|
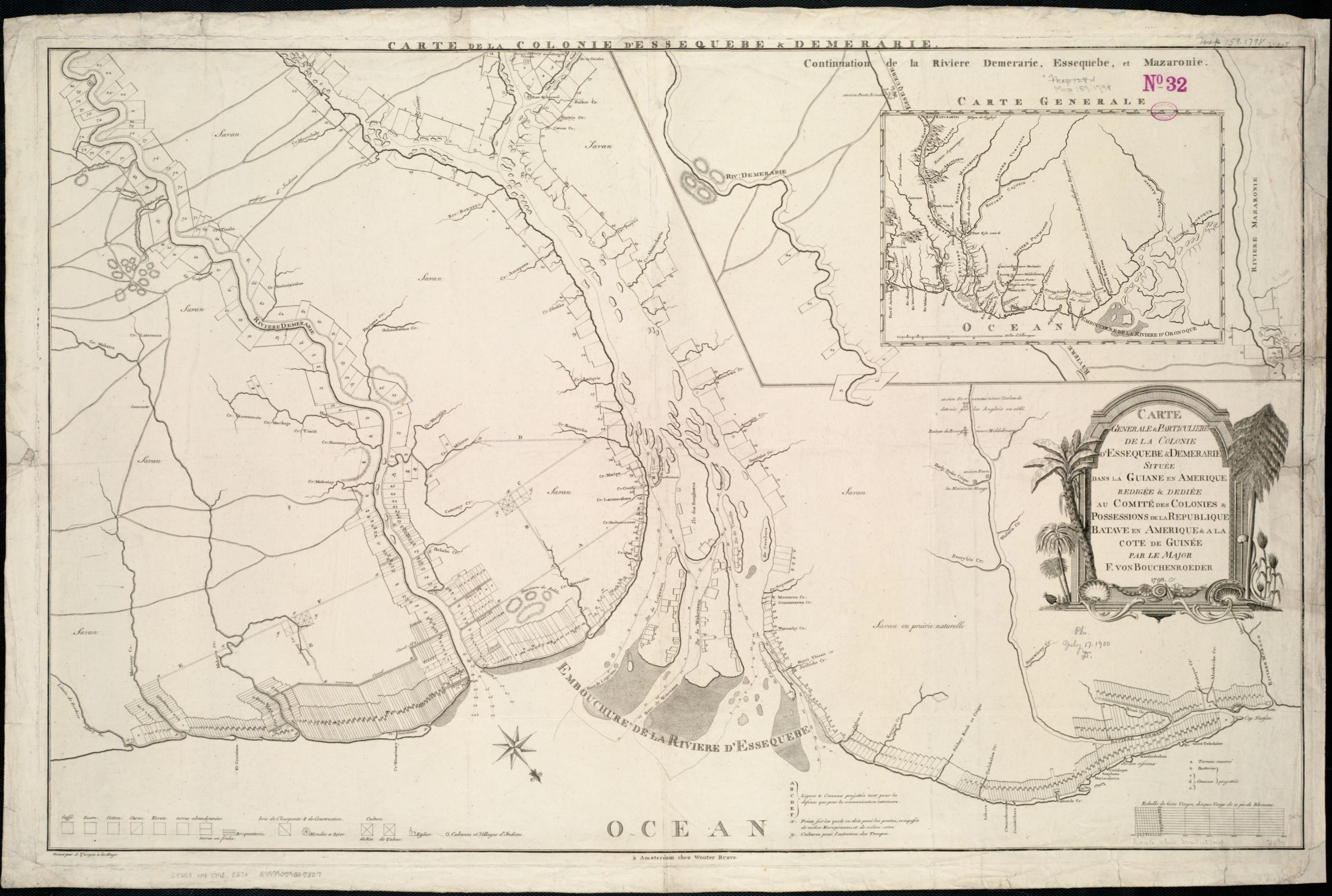
Louis IV Of Legnica
Louis IV of Legnica ( pl, Ludwik; Brzeg, 19 April 1616 – Legnica, 24 November 1663) was a duke of Brzeg from 1633 (together with his brothers until 1654), of Wołów (during 1653–1654 with his brothers) and of Legnica from 1653 (until 1654 with his brothers, after this alone). He was the fifth but second surviving son of John Christian, Duke of Brzeg- Legnica-Wołów-Oława, by his first wife, Dorothea Sibylle, daughter of John George, Elector of Brandenburg. Life After the death of their father in 1639, Louis IV and his younger brother Christian inherited Brzeg and Oława together with their oldest brother George III, who had been appointed administrator of the Duchies by the Emperor six years before. After the death of their uncle George Rudolf in 1653 without issue, the brothers inherited his lands of Legnica and Wołów. In 1654, they decided to a division of their domains: Louis IV obtained Legnica, George III retained Brzeg, and Christian received the small towns o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silesian Piasts
The Silesian Piasts were the elder of four lines of the Polish Piast dynasty beginning with Władysław II the Exile (1105–1159), eldest son of Duke Bolesław III of Poland. By Bolesław's testament, Władysław was granted Silesia as his hereditary province and also the Lesser Polish Seniorate Province at Kraków according to the principle of agnatic seniority. Early history The history of the Silesian Piasts began with the feudal fragmentation of Poland in 1138 following the death of the Polish duke Bolesław III Wrymouth. While the Silesian province and the Kraków seniorate were assigned to Władysław II the Exile, his three younger half–brothers Bolesław IV the Curly, Mieszko III the Old, and Henry of Sandomierz received Masovia, Greater Poland and Sandomierz, respectively, according to the Testament of Boleslaw III. Władysław soon entered into fierce conflicts with his brothers and the Polish nobility. When in 1146 he attempted to take control of the whole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cousin
Most generally, in the lineal kinship system used in the English-speaking world, a cousin is a type of familial relationship in which two relatives are two or more familial generations away from their most recent common ancestor. Commonly, "cousin" refers to a first cousin – a relative of the same generation whose most recent common ancestor with the subject is a grandparent. Degrees and removals are separate measures used to more precisely describe the relationship between cousins. ''Degree'' measures the separation, in generations, from the most recent common ancestor(s) to a parent of one of the cousins (whichever is closest), while ''removal'' measures the difference in generations between the cousins themselves, relative to their most recent common ancestor(s). To illustrate usage, a second cousin is a cousin with a ''degree'' of two; there are three (not two) generations from the common ancestor(s). When the degree is not specified, first cousin is assumed. A cousin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1663 Deaths
Events January–March * January 10 – The Royal African Company is granted a Royal Charter by Charles II of England. * January 23 – The Treaty of Ghilajharighat is signed in India between representatives of the Mughal Empire and the independent Ahom Kingdom (in what is now the Assam state), with the Mughals ending their occupation of the Ahom capital of Garhgaon, in return for payment by Ahom in silver and gold for costs of the occupation, and King Sutamla of Ahom sending one of his daughters to be part of the harem of Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb. * February 5 - A magnitude 7.3 to 7.9 earthquake hits Canada's Quebec Province. * February 8 – English pirates led by Christopher Myngs and Edward Mansvelt carry out the sack of Campeche in Mexico, looting the town during a two week occupation that ends on February 23. * February 10 – The army of the Kingdom of Siam (now Thailand) captures Chiang Mai from the Kingdom of Burma (now Myanmar), using it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1616 Births
Events January–June * January ** Six-year-old António Vieira arrives from Portugal, with his parents, in Bahia (present-day Salvador) in Colonial Brazil, where he will become a diplomat, noted author, leading figure of the Church, and protector of Brazilian indigenous peoples, in an age of intolerance. ** Officials in Württemberg charge astronomer Johannes Kepler with practicing "forbidden arts" (witchcraft). His mother had also been so charged and spent 14 months in prison. * January 1 – King James I of England attends the masque ''The Golden Age Restored'', a satire by Ben Jonson on fallen court favorite the Robert Carr, 1st Earl of Somerset, Earl of Somerset. The king asks for a repeat performance on January 6. * January 3 – In the court of James I of England, the king's favorite George Villiers, 1st Duke of Buckingham, George Villiers becomes Master of the Horse (encouraging development of the thoroughbred horse); on April 24 he receives the Order of the Gart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Rudolf Of Legnica
George Rudolf of Liegnitz (german: Georg Rudolf von Liegnitz; pl, Jerzy Rudolf Legnicki) (22 January 1595 – 14 January 1653) was duke of Liegnitz-Wohlau (present-day Legnica-Wołów) from 1602 to 1653. A humanist, patron of arts, composer and poet, he was also Upper Governor of Silesia during 1621-1628 and from 1641 onwards. Life George Rudolf was born in Ohlau, the third but second surviving son of Joachim Frederick of Brieg, Duke of Liegnitz-Brieg (Legnica-Brzeg) and Anna Maria of Anhalt, daughter of Joachim Ernest, Prince of Anhalt. At the death of their father in 1602, George Rudolf and his older brother John Christian were minors, and their mother, the Dowager Duchess Anna Maria, became regent. After her death in 1605, the regency was taken by the paternal aunt of the young Dukes (the only surviving sibling of the late Joachim Frederick), Elisabeth Magdalena of Brieg and her husband, Karl II of Poděbrady, Duke of Münsterberg-Oels (Ziębice-Oleśnica). In 1609 John C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian, Duke Of Brieg
Christian of Brieg-Legnica (german: Christian von Liegnitz-Brieg, pl, Chrystian Brzeski-Legnicki, cz, Kristián Břežsko-Lehnický; 19 April 1618 in Oława – 28 February 1672 in Oława) was a Duke of Legnica (during 1653–1654 and 1663–1664 with his brothers), Brzeg (during 1639–1654 with his brothers), Wołów (during 1653–1654 with his brothers, then alone) and Oława (during 1639–1654 with his brothers, then alone). Since 1664, he was the sole ruler as Duke of Legnica-Brzeg-Wołów-Oława. He is descended from the Legnica branch of the Silesian Piasts dynasty. He was the seventh but third surviving son of John Christian, Duke of Brzeg-Legnica-Wołów-Oława, by his first wife Dorothea Sybille, daughter of John George, Elector of Brandenburg. Life In his early years, along with his older brothers, Christian made his Grand Tour to Europe, during which he visited the courts of Kings Louis XIII of France and Charles I of England. Upon his return to Silesia, his coun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George III Of Brieg
George III of Brieg ( pl, Jerzy III Brzeski; Brzeg, 4 September 1611 – Brzeg, 4 July 1664), was a Duke of Brzeg since 1633 (as administrator; in 1639 he took formally the title, together with his brothers until 1654) and Legnica-Wołów during 1653-1654 (with his brothers). He was the eldest son of John Christian, Duke of Brzeg-Legnica-Wołów-Oława, by his first wife Dorothea Sybille, daughter of John George, Elector of Brandenburg. Life The invasion of the Imperial troops in Brzeg (1633), forced the escape of John Christian and his morganatic family to Poland. In 1635, Emperor Ferdinand II entrusted George III the administration of Brzeg during the absence of his father, who never returned home. John Christian died in 1639 and George III, together with his two only surviving brothers Louis IV and Christian inherited Brzeg and Oława. After the death of their uncle George Rudolf in 1653, the brothers inherited Legnica and Wołów; however, only one year later (1654), they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Silesia
The Duchy of Silesia ( pl, Księstwo śląskie, german: Herzogtum Schlesien, cs, Slezské knížectví) with its capital at Wrocław was a medieval duchy located in the historic Silesian region of Poland. Soon after it was formed under the Piast dynasty in 1138, it fragmented into various Silesian duchies. In 1327, the remaining Duchy of Wrocław as well as most other duchies ruled by the Silesian Piasts passed to the Kingdom of Bohemia as Duchies of Silesia. The acquisition was completed when King Casimir III the Great of Poland renounced his rights to Silesia in the 1335 Treaty of Trentschin. Geography During the time of its establishment, the Silesian lands covered the basin of the upper and middle Oder river. In the south the Sudetes mountain range up to the Moravian Gate formed the border with the lands of Bohemia - including Kłodzko Land - and Moravia. After a more than century-long struggle, the boundary had just been determined by an 1137 agreement with the Bohemian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Piast
The House of Piast was the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. The first documented Polish monarch was Duke Mieszko I (c. 930–992). The Piasts' royal rule in Poland ended in 1370 with the death of king Casimir III the Great. Branches of the Piast dynasty continued to rule in the Duchy of Masovia and in the Duchies of Silesia until the last male Silesian Piast died in 1675. The Piasts intermarried with several noble lines of Europe, and possessed numerous titles, some within the Holy Roman Empire. The Jagiellonian kings after John I Albert were also descended in the female line from Casimir III's daughter. Origin of the name The early dukes and kings of Poland are said to have regarded themselves as descendants of the semi-legendary Piast the Wheelwright (''Piast Kołodziej''), first mentioned in the '' Cronicae et gesta ducum sive principum Polonorum'' (Chronicles and deeds of the dukes or princes of the Poles), written c. 1113 by Gallus Anonymus. However, the ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
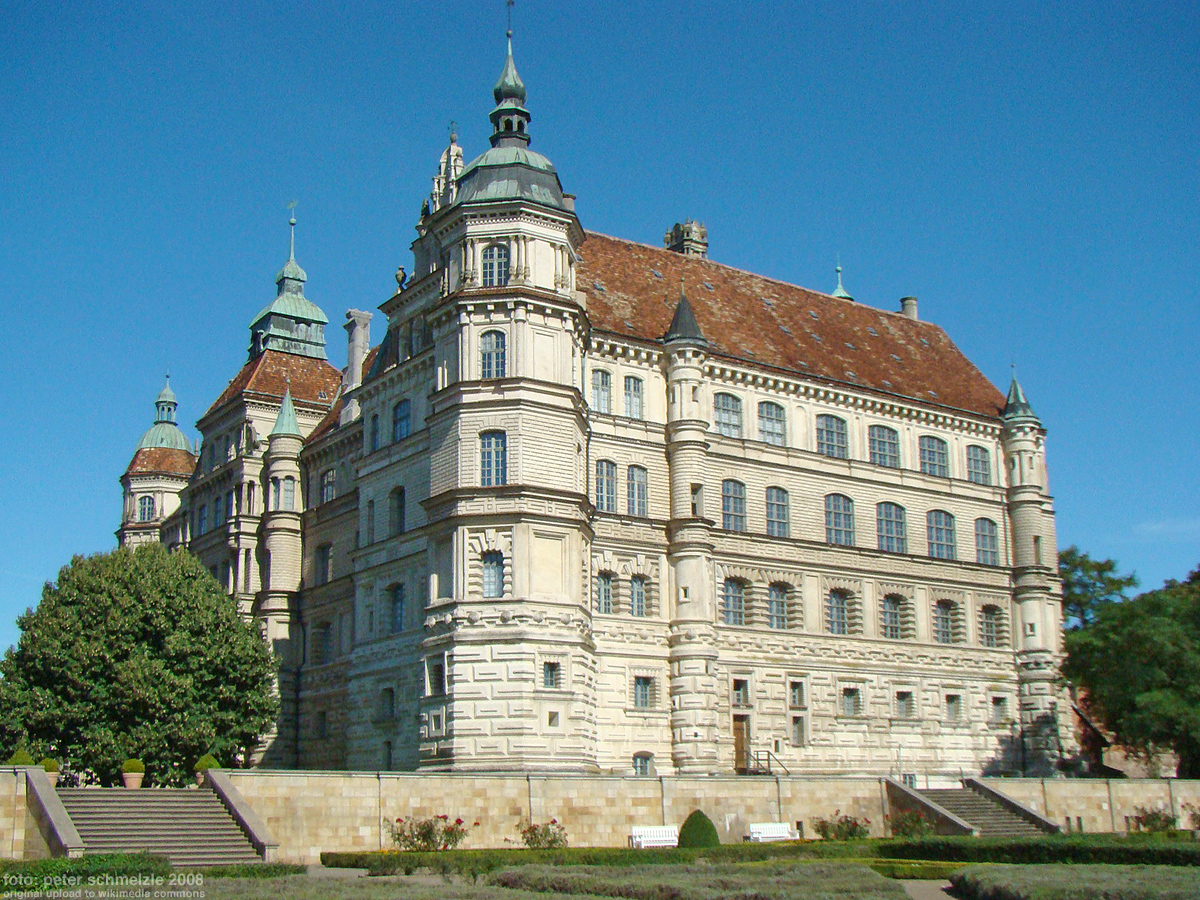
Mecklenburg-Güstrow
Mecklenburg-Güstrow was a state of the Holy Roman Empire in Northern Germany, that existed on three occasions ruled by the House of Mecklenburg at Güstrow. History A first short-lived predecessor existed after the death of Henry IV, Duke of Mecklenburg in 1477 and the subsequent partition of his lands among his sons in 1480. Albert VI received the estates of the former Lordship of Werle around Güstrow. However, Albert died without issue in 1483 and his lands were inherited by his younger brother Magnus II, Duke of Mecklenburg-Schwerin. When Magnus died in 1503, his sons Henry V and Albert VII at first ruled jointly over the entire Mecklenburg duchy until its renewed division by the 1520 Neubrandenburg Treaty. Albert, a fierce opponent of the Protestant Reformation, had insisted on the partition and became duke of Mecklenburg-Güstrow, while his brother Henry retained Mecklenburg-Schwerin. However Mecklenburg ''de jure'' remained undivided; both brothers held the title of Duk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Christian Of Brieg
John Christian of Brieg ( pl, Jan Chrystian; german: Johann Christian; Ohlau, 28 August 1591 – Osterode in Ostpreußen (today Ostróda), 25 December 1639), was a Duke of Brzeg– Legnica–Wołów (since 1602; with his brother as co-ruler in Legnica and Wołów until 1612; in Oława since 1605). He was the second but eldest surviving son of Joachim Frederick, Duke of Brzeg–Oława–Legnica–Wołów, by his wife Anna Maria, daughter of Joachim Ernest, Prince of Anhalt. In his baptism, who was realized two weeks after his birth, on 14 September, he received the names of both uncles: John George of Oława and Christian of Anhalt. Life Youth Joachim Frederick died on 25 March 1602, leaving his two sons as the heirs of his domains. John Christian had eleven-years and his younger brother George Rudolf had only seven, the regency of the Duchies was taken by their mother, the Dowager Duchess Anna Maria (who held Oława as her dower). After Anna Maria's death in 1605, the regen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Albert II, Duke Of Mecklenburg
John Albert II, Duke of MecklenburgGüstrow(5 May 1590 in Waren – 23 April 1636 in Güstrow) was a Duke of Mecklenburg. From 1608 to 1611, he was the nominal ruler of Mecklenburg-Schwerin; the actual ruler being the regent, his great-uncle Charles I. From 1611 to 1621 John Albert and his brother Adolf Frederick I jointly ruled the whole Duchy of Mecklenburg. From 1621, John Albert ruled Mecklenburg-Güstrow alone. Life John Albert was the son of Duke John VII and Sophia of Schleswig-Holstein-Gottorp. He reigned from 16 April 1608, under the regency of his great-uncle Duke Charles I, jointly with his brother Adolf Frederick I in the Mecklenburg-Schwerin part of the country. After Charles's death, the Emperor declared Adolf Frederick an adult and he ruled alone until John Albert came of age and they began to rule jointly. In 1617 he converted to Protestantism. In the division of Mecklenburg of 1621, John Albert received Mecklenburg-Güstrow. In 1623, both brothers joi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |