|
Lotka's Law
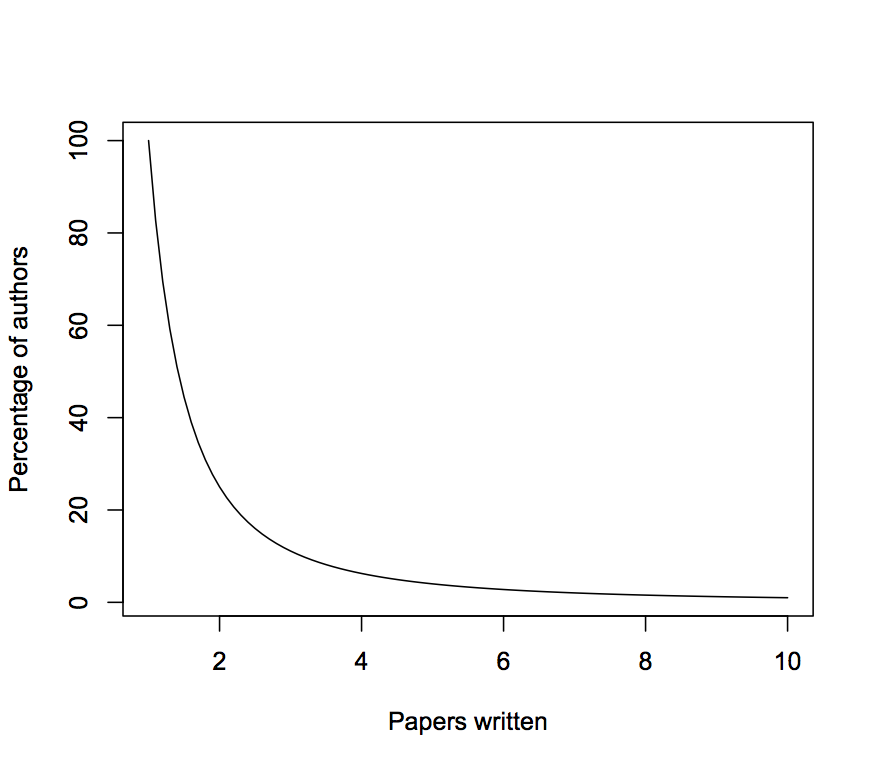
Lotka's law, named after Alfred J. Lotka, is one of a variety of special applications of Zipf's law. It describes the frequency of publication by authors in any given field. It states that the number of authors making x contributions in a given period is a fraction of the number making a single contribution, following the formula 1/x^ where a nearly always equals two, i.e., an approximate inverse-square law, where the number of authors publishing a certain number of articles is a fixed ratio to the number of authors publishing a single article. As the number of articles published increases, authors producing that many publications become less frequent. There are 1/4 as many authors publishing two articles within a specified time period as there are single-publication authors, 1/9 as many publishing three articles, 1/16 as many publishing four articles, etc. Though the law itself covers many disciplines, the actual ratios involved (as a function of 'a') are discipline-spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred J
Alfred may refer to: Arts and entertainment *'' Alfred J. Kwak'', Dutch-German-Japanese anime television series * ''Alfred'' (Arne opera), a 1740 masque by Thomas Arne * ''Alfred'' (Dvořák), an 1870 opera by Antonín Dvořák *"Alfred (Interlude)" and "Alfred (Outro)", songs by Eminem from the 2020 album ''Music to Be Murdered By'' Business and organisations * Alfred, a radio station in Shaftesbury, England *Alfred Music, an American music publisher * Alfred University, New York, U.S. * The Alfred Hospital, a hospital in Melbourne, Australia People * Alfred (name) includes a list of people and fictional characters called Alfred * Alfred the Great (848/49 – 899), or Alfred I, a king of the West Saxons and of the Anglo-Saxons Places Antarctica * Mount Alfred (Antarctica) Australia * Alfredtown, New South Wales * County of Alfred, South Australia Canada * Alfred and Plantagenet, Ontario * Alfred Island, Nunavut * Mount Alfred, British Columbia United States * Alfred, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverse-square Law
In science, an inverse-square law is any scientific law stating that a specified physical quantity is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source of that physical quantity. The fundamental cause for this can be understood as geometric dilution corresponding to point-source radiation into three-dimensional space. Radar energy expands during both the signal transmission and the reflected return, so the inverse square for both paths means that the radar will receive energy according to the inverse fourth power of the range. To prevent dilution of energy while propagating a signal, certain methods can be used such as a waveguide, which acts like a canal does for water, or how a gun barrel restricts hot gas expansion to one dimension in order to prevent loss of energy transfer to a bullet. Formula In mathematical notation the inverse square law can be expressed as an intensity (I) varying as a function of distance (d) from some centre. The intensity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lotka Plot
Alfred James Lotka (March 2, 1880 – December 5, 1949) was a US mathematician, physical chemist, and statistician, famous for his work in population dynamics and energetics. An American biophysicist, Lotka is best known for his proposal of the predator–prey model, developed simultaneously but independently of Vito Volterra. The Lotka–Volterra model is still the basis of many models used in the analysis of population dynamics in ecology. Life Lotka was born in Lwów, Austria-Hungary (now in Ukraine) to Polish-American parents. His parents, Jacques and Marie (Doebely) Lotka, were US nationals. He gained his B.Sc. in 1901 at the University of Birmingham, England, he did graduate work in 1901–02 at Leipzig University, received an M.A. in 1909 at Cornell University and a D. Sc. at Birmingham University in 1912. ;Occupations * Assistant chemist for General Chemical Company (1902–1908, 1914–1919) * Patent examiner for US Patent Office (1909) * Assistant physic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Price's Law
Derek John de Solla Price (22 January 1922 – 3 September 1983) was a British physicist, historian of science, and information scientist. He was known for his investigation of the Antikythera mechanism, an ancient Greek planetary computer, and for quantitative studies on scientific publications, which led to his being described as the "Herald of scientometrics". Biography Price was born in Leyton, England, to Philip Price, a tailor, and Fanny de Solla, a singer. He began work in 1938 as an assistant in a physics laboratory at the South West Essex Technical College, before studying Physics and Mathematics at the University of London, where he received a Bachelor of Science in 1942. He then worked as an assistant to Harry Lowery carrying out research on hot and molten metals, and working towards a London external Ph.D. in experimental physics which he obtained in 1946. This work led to several research papers and to a patent for an emissive-correcting optical pyrometer. He th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Rich Get Richer And The Poor Get Poorer
"The rich get richer and the poor get poorer" is an aphorism due to Percy Bysshe Shelley. In ''A Defence of Poetry'' (1821, not published until 1840) Shelley remarked that the promoters of utility had exemplified the saying, "To him that hath, more shall be given; and from him that hath not, the little that he hath shall be taken away. The rich have become richer, and the poor have become poorer; and the vessel of the State is driven between the Scylla and Charybdis of anarchy and despotism." It describes a Positive feedback loop (a corresponding Negative feedback loop would be e.g. Progressive tax). "To him that hath" etc. is a reference to Matthew 25:29 (the parable of the talents, see also Matthew effect). The aphorism is commonly evoked, with variations in wording, as a synopsis of the effect of free market capitalism producing excessive inequality. Predecessors Andrew Jackson, the seventh President of the U.S. (1829–1837), in his 1832 bank veto, said that "when the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bibliometrics
Bibliometrics is the use of statistical methods to analyse books, articles and other publications, especially in regard with scientific contents. Bibliometric methods are frequently used in the field of library and information science. Bibliometrics is closely associated with scientometrics, that is the analysis of scientific metrics and indicators, to the point that both fields largely overlap. Bibliometrics studies first appeared in the late 19th century. They have known a significative development after the Second World War in a context of "periodical crisis" and new technical opportunities offered by computing tools. In the early 1960s, the Science Citation Index of Eugene Garfield and the citation network analysis of Derek John de Solla Price laid the fundamental basis of a structured research program on bibliometrics. Citation analysis is a commonly used bibliometric method which is based on constructing the citation graph, a network or graph representation of the cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |