|
Low Plasticity Burnishing
Low plasticity burnishing (LPB) is a method of metal improvement that provides deep, stable surface compressive residual stresses with little cold work for improved damage tolerance and metal fatigue life extension. Improved fretting fatigue and stress corrosion performance has been documented, even at elevated temperatures where the compression from other metal improvement processes relax. The resulting deep layer of compressive residual stress has also been shown to improve high cycle fatigue (HCF) and low cycle fatigue (LCF) performance. History Unlike LPB, traditional burnishing tools consist of a hard wheel or fixed lubricated ball pressed into the surface of an asymmetrical work piece with sufficient force to deform the surface layers, usually in a lathe. The process does multiple passes over the work pieces, usually under increasing load, to improve surface finish and deliberately cold work the surface. Roller and ball burnishing have been studied in Russia and Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Residual Stress
In materials science and solid mechanics, residual stresses are stresses that remain in a solid material after the original cause of the stresses has been removed. Residual stress may be desirable or undesirable. For example, laser peening imparts deep beneficial compressive residual stresses into metal components such as turbine engine fan blades, and it is used in toughened glass to allow for large, thin, crack- and scratch-resistant glass displays on smartphones. However, unintended residual stress in a designed structure may cause it to fail prematurely. Residual stresses can result from a variety of mechanisms including inelastic (plastic) deformations, temperature gradients (during thermal cycle) or structural changes ( phase transformation). Heat from welding may cause localized expansion, which is taken up during welding by either the molten metal or the placement of parts being welded. When the finished weldment cools, some areas cool and contract more than others ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
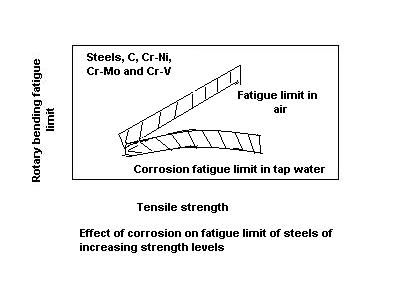
Corrosion Fatigue
Corrosion fatigue is fatigue in a corrosive environment. It is the mechanical degradation of a material under the joint action of corrosion and cyclic loading. Nearly all engineering structures experience some form of alternating stress, and are exposed to harmful environments during their service life. The environment plays a significant role in the fatigue of high-strength structural materials like steel, aluminum alloys and titanium alloys. Materials with high specific strength are being developed to meet the requirements of advancing technology. However, their usefulness depends to a large extent on the degree to which they resist corrosion fatigue. The effects of corrosive environments on the fatigue behavior of metals were studied as early as 1930. The phenomenon should not be confused with stress corrosion cracking, where corrosion (such as pitting) leads to the development of brittle cracks, growth and failure. The only requirement for corrosion fatigue is that the sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrasonic Impact Treatment
Ultrasonic impact treatment (UIT) is a metallurgical processing technique, similar to work hardening, in which ultrasonic energy is applied to a metal object. This technique is part of the High Frequency Mechanical Impact (HFMI) processes. Other acronyms are also equivalent: Ultrasonic Needle Peening (UNP), Ultrasonic Peening (UP). Ultrasonic impact treatment can result in controlled residual compressive stress, grain refinement and grain size reduction. Low and high cycle fatigue are enhanced and have been documented to provide increases up to ten times greater than non-UIT specimens. Theory In UIT, ultrasonic waves are produced by an electro-mechanical ultrasonic transducer, and applied to a workpiece. An acoustically tuned resonator bar is caused to vibrate by energizing it with a magnetostrictive or Piezoelectric ultrasonic transducer. The energy generated from these high frequency impulses is imparted to the treated surface through the contact of specially designed ste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stress Corrosion Cracking
Stress corrosion cracking (SCC) is the growth of crack formation in a corrosive environment. It can lead to unexpected and sudden failure of normally ductile metal alloys subjected to a tensile stress, especially at elevated temperature. SCC is highly chemically specific in that certain alloys are likely to undergo SCC only when exposed to a small number of chemical environments. The chemical environment that causes SCC for a given alloy is often one which is only mildly corrosive to the metal. Hence, metal parts with severe SCC can appear bright and shiny, while being filled with microscopic cracks. This factor makes it common for SCC to go undetected prior to failure. SCC often progresses rapidly, and is more common among alloys than pure metals. The specific environment is of crucial importance, and only very small concentrations of certain highly active chemicals are needed to produce catastrophic cracking, often leading to devastating and unexpected failure.ASM Internatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shot Peening
Shot peening is a cold working process used to produce a compressive residual stress layer and modify the mechanical properties of metals and composites. It entails striking a surface with shot (round metallic, glass, or ceramic particles) with force sufficient to create plastic deformation."Shot Peening," ''Tool and Manufacturing Engineers Handbook'' (TMEH), Volume 3, Society of Manufacturing Engineers, 1985 In machining, shot peening is used to strengthen and relieve stress in components like steel automobile crankshafts and connecting rods. In architecture it provides a muted finish to metal. Shot peening is similar mechanically to sandblasting, though its purpose is not to remove material, but rather it employs the mechanism of plasticity to achieve its goal, with each particle functioning as a ball-peen hammer. Details Peening a surface spreads it plastically, causing changes in the mechanical properties of the surface. Its main application is to avoid the propagation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Residual Stress
In materials science and solid mechanics, residual stresses are stresses that remain in a solid material after the original cause of the stresses has been removed. Residual stress may be desirable or undesirable. For example, laser peening imparts deep beneficial compressive residual stresses into metal components such as turbine engine fan blades, and it is used in toughened glass to allow for large, thin, crack- and scratch-resistant glass displays on smartphones. However, unintended residual stress in a designed structure may cause it to fail prematurely. Residual stresses can result from a variety of mechanisms including inelastic (plastic) deformations, temperature gradients (during thermal cycle) or structural changes ( phase transformation). Heat from welding may cause localized expansion, which is taken up during welding by either the molten metal or the placement of parts being welded. When the finished weldment cools, some areas cool and contract more than others ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peening
In metallurgy, peening is the process of working a metal's surface to improve its material properties, usually by mechanical means, such as hammer blows, by blasting with shot (shot peening), or focusing light ( laser peening). Peening is normally a cold work process, with laser peening being a notable exception. It tends to expand the surface of the cold metal, thereby inducing compressive stresses or relieving tensile stresses already present. Peening can also encourage strain hardening of the surface metal. Residual stress Plastic deformation from peening induces a residual compressive stress in a peened surface, along with tensile stress in the interior. This stress state resembles the one seen in toughened glass, and is useful for similar reasons. Surface compressive stresses confer resistance to metal fatigue and to some forms of corrosion, since cracks will not grow in a compressive environment. The benefit comes at the expense of higher tensile stresses deeper in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal Fatigue
In materials science, fatigue is the initiation and propagation of cracks in a material due to cyclic loading. Once a fatigue crack has initiated, it grows a small amount with each loading cycle, typically producing striations on some parts of the fracture surface. The crack will continue to grow until it reaches a critical size, which occurs when the stress intensity factor of the crack exceeds the fracture toughness of the material, producing rapid propagation and typically complete fracture of the structure. Fatigue has traditionally been associated with the failure of metal components which led to the term metal fatigue. In the nineteenth century, the sudden failing of metal railway axles was thought to be caused by the metal ''crystallising'' because of the brittle appearance of the fracture surface, but this has since been disproved. Most materials, such as composites, plastics and ceramics, seem to experience some sort of fatigue-related failure. To aid in predicting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Peening
Laser peening (LP), or laser shock peening (LSP), is a surface engineering process used to impart beneficial residual stresses in materials. The deep, high-magnitude compressive residual stresses induced by laser peening increase the resistance of materials to surface-related failures, such as fatigue, fretting fatigue and stress corrosion cracking. Laser shock peening can also be used to strengthen thin sections, harden surfaces, shape or straighten parts (known as laser peen forming), break up hard materials, compact powdered metals and for other applications where high pressure, short duration shock waves offer desirable processing results. History Discovery and development (1960s) Initial scientific discoveries towards modern day laser peening began in the early 1960s as pulsed laser technology began to proliferate across the globe. In an early investigation of the laser interaction with materials by Gurgen Askaryan and E.M. Moroz, they documented pressure measurements on a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Frequency Impact Treatment
The high-frequency impact treatment or HiFIT – Method is the treatment of welded steel constructions at the weld transition to increase the fatigue strength. Features The durability and life of dynamically loaded, welded steel structures is determined in many cases by the welds, in particular the weld transitions. Through selective treatment of the transitions (grinding (abrasive cutting), abrasive blasting, hammering, etc.), the durability of many designs increase significantly. Hammering methods have proven to be particularly effective treatment methods and were within the joint project REFRESH extensively studied and developed. The HiFIT (High-Frequency Impact Treatment (also called HFMI (High Frequency Mechanical Impact))) process is such a hammering method that is universally applicable, requires only a low tech equipment and still offers high reproducibility and the possibility for quality control. Operation The HiFIT hammer operates with a hardened pin with a ball ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fretting
Fretting refers to wear and sometimes corrosion damage of loaded surfaces in contact while they encounter small oscillatory movements tangential to the surface. Fretting is caused by adhesion of contact surface asperities, which are subsequently broken again by the small movement. This breaking causes wear debris to be formed. If the debris and/or surface subsequently undergo chemical reaction, i.e., mainly oxidation, the mechanism is termed fretting corrosion. Fretting degrades the surface, leading to increased surface roughness and micropits, which reduces the fatigue strength of the components. The amplitude of the relative sliding motion is often in the order of micrometers to millimeters, but can be as low as 3 nanometers. Typically fretting is encountered in shrink fits, bearing seats, bolted parts, splines, and dovetail connections. Materials Steel Fretting damage in steel can be identified by the presence of a pitted surface and fine 'red' iron oxide dust rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreign Object Damage
In aviation and aerospace, foreign object debris (FOD), is any particle or substance, alien to an aircraft or system, which could potentially cause damage. External FOD hazards include bird strikes, hail, ice, sandstorms, ash-clouds or objects left on the runway. Internal FOD hazards include items left in the cockpit that interfere with flight safety by getting tangled in control cables, jam moving parts or short-out electrical connections. The term FOD is used to describe both the foreign objects themselves, and any damage attributed to them. Jet engine design and FOD Modern jet engines can suffer major damage from even small objects being sucked into the engine. The FAA (Federal Aviation Administration) requires that all engine types pass a test which includes firing a fresh chicken (dead, but not frozen) into a running jet engine from a small cannon. The engine does not have to remain functional after the test, but it must not cause significant damage to the rest of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |