|
Lund Astronomical Clock
Lund astronomical clock, occasionally and at least since the 16th century referred to as Horologium mirabile Lundense (''Latin'': "the wonderful clock in Lund"), is a 15th-century astronomical clock in Lund Cathedral. Mentioned in written sources for the first time in 1442, it was probably made and installed sometime around 1423–1425, possibly by Nikolaus Lilienfeld. It is part of a group of related medieval astronomical clocks found in the area around the south Baltic Sea. In 1837 the clock was dismantled. Between 1909 and 1923, it was restored by the Danish clockmaker Julius Bertram-Larsen and the Swedish architect responsible for the upkeep of the cathedral, . From the old clock, the face of the clock as well as the mechanism, which was largely replaced during the 18th century, was salvaged and re-used. The casing, most parts of the calendar which occupies the lower part, and the middle section were made anew. The clock displays a medieval concept of time, based on a geoce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunds Astronomiska Ur-2
Lund Food Holdings, Inc is an American supermarket operator. Headquartered in Edina, Minnesota, Edina, it owns the upscale supermarket chain Lunds & Byerlys. The company opened its first supermarkets in the Uptown, Minneapolis, Uptown area of Minneapolis. In 2015, it changed its name from Lunds to Lunds & Byerlys. It operates 28 stores in Minneapolis-St. Paul metro area of Minnesota. History Lunds History Russell T. Lund Sr. founded a grocery called Hove's in 1939 at the corner of Lake Street (Minneapolis), Lake Street and Hennepin Avenue in the Uptown, Minneapolis, Uptown neighborhood of Minneapolis. Russell Lund Sr., an employee, took an equity stake in the cheese and cracker department in 1922 and after founding a popcorn business, a larger stake in 1939. The chain took the Lunds name in 1964. Lunds and Byerly's were competing companies until 1997 when Lunds acquired Byerly's. They continued to operate under their individual names until April 2015, when the stores were rebr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to the German states of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania and Brandenburg, while the eastern part belongs to the West Pomeranian, Pomeranian and Kuyavian-Pomeranian voivodeships of Poland. Its historical border in the west is the Mecklenburg-Western Pomeranian border '' Urstromtal'' which now constitutes the border between the Mecklenburgian and Pomeranian part of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, while it is bounded by the Vistula River in the east. The easternmost part of Pomerania is alternatively known as Pomerelia, consisting of four sub-regions: Kashubia inhabited by ethnic Kashubians, Kociewie, Tuchola Forest and Chełmno Land. Pomerania has a relatively low population density, with its largest cities being Gdańsk and Szczecin. Ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Georg Brunius
Carl Georg Brunius (23 March 1793 – 12 November 1869) was a classical scholar, art historian, archaeologist and architect. He served as a professor and rector at Lund University. During 1833-59, he led the restoration work of Lund Cathedral. Biography Brunius was born at Tanum parish in Tanum Municipality in Västra Götaland County, Sweden. He was the son of the vicar Gomer Brunius and his wife Mariana Rodhe. He studied at Lund University, where he became a candidate in philology in 1813, a candidate in philosophy in 1814, a master of philosophy in 1814. He became an associate professor of Greek language at Lund University in 1815 and extra regular assistant professor in 1816, assistant professor in 1820. He became professor of Greek in 1824 filling the vacancy created when Esaias Tegnér (1782–1846) became Bishop of the Diocese of Växjö. Brunius also served as rector in 1831 and 1841 and retired as professor emeritus in 1858. Brunius spent most of his career ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopédie
''Encyclopédie, ou dictionnaire raisonné des sciences, des arts et des métiers'' (English: ''Encyclopedia, or a Systematic Dictionary of the Sciences, Arts, and Crafts''), better known as ''Encyclopédie'', was a general encyclopedia published in France between 1751 and 1772, with later supplements, revised editions, and translations. It had many writers, known as the Encyclopédistes. It was edited by Denis Diderot and, until 1759, co-edited by Jean le Rond d'Alembert. The ''Encyclopédie'' is most famous for representing the thought of the Enlightenment. According to Denis Diderot in the article "Encyclopédie", the ''Encyclopédies aim was "to change the way people think" and for people (bourgeoisie) to be able to inform themselves and to know things. He and the other contributors advocated for the secularization of learning away from the Jesuits. Diderot wanted to incorporate all of the world's knowledge into the ''Encyclopédie'' and hoped that the text could dissemina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strasbourg Astronomical Clock
The Strasbourg astronomical clock is located in the Cathédrale Notre-Dame of Strasbourg, Alsace, France. It is the third clock on that spot and dates from the time of the first French possession of the city (1681–1870). The first clock had been built in the 14th century, the second in the 16th century, when Strasbourg was a Free imperial city of the Holy Roman Empire. The current, third clock dates from 1843. Its main features, besides the automata, are a perpetual calendar (including a ''computus''), an orrery (planetary dial), a display of the real position of the Sun and the Moon, and solar and lunar eclipses. The main attraction is the procession of the 18 inch high figures of Christ and the Apostles, which occurs every day at solar noon, while the life-size cock crows thrice. Clocks First clock The Third of its kind against the south transept. The name of its maker is not known. This clock was known as the "Three Kings clock" and had several automata. One of them ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Bell
A church bell in Christian architecture is a bell which is rung in a church for a variety of religious purposes, and can be heard outside the building. Traditionally they are used to call worshippers to the church for a communal service, and to announce the fixed times of daily Christian prayer, called the canonical hours, which number seven and are contained in breviaries. They are also rung on special occasions such as a wedding, or a funeral service. In some religious traditions they are used within the liturgy of the church service to signify to people that a particular part of the service has been reached. The ringing of church bells, in the Christian tradition, is also believed to drive out demons. The traditional European church bell ''(see cutaway drawing)'' used in Christian churches worldwide consists of a cup-shaped metal resonator with a pivoted clapper hanging inside which strikes the sides when the bell is swung. It is hung within a steeple or belltower of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippa Of England
Philippa of England (mid-1394 – 5 January 1430), also known as Philippa of Lancaster, was Queen of Denmark, Norway and Sweden from 1406 to 1430 by marriage to King Eric of the Kalmar Union. She was the daughter of King Henry IV of England by his first spouse Mary de Bohun and the younger sister of King Henry V. Queen Philippa participated significantly in state affairs during the reign of her spouse, and served as regent of Denmark from 1423 to 1425. Biography Early life Philippa was born to Henry Bolingbroke and Mary de Bohun, at Peterborough Castle, Peterborough. Her father became king in 1399. She is mentioned a couple of times during her childhood: in 1403, she was present at her widowed father's wedding to Joan of Navarre, and the same year, she made a pilgrimage to Canterbury. She mainly lived at Berkhamsted Castle and Windsor Castle. Marriage In 1400 or 1401, King Henry suggested to Queen Margaret I of Denmark, Norway and Sweden that an alliance be formed between Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wells Cathedral
Wells Cathedral is an Anglican cathedral in Wells, Somerset, England, dedicated to St Andrew the Apostle. It is the seat of the Bishop of Bath and Wells, whose cathedra it holds as mother church of the Diocese of Bath and Wells. Built as a Roman Catholic cathedral from around 1175 to replace an earlier church on the site since 705, it became an Anglican cathedral when King Henry VIII split from Rome. It is moderately sized for an English cathedral. Its broad west front and large central tower are dominant features. It has been called "unquestionably one of the most beautiful" and "most poetic" of English cathedrals. Its Gothic architecture is mostly inspired from Early English style of the late 12th to early 13th centuries, lacking the Romanesque work that survives in many other cathedrals. Building began about 1175 at the east end with the choir. Historian John Harvey sees it as Europe's first truly Gothic structure, breaking the last constraints of Romanesque. The stonew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacquemart (bellstriker)
A jacquemart (sometimes jaquemart and also called a quarter-jack) is an automaton, an animated, mechanised figure of a person, usually made from wood or metal, which strikes the hours on a bell with a hammer. Jacquemarts are usually part of clocks or clocktowers, and are often near or at the top of the construction. The figurine is also known as Jack of the Clock or Jack o'Clock. One of the oldest and best-known jacquemarts is found on the south tower of the cathedral Church of Notre Dame of Dijon: it was installed by Philippe II of Burgundy in 1383. Other well-known historic jacquemarts are found on top of the Zytglogge tower in Bern, Switzerland and the Moors on the Torre dell'Orlogio di San Marco in Venice, Italy. The word is originally French but is sometimes used in English as well. The origin of the word is disputed, but one theory relates it to a tool called a 'jacke', used by the craftsmen building church towers, the steeplejacks. Notable jaquemart figures * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Clock, St
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies astronomical object, celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and chronology of the Universe, evolution. Objects of interest include planets, natural satellite, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxy, galaxies, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Babylonian astronomy, Babylonians, Greek astronomy, Greeks, Indian astronomy, Indians, Egyptian astronomy, Egyptians, Chinese astronomy, Chinese, Maya civilization, Maya, and many anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wismar
Wismar (; Low German: ''Wismer''), officially the Hanseatic City of Wismar (''Hansestadt Wismar'') is, with around 43,000 inhabitants, the sixth-largest city of the northeastern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, and the fourth-largest city of Mecklenburg after Rostock, Schwerin and Neubrandenburg. The city was the third-largest port city in former East Germany after Rostock and Stralsund. Wismar is located on the Bay of Wismar of the Baltic Sea, directly opposite the island of Poel, that separates the Bay of Wismar from the larger Bay of Mecklenburg. The city lies in the middle between the two larger port cities of Lübeck in the west, and Rostock in the east, and the state capital of Schwerin is located south of the city on Lake Schwerin. Wismar lies in the northeastern corner of the Hamburg Metropolitan Region, and is the capital of the district of Northwestern Mecklenburg. The city's natural harbour is protected by a promontory. The uninhabited island of Walfisch, ly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stendal
The Hanseatic City of Stendal () is a town in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It is the capital of the Stendal District and the unofficial capital of the Altmark region. Geography Situated west of the Elbe valley, the Stendal town centre is located some west of Berlin, around east of Hanover, and north of the state capital Magdeburg. Stendal is the seat of a University of Applied Sciences (''Fachhochschule'') and preserves a picturesque old town including a historic market and several churches. The nearby village Uchtspringe is home to a psychiatric rehabilitation clinic. Divisions The town Stendal consists of Stendal proper and the following 18 ''Ortschaften'' or municipal divisions:Hauptsatzung der Hansestadt Stendal November 2018. *Bindfelde *Borstel * [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


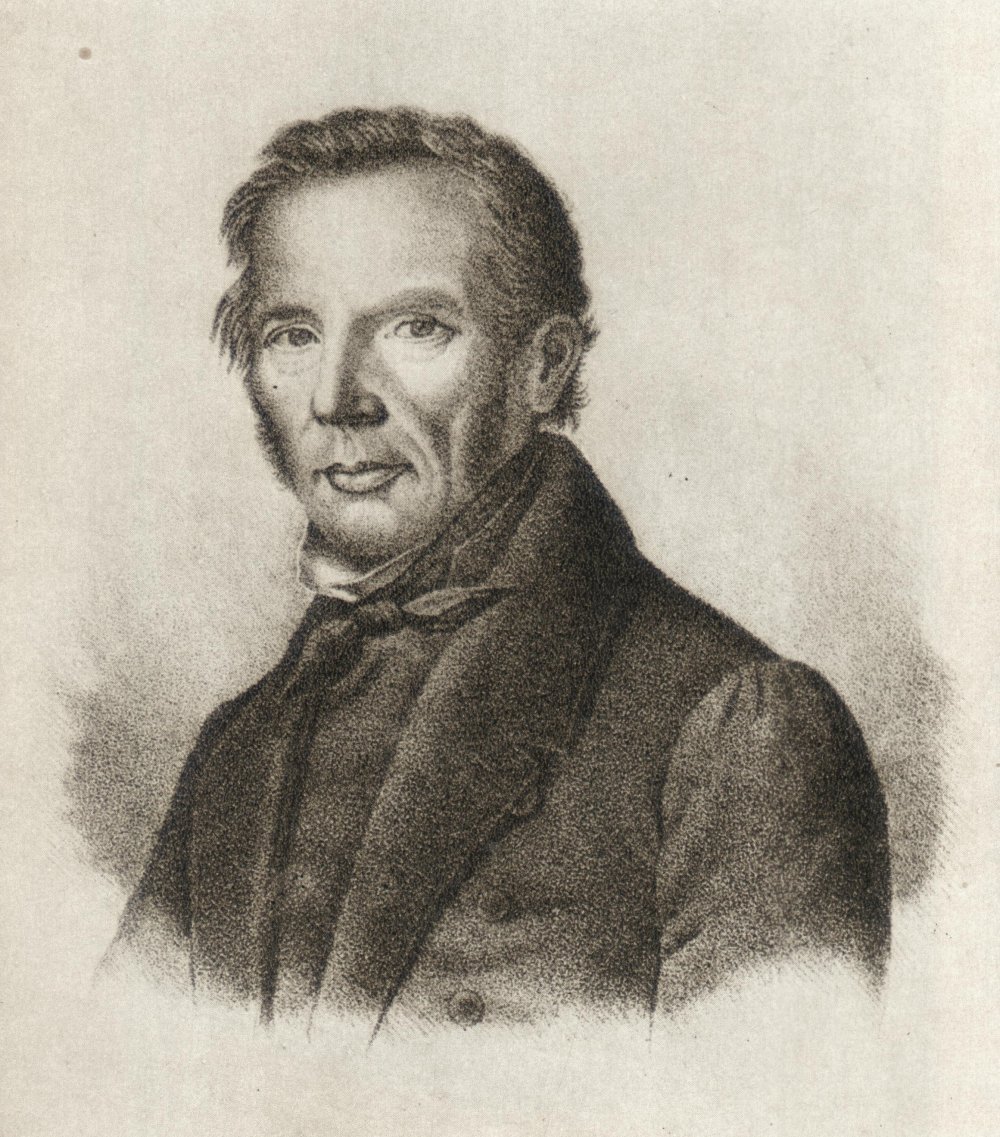




.jpg)
