|
Loniu Language
Loniu is an Austronesian language spoken along the southern coast of Los Negros Island in the Manus Province, immediately east of Manus Island in Manus Province, Papua New Guinea. Loniu is spoken in the villages of Loniu and Lolak, and there are estimated to be 450–500 native speakers, although some live in other Manus villages or on the mainland of PNG. Loniu generally fits with most of the observations made about Oceanic languages, specifically the Admiralty Islands languages. The six morphosyntactic features of 'Type B' Oceanic Languages (which include the Admiralties languages) as noted by Ross are found in Loniu. The language is essentially SVO and contains prepositions. Phonology Consonant Phonemes Vowel Phonemes References Notes Sources * * External links * Kaipuleohone's Robert Blust collection includes written Writing is a medium of human communication which involves the representation of a language through a system of physically inscribed, mecha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini; ho, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niu Gini), is a country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and its offshore islands in Melanesia (a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean north of Australia). Its capital, located along its southeastern coast, is Port Moresby. The country is the world's third largest island country, with an area of . At the national level, after being ruled by three external powers since 1884, including nearly 60 years of Australian administration starting during World War I, Papua New Guinea established its sovereignty in 1975. It became an independent Commonwealth realm in 1975 with Elizabeth II as its queen. It also became a member of the Commonwealth of Nations in its own right. There are 839 known languages of Papua New Guinea, one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10125/33171
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Blust
Robert A. Blust (; ; May 9, 1940 – January 5, 2022) was an American linguist who worked in several areas, including historical linguistics, lexicography and ethnology. He was Professor of Linguistics at the University of Hawaii at Mānoa. Blust specialized in the Austronesian languages and made major contributions to the field of Austronesian linguistics. Early life and career Blust was born in Cincinnati, Ohio on May 9, 1940, and raised in California. He received both a Bachelor of Arts in anthropology in 1967 and a PhD in linguistics in 1974 from the University of Hawaii at Mānoa. He taught at Leiden University in The Netherlands from 1976 to 1984, after which he returned to the Department of Linguistics at Mānoa for the rest of his career, serving as department chair from 2005 to 2008. He was a Fellow of the Linguistic Society of America. Austronesian languages Until 2018, he served as the review editor for ''Oceanic Linguistics'', an academic journal that covers the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaipuleohone
Kaipuleohone is a digital ethnographic archive that houses audio and visual files, photographs, as well as hundreds of textual material such as notes, dictionaries, and transcriptions relating to small and endangered languages. The archive is stored in the ScholarSpace repository of the University of Hawai‘i at Mānoa and maintained by the Department of Linguistics of the University's College of Languages, Linguistics and Literature. Kaipuleohone was established by Nick Thieberger in 2008. It is a member of thDigital Endangered Languages and Musics Archiving Network(DELAMAN). The term ''kaipuleohone'' means 'gourd of sweet words' and symbolizes the impression of an accumulation of language material. Kaipuleohone comprises several collections including Kaipuleohone Audio Files, the Bickerton Collection, the Blust Collection, the Bradshaw Collection, and the Sato Collection. The archive director is Andrea L. Berez-Kroeker. See also *Language Documentation & Conservation *ScholarSpa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Admiralty Islands
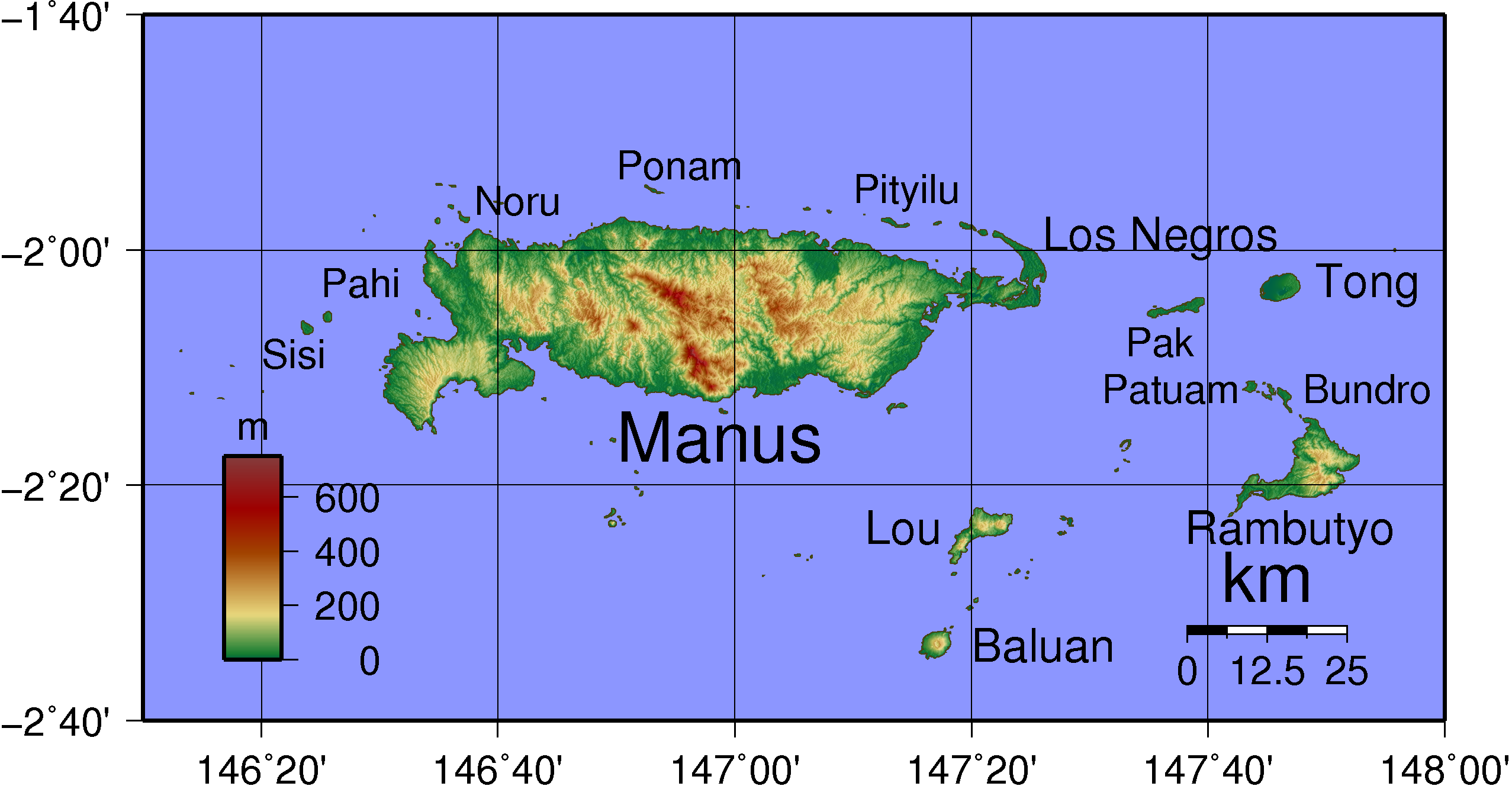
The Admiralty Islands are an archipelago group of 18 islands in the Bismarck Archipelago, to the north of New Guinea in the South Pacific Ocean. These are also sometimes called the Manus Islands, after the largest island. These rainforest-covered islands form part of Manus Province, the smallest and least-populous province of Papua New Guinea, in its Islands Region. The total area is . Many of the Admiralty Islands are atolls and uninhabited. Islands The larger islands in the center of the group are Manus Island and Los Negros Island. The other larger islands are Tong Island, Pak Island, Rambutyo Island, Lou Island, and Baluan Island to the east, Mbuke Island to the south and Bipi Island to the west of Manus Island. Other islands that have been noted as significant places in the history of Manus include Ndrova Island, Pitylu Island and Ponam Island. Geography The temperature of the Admiralty Islands varies little throughout the year, reaching daily highs of and at night. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loniu
Loniu is an Austronesian language spoken along the southern coast of Los Negros Island in the Manus Province, immediately east of Manus Island in Manus Province, Papua New Guinea. Loniu is spoken in the villages of Loniu and Lolak, and there are estimated to be 450–500 native speakers, although some live in other Manus villages or on the mainland of PNG. Loniu generally fits with most of the observations made about Oceanic languages, specifically the Admiralty Islands languages. The six morphosyntactic features of 'Type B' Oceanic Languages (which include the Admiralties languages) as noted by Ross are found in Loniu. The language is essentially SVO and contains prepositions. Phonology Consonant Phonemes Vowel Phonemes References Notes Sources * * External links * Kaipuleohone's Robert Blust collection includes written Writing is a medium of human communication which involves the representation of a language through a system of physically inscribed, mec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manus Island
Manus Island is part of Manus Province in northern Papua New Guinea and is the largest of the Admiralty Islands. It is the fifth-largest island in Papua New Guinea, with an area of , measuring around . Manus Island is covered in rugged jungles which can be broadly described as lowland tropical rain forest. The highest point on Manus Island is Mt. Dremsel, above sea level at the centre of the south coast. Manus Island is volcanic in origin and probably broke through the ocean's surface in the late Miocene, 8 to 10 million years ago. The substrate of the island is either directly volcanic or from uplifted coral limestone. Lorengau, the capital of Manus Province, is located on the island. Momote Airport, the terminal for Manus Province, is located on nearby Los Negros Island. A bridge connects Los Negros Island to Manus Island and the provincial capital of Lorengau. In the 2000 census, the whole Manus Province had a population of 50,321. The Austronesian Manus languages are sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Manus Languages
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth. Etymology The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some Romance languages (''ouest'' in French, ''oest'' in Catalan, ''ovest'' in Italian, ''oeste'' in Spanish and Portuguese). As in other languages, the word formation stems from the fact that west is the direction of the setting sun in the evening: 'west' derives from the Indo-European root ''*wes'' reduced from ''*wes-pero'' 'evening, night', cognate with Ancient Greek ἕσπερος hesperos 'evening; evening star; western' and Latin vesper 'evening; west'. Examples of the same formation in other languages include Latin occidens 'west' from occidō 'to go down, to set' and Hebrew מַעֲרָב maarav 'west' from עֶרֶב erev 'evening'. Navigation To go west using a compass for navigation (in a place where magnetic north is the same dire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Los Negros Island
Los Negros Island is the third largest of the Admiralty Islands. It is significant because it contains the main airport of Manus Province on its eastern coastline, at Momote. It is connected to Lorengau, the capital of the province, on Manus Island via a highway and bridge across the Lonui Passage, which separates Los Negros from the larger Manus Island. One of Australia's regional centres for asylum seekers caught in Australian waters, the Manus Island Regional Processing Centre, was situated on the island until it closed in November 2017. Remaining asylum seekers were housed in accommodation in Lorengau. History Los Negros was formerly a Japanese base during World War II, and was heavily assaulted on February 29, 1944 by Allied forces, during the Battle of Los Negros which was the spearhead for the Admiralty Islands campaign. After its capture by allied forces, Los Negros was developed over the spring and summer of 1944 into an important air and sea base that was used by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manus Languages
The Manus languages are a subgroup of about two dozen Oceanic languages located on Manus Island and nearby offshore islands in Manus Province of Papua New Guinea. The exact number of languages is difficult to determine because they form a dialect continuum (Blust 2007:302). The name 'Manus' (or 'Moanus') originally designated an ethnic group whose members spoke closely related languages and whose coastal dwellers tended to build their houses on stilts out over the sea (Bowern 2011:6). Nowadays the whole population of Manus Province may call themselves 'Manus' people, so the original Manus are distinguished as ''Manus tru'' 'real Manus' (or 'Manus sensu stricto'). The language of the Manus people most intensively studied by anthropologists, from Georg Thilenius in the early 1900s through Margaret Mead in the mid-1900s, is now called Titan (Bowern 2011). Languages According to Lynch, Ross, & Crowley (2002), the structure of the family is: *Manus **West Manus: Nyindrou, Sori-Har ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Admiralty Islands Languages
The Admiralty Islands languages are a group of some thirty Oceanic languages spoken on the Admiralty Islands The Admiralty Islands are an archipelago group of 18 islands in the Bismarck Archipelago, to the north of New Guinea in the South Pacific Ocean. These are also sometimes called the Manus Islands, after the largest island. These rainforest-co .... They may include Yapese, which has proven difficult to classify. Languages According to Lynch, Ross, & Crowley (2002), the structure of the family is: *Eastern ** Manus **Southeast: Baluan-Pam, Lenkau, Lou, Nauna, Penchal *Western ** Northern Kaniet and Southern Kaniet (†) ** Seimat ** Wuvulu-Aua (as two languages) As noted, Yapese and Nguluwan may be part of the Admiralty Islands languages as well. References * Blust, Robert (2007). The prenasalised trills of Manus. In ''Language description, history, and development: Linguistic indulgence in memory of Terry Crowley,'' ed. by Jeff Siegel, John Lynch, and Dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |