|
Lp-LpA2
Lipoprotein Associated Phospholipase A2 has been identified and verified in multiple human trials as an enzymatic activity which is an independent predictor of atherosclerotic disease progression and events in humans, including coronary heart disease, because it promotes oxidation of lipoproteins and certain fatty acids. It is available to physicians and patients as a blood test from multiple clinical labs, including LipoScience, and is commonly promoted as the PLAC test. It does not actually measure or reflect the amount of atherosclerotic plaque present, only one factor affecting progression of existing atherosclerotic plaques. As of 2009, there is no treatment for elevated levels of this enzymatic activity, though inhibitors are in development and clinical trial Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a pattern of the disease arteriosclerosis in which the wall of the artery develops abnormalities, called lesions. These lesions may lead to narrowing due to the buildup of atheroma, atheromatous plaque. At onset there are usually no symptoms, but if they develop, symptoms generally begin around middle age. When severe, it can result in coronary artery disease, stroke, peripheral artery disease, or kidney problems, depending on which Artery, arteries are affected. The exact cause is not known and is proposed to be multifactorial. Risk factors include dyslipidemia, abnormal cholesterol levels, elevated levels of inflammatory markers, high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, obesity, family history, genetic, and an unhealthy diet. Atheroma, Plaque is made up of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances found in the blood. The narrowing of Artery, arteries limits the flow of oxygen-rich blood to parts of the body. Diagnosis is based upon a physical exam, ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipoprotein-associated Phospholipase A2
Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) also known as platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase (PAF-AH) is a phospholipase A2 enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PLA2G7'' gene. Lp-PLA2 is a 45-kDa protein of 441 amino acids. It is one of several PAF acetylhydrolases. Function In the blood Lp-PLA2 travels mainly with low-density lipoprotein (LDL). Less than 20% is associated with high-density lipoprotein HDL. Several lines of evidence suggest that HDL-associated Lp-PLA2 may substantially contribute to the HDL antiatherogenic activities. It is an enzyme produced by inflammatory cells and hydrolyzes oxidized phospholipids in LDL. Lp-PLA2 is platelet-activating factor ( PAF) acetylhydrolase (EC 3.1.1.47), a secreted enzyme that catalyzes the degradation of PAF to inactive products by hydrolysis of the acetyl group at the sn-2 position, producing the biologically inactive products LYSO-PAF and acetate. Clinical significance Lp-PLA2 is involved in the developm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme Catalysis
Enzyme catalysis is the increase in the rate of a process by a biological molecule, an "enzyme". Most enzymes are proteins, and most such processes are chemical reactions. Within the enzyme, generally catalysis occurs at a localized site, called the active site. Most enzymes are made predominantly of proteins, either a single protein chain or many such chains in a multi-subunit complex. Enzymes often also incorporate non-protein components, such as metal ions or specialized organic molecules known as cofactor (e.g. adenosine triphosphate). Many cofactors are vitamins, and their role as vitamins is directly linked to their use in the catalysis of biological process within metabolism. Catalysis of biochemical reactions in the cell is vital since many but not all metabolically essential reactions have very low rates when uncatalysed. One driver of protein evolution is the optimization of such catalytic activities, although only the most crucial enzymes operate near catalytic e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
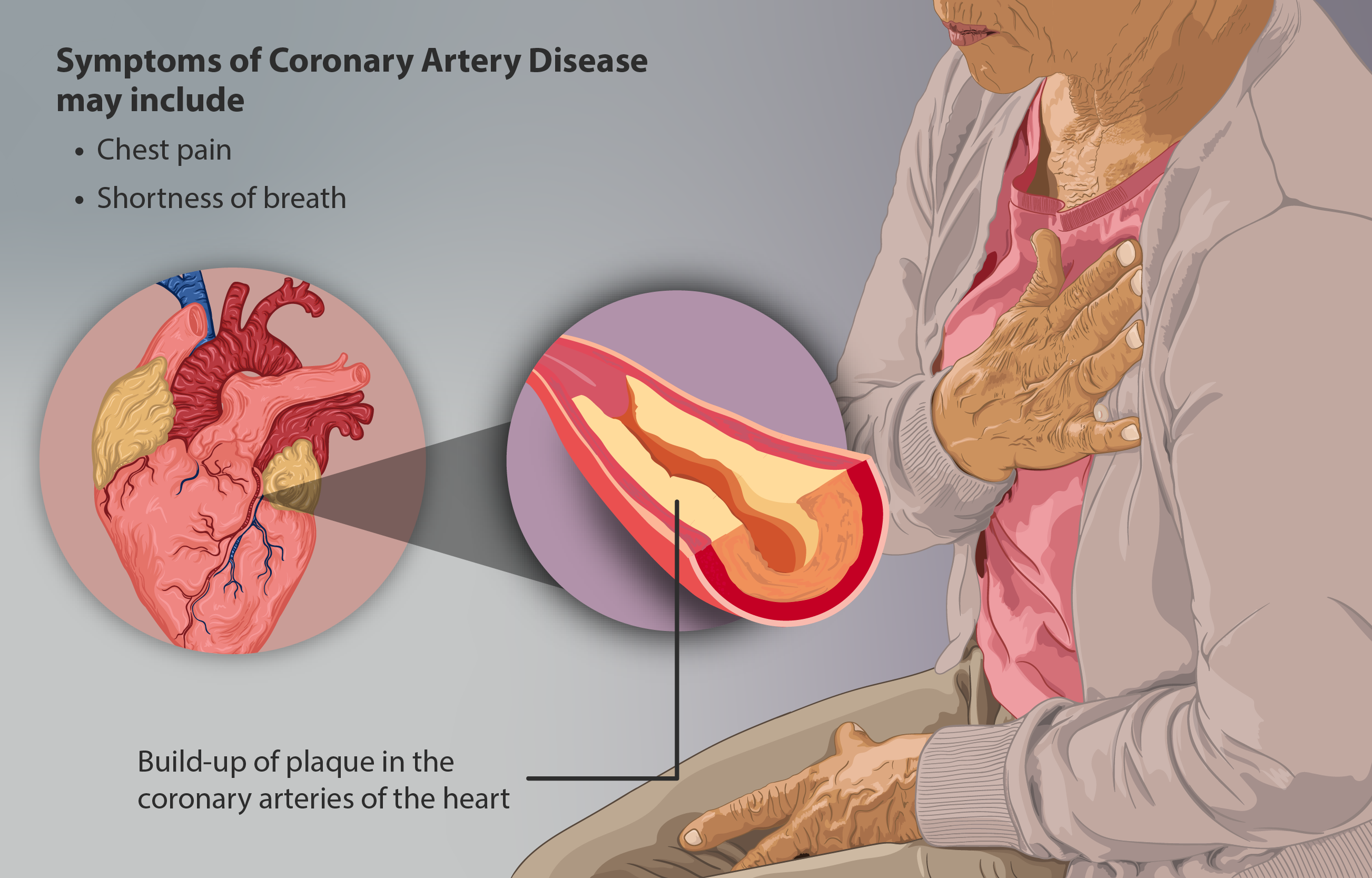
Coronary Heart Disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves the reduction of blood flow to the heart muscle due to build-up of atherosclerotic plaque in the arteries of the heart. It is the most common of the cardiovascular diseases. Types include stable angina, unstable angina, myocardial infarction, and sudden cardiac death. A common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Occasionally it may feel like heartburn. Usually symptoms occur with exercise or emotional stress, last less than a few minutes, and improve with rest. Shortness of breath may also occur and sometimes no symptoms are present. In many cases, the first sign is a heart attack. Other complications include heart failure or an abnormal heartbeat. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipoprotein
A lipoprotein is a biochemical assembly whose primary function is to transport hydrophobic lipid (also known as fat) molecules in water, as in blood plasma or other extracellular fluids. They consist of a triglyceride and cholesterol center, surrounded by a phospholipid outer shell, with the hydrophilic portions oriented outward toward the surrounding water and lipophilic portions oriented inward toward the lipid center. A special kind of protein, called apolipoprotein, is embedded in the outer shell, both stabilising the complex and giving it a functional identity that determines its role. Many enzymes, transporters, structural proteins, antigens, adhesins, and toxins are lipoproteins. Examples include plasma lipoprotein particles ( HDL, LDL, IDL, VLDL and chylomicrons). Subgroups of these plasma particles are primary drivers or modulators of atherosclerosis. Scope Transmembrane lipoproteins Some transmembrane proteolipids, especially those found in bacteria, are referred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatty Acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are a major component of the lipids (up to 70% by weight) in some species such as microalgae but in some other organisms are not found in their standalone form, but instead exist as three main classes of esters: triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesteryl esters. In any of these forms, fatty acids are both important dietary sources of fuel for animals and important structural components for cells. History The concept of fatty acid (''acide gras'') was introduced in 1813 by Michel Eugène Chevreul, though he initially used some variant terms: ''graisse acide'' and ''acide huileux'' ("acid fat" and "oily acid"). Types of fatty acids Fatty acids are classified in many ways: by length, by saturation vs unsaturati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Test
A blood test is a laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a hypodermic needle, or via fingerprick. Multiple tests for specific blood components, such as a glucose test or a cholesterol test, are often grouped together into one test panel called a blood panel or blood work. Blood tests are often used in health care to determine physiological and biochemical states, such as disease, mineral content, pharmaceutical drug effectiveness, and organ function. Typical clinical blood panels include a basic metabolic panel or a complete blood count. Blood tests are also used in drug tests to detect drug abuse. Extraction A venipuncture is useful as it is a minimally invasive way to obtain cells and extracellular fluid ( plasma) from the body for analysis. Blood flows throughout the body, acting as a medium that provides oxygen and nutrients to tissues and carries waste products back to the excretory systems for disposal. Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atheroma
An atheroma, or atheromatous plaque, is an abnormal and reversible accumulation of material in the inner layer of an arterial wall. The material consists of mostly macrophage cells, or debris, containing lipids, calcium and a variable amount of fibrous connective tissue. The accumulated material forms a swelling in the artery wall, which may intrude into the lumen of the artery, narrowing it and restricting blood flow. Atheroma is the pathological basis for the disease entity atherosclerosis, a subtype of arteriosclerosis. Signs and symptoms For most people, the first symptoms result from atheroma progression within the heart arteries, most commonly resulting in a heart attack and ensuing debility. The heart arteries are difficult to track because they are small (from about 5 mm down to microscopic), they are hidden deep within the chest and they never stop moving. Additionally, all mass-applied clinical strategies focus on both minimal cost and the overall safety of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinical Trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, drugs, dietary choices, dietary supplements, and medical devices) and known interventions that warrant further study and comparison. Clinical trials generate data on dosage, safety and efficacy. They are conducted only after they have received health authority/ethics committee approval in the country where approval of the therapy is sought. These authorities are responsible for vetting the risk/benefit ratio of the trial—their approval does not mean the therapy is 'safe' or effective, only that the trial may be conducted. Depending on product type and development stage, investigators initially enroll volunteers or patients into small pilot studies, and subsequently conduct progressively larger scale comparative studies. Clinical trials can vary i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)