oxford University Press See also *Lundberg lag The Lundberg lag, named after the Swedish economist Erik Lundberg Erik Filip Lundberg (13 August 1907 – 14 September 1987) was a Swedish economist, born in Stockholm. He was a professor of political economics at Stockholm University and a m ... Notes and references Consumer theory Consumption {{Econ-theory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |