|
Low-dose Naltrexone
Low-dose naltrexone describes the off-label, experimental use of the medication naltrexone at low doses for diseases such as Crohn's disease and multiple sclerosis. Naltrexone is typically prescribed for opioid dependence or alcohol dependence, as it is a strong opioid antagonist. It has been suggested that low-dose naltrexone might operate as an anti-inflammatory agent and therefore could be used to treat some chronic conditions involving immune system dysregulation. Anecdotal reports have suggested that low-dose naltrexone may be effective in treating a wide range of diseases, including cancer, chronic Lyme Disease, chronic fatigue syndrome HIV/AIDS, fibromyalgia patients, arthritis, and immunity for immunosuppressed patients. Its use is increasing due to its anti-inflammatory properties and minimal side effects. LDN's mechanism of action (if any) is still incompletely understood. Mechanism of action Action of naltrexone at normal dose Naltrexone and its active metabolite 6-╬ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Off-label Use
Off-label use is the use of pharmaceutical drugs for an unapproved indication (medicine), indication or in an unapproved age group, dose (biochemistry), dosage, or route of administration. Both prescription drugs and over-the-counter drugs (OTCs) can be used in off-label ways, although most studies of off-label use focus on prescription drugs. Off-label use is very common and generally legal unless it violates ethical guidelines or safety regulations. The ability to prescribe drugs for uses beyond the officially approved indications is commonly used to good effect by healthcare providers. For example, methotrexate is commonly used off-label because its immunomodulatory effects relieve various disorders. However, off-label use can entail health risks and differences in legal liability. Pharmaceutical marketing, Marketing of pharmaceuticals for off-label use is usually prohibited. Indications and labeling laws An ''Indication (medicine), indication'' is when a drug is medically ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
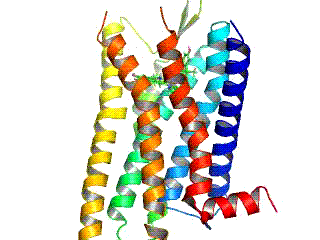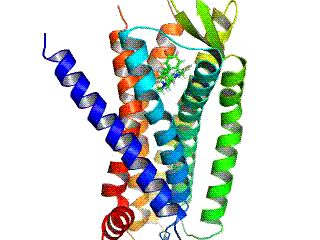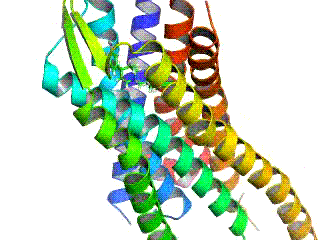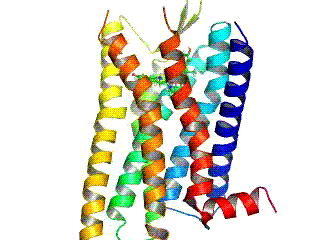
╬╝-opioid Receptor
The ╬╝-opioid receptors (MOR) are a class of opioid receptors with a high affinity for enkephalins and beta-endorphin, but a low affinity for dynorphins. They are also referred to as ╬╝(''mu'')-opioid peptide (MOP) receptors. The prototypical ╬╝-opioid receptor agonist is morphine, the primary psychoactive alkaloid in opium. It is an inhibitory G-protein coupled receptor that activates the Gi alpha subunit, inhibiting adenylate cyclase activity, lowering cAMP levels. Structure The structure of the ╬╝-opioid receptor has been determined with the antagonist ╬▓-FNA, the agonist BU72, and in a complex with DAMGO and Gi protein. Splice variants Three variants of the ╬╝-opioid receptor are well characterized, though RT-PCR has identified up to 10 total splice variants in humans. Location They can exist either presynaptically or postsynaptically depending upon cell types. The ╬╝-opioid receptors exist mostly presynaptically in the periaqueductal gray region, and in the superfi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinical Rheumatology
''Clinical Rheumatology'' is a peer-reviewed medical journal covering rheumatology. It is published by Springer Science+Business Media on behalf of the International League of Associations of Rheumatology. The journal was established in 1945 as the official journal of the Belgian Rheumatology Society and carried different titles before obtaining its current title in 1982. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 2.980. References External links *{{Official website, https://www.springer.com/medicine/rheumatology/journal/10067 Rheumatology journals Springer Science+Business Media academic journals Publications established in 1945 Monthly journals English-language journals Acade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Current Pain And Headache Reports
''Current Pain and Headache Reports'' is a bimonthly peer-reviewed medical journal publishing review articles in the field of anesthesiology. It was established in 1994 as ''Current Review of Pain'', obtaining its current name in 2001. It is published by Springer Science+Business Media and the editors-in-chief are Stephen D. Silberstein, MD (Thomas Jefferson University) and Lawrence C. Newman, MD, (NYU Langone Medical Center). According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2018 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 2.767. References External links *{{Official website, https://www.springer.com/medicine/journal/11916 Anesthesiology and palliative medicine journals Springer Science+Business Media academic journals Review journals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opioid Analgesic
Opioids are substances that act on opioid receptors to produce morphine-like effects. Medically they are primarily used for pain relief, including anesthesia. Other medical uses include suppression of diarrhea, replacement therapy for opioid use disorder, reversing opioid overdose, and suppressing cough. Extremely potent opioids such as carfentanil are approved only for veterinary use. Opioids are also frequently used non-medically for their euphoric effects or to prevent withdrawal. Opioids can cause death and have been used for executions in the United States. Side effects of opioids may include itchiness, sedation, nausea, respiratory depression, constipation, and euphoria. Long-term use can cause tolerance, meaning that increased doses are required to achieve the same effect, and physical dependence, meaning that abruptly discontinuing the drug leads to unpleasant withdrawal symptoms. The euphoria attracts recreational use, and frequent, escalating recreational use of o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microglia
Microglia are a type of neuroglia (glial cell) located throughout the brain and spinal cord. Microglia account for about 7% of cells found within the brain. As the resident macrophage cells, they act as the first and main form of active immune defense in the central nervous system (CNS). Microglia (and other neuroglia including astrocytes) are distributed in large non-overlapping regions throughout the CNS. Microglia are key cells in overall brain maintenanceÔÇöthey are constantly scavenging the CNS for plaques, damaged or unnecessary neurons and synapses, and infectious agents. Since these processes must be efficient to prevent potentially fatal damage, microglia are extremely sensitive to even small pathological changes in the CNS. This sensitivity is achieved in part by the presence of unique potassium channels that respond to even small changes in extracellular potassium. Recent evidence shows that microglia are also key players in the sustainment of normal brain functions und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrophages
Macrophages (abbreviated as M ¤ć, M╬Ž or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''╬╝╬▒╬║¤ü¤î¤é'' (') = large, ''¤ć╬▒╬│╬Áß┐ľ╬Ż'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris, and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that are specific to healthy body cells on their surface. The process is called phagocytosis, which acts to defend the host against infection and injury. These large phagocytes are found in essentially all tissues, where they patrol for potential pathogens by amoeboid movement. They take various forms (with various names) throughout the body (e.g., histiocytes, Kupffer cells, alveolar macrophages, microglia, and others), but all are part of the mononuclear phagocyte system. Besides phagocytosis, they play a critical role in nonspecific defense (innate immunity) and also help initiate specific defense mechanisms (adaptive immunity) by recruiting other immun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
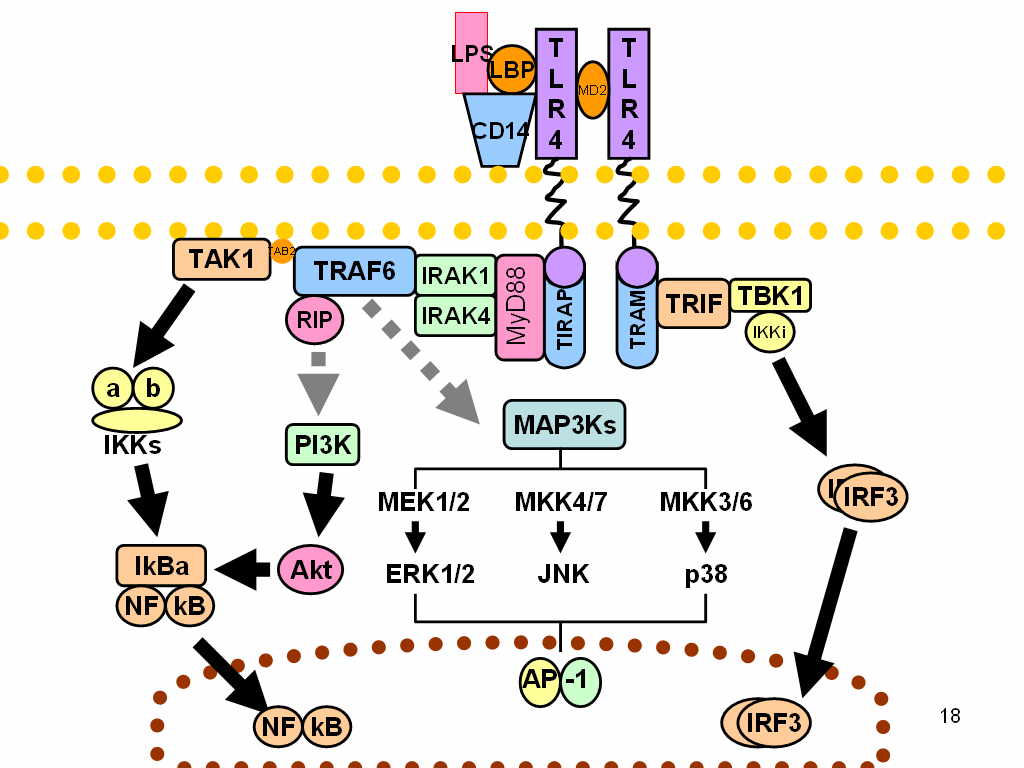
Toll-like Receptor 4
Toll-like receptor 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TLR4'' gene. TLR4 is a transmembrane protein, member of the toll-like receptor family, which belongs to the pattern recognition receptor (PRR) family. Its activation leads to an intracellular signaling pathway NF-╬║B and inflammatory cytokine production which is responsible for activating the innate immune system. TLR4 expressing cells are myeloid (erythrocytes, granulocytes, macrophages) rather than lymphoid (T-cells, B-cells, NK cells). Most myeloid cells also express high levels of CD14, which facilitates activation of TLR4 by LPS. It is most well known for recognizing lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a component present in many Gram-negative bacteria (e.g. ''Neisseria'' spp.) and selected Gram-positive bacteria. Its ligands also include several viral proteins, polysaccharide, and a variety of endogenous proteins such as low-density lipoprotein, beta-defensins, and heat shock protein. Palmitic acid and lauric acid ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endorphins
Endorphins (contracted from endogenous morphine) are chemical signals in the brain that block the perception of pain and increase feelings of wellbeing. They are produced and stored in an area of the brain known as the pituitary gland. History Opioid peptides in the brain were first discovered in 1973 by investigators at the University of Aberdeen, John Hughes and Hans Kosterlitz. They isolated "enkephalins" (from the Greek , ') from pig brain, identified as Met-enkephalin and Leu-enkephalin. This came after the discovery of a receptor that was proposed to produce the pain-relieving analgesic effects of morphine and other opioids, which led Kosterlitz and Hughes to their discovery of the endogenous opioid ligands. Research during this time was focused on the search for a painkiller that did not have the addictive character or overdose risk of morphine. Rabi Simantov and Solomon H. Snyder isolated morphine-like peptides from calf brain. Eric J. Simon, who independently di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opioid Receptors
Opioid receptors are a group of inhibitory G protein-coupled receptors with opioids as ligands. The endogenous opioids are dynorphins, enkephalins, endorphins, endomorphins and nociceptin. The opioid receptors are ~40% identical to somatostatin receptors (SSTRs). Opioid receptors are distributed widely in the brain, in the spinal cord, on peripheral neurons, and digestive tract. Discovery By the mid-1960s, it had become apparent from pharmacologic studies that opiate drugs were likely to exert their actions at specific receptor sites, and that there were likely to be multiple such sites. Early studies had indicated that opiates appeared to accumulate in the brain. The receptors were first identified as specific molecules through the use of binding studies, in which opiates that had been labeled with radioisotopes were found to bind to brain membrane homogenates. The first such study was published in 1971, using 3H-levorphanol. In 1973, Candace Pert and Solomon H. Snyder publis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reward System
The reward system (the mesocorticolimbic circuit) is a group of neural structures responsible for incentive salience (i.e., "wanting"; desire or craving for a reward and motivation), associative learning (primarily positive reinforcement and classical conditioning), and positively-valenced emotions, particularly ones involving pleasure as a core component (e.g., joy, euphoria and ecstasy). Reward is the attractive and motivational property of a stimulus that induces appetitive behavior, also known as approach behavior, and consummatory behavior. A rewarding stimulus has been described as "any stimulus, object, event, activity, or situation that has the potential to make us approach and consume it is by definition a reward". In operant conditioning, rewarding stimuli function as positive reinforcers; however, the converse statement also holds true: positive reinforcers are rewarding. The reward system motivates animals to approach stimuli or engage in behaviour that increases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic compound, organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine constitutes about 80% of the catecholamine content in the brain. It is an amine synthesized by removing a carboxyl group from a molecule of its precursor (chemistry), precursor chemical, L-DOPA, which is biosynthesis, synthesized in the brain and kidneys. Dopamine is also synthesized in plants and most animals. In the brain, dopamine functions as a neurotransmitterÔÇöa chemical released by neurons (nerve cells) to send signals to other nerve cells. Neurotransmitters are synthesized in specific regions of the brain, but affect many regions systemically. The brain includes several distinct dopaminergic pathway, dopamine pathways, one of which plays a major role in the motivational component of reward system, reward-motivated behavior. The anticipa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |