|
Litten's Sign
Litten's sign is a clinical sign in which cotton wool spots are seen on fundoscopic examination of the retina in patients with infective endocarditis. The sign is named after Moritz Litten. See also * Roth's spot Roth's spots, also known as Litten spots or the Litten sign, are non-specific red spots with white or pale centres, seen on the retina and although traditionally associated with infective endocarditis, can occur in a number of other conditions incl ... References Medical signs Cardiology {{med-sign-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Sign
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showing on a medical scan. A symptom is something out of the ordinary that is experienced by an individual such as feeling feverish, a headache or other pain or pains in the body. Signs and symptoms Signs A medical sign is an objective observable indication of a disease, injury, or abnormal physiological state that may be detected during a physical examination, examining the patient history, or diagnostic procedure. These signs are visible or otherwise detectable such as a rash or bruise. Medical signs, along with symptoms, assist in formulating diagnostic hypothesis. Examples of signs include elevated blood pressure, nail clubbing of the fingernails or toenails, staggering gait, and arcus senilis and arcus juvenilis of the eyes. Indicati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cotton Wool Spots
Cotton wool spots are opaque fluffy white patches on the retina of the eye that are considered an abnormal finding during a funduscopic exam (also called an ophthalmoscopic exam). Cotton wool spots are typically a sign of another disease state, most common of which is diabetic retinopathy. The irregularly shaped white patches are a result of ischemia, or reduced blood flow and oxygen, in the retinal nerve fiber layer, which is located in the distribution of the capillaries of the superficial layer of the retina. These areas with reduced blood flow reflect the obstruction of axoplasmic flow due to mechanical or vascular causes and the consequential accumulation as a result of decreased axonal transport. This reduced axonal transport can then cause swelling or bulging on the surface layer of the retina, increasing the potential for nerve fiber damage. The presence of cotton wool spots may resolve independently over time, typically in 4-12 weeks, or may depend on the underlying disea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fundoscope
Ophthalmoscopy, also called funduscopy, is a test that allows a health professional to see inside the fundus of the eye and other structures using an ophthalmoscope (or funduscope). It is done as part of an eye examination and may be done as part of a routine physical examination. It is crucial in determining the health of the retina, optic disc, and vitreous humor. The pupil is a hole through which the eye's interior will be viewed. Opening the pupil wider (dilating it) is a simple and effective way to better see the structures behind it. Therefore, dilation of the pupil ( mydriasis) is often accomplished with medicated eye drops before funduscopy. However, although dilated fundus examination is ideal, undilated examination is more convenient and is also helpful (albeit not as comprehensive), and it is the most common type in primary care. An alternative or complement to ophthalmoscopy is to perform a fundus photography, where the image can be analysed later by a professional. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retina
The retina (from la, rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then processes that image within the retina and sends nerve impulses along the optic nerve to the visual cortex to create visual perception. The retina serves a function which is in many ways analogous to that of the film or image sensor in a camera. The neural retina consists of several layers of neurons interconnected by synapses and is supported by an outer layer of pigmented epithelial cells. The primary light-sensing cells in the retina are the photoreceptor cells, which are of two types: rods and cones. Rods function mainly in dim light and provide monochromatic vision. Cones function in well-lit conditions and are responsible for the perception of colour through the use of a range of opsins, as well as high-acuity vision used for task ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
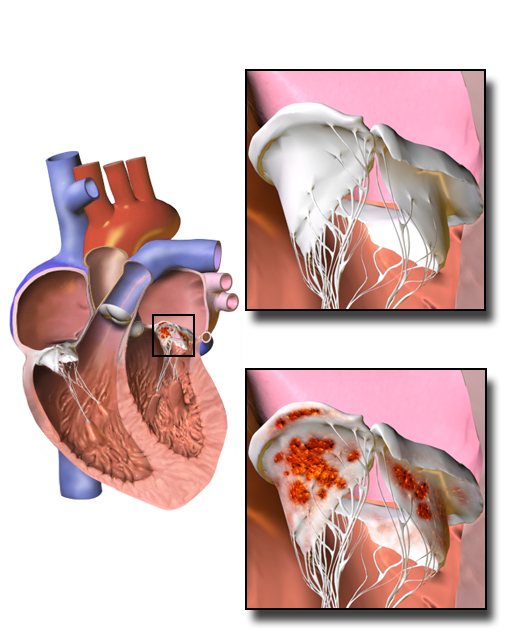
Infective Endocarditis
Infective endocarditis is an infection of the inner surface of the heart, usually the valves. Signs and symptoms may include fever, small areas of bleeding into the skin, heart murmur, feeling tired, and low red blood cell count. Complications may include backward blood flow in the heart, heart failure – the heart struggling to pump a sufficient amount of blood to meet the body's needs, abnormal electrical conduction in the heart, stroke, and kidney failure. The cause is typically a bacterial infection and less commonly a fungal infection. Risk factors include valvular heart disease, including rheumatic disease, congenital heart disease, artificial valves, hemodialysis, intravenous drug use, and electronic pacemakers. The bacteria most commonly involved are streptococci or staphylococci. Diagnosis is suspected based on symptoms and supported by blood cultures or ultrasound of the heart. There is also a noninfective form of endocarditis. The usefulness of antibiotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moritz Litten
Moritz Litten (August 10, 1845 – May 31, 1907) was a German physician who was a native of Berlin. He was a son-in-law to pathologist Ludwig Traube (1818–1876). Biography He studied medicine at the Universities of Heidelberg, Marburg and Berlin, earning his medical doctorate in 1868. From 1872 to 1876 he worked at the Allerheiligen Hospital in Breslau, and in the meantime, served as an assistant to Julius Friedrich Cohnheim (1839–1884). From 1876 to 1882 he worked in the clinic of Friedrich Theodor von Frerichs at Berlin- Charité. In 1884 he obtained the title of professor. Litten is remembered for being the first physician to describe vitreous bleeding in correlation with subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH). In 1881 he published his findings in ''Ueber einige vom allgemein-klinischen Standpunkt aus interessante Augenveränderungen'' (Berl Klin Wochenschr 18: 23– 27). Several years later, French ophthalmologist Albert Terson noticed these symptoms in a patient, and the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roth's Spot
Roth's spots, also known as Litten spots or the Litten sign, are non-specific red spots with white or pale centres, seen on the retina and although traditionally associated with infective endocarditis, can occur in a number of other conditions including hypertension, diabetes, collagen vascular disease, extreme hypoxia, leukemia and HIV. Red and white retinal spots were first observed in 1872 by Swiss physician Moritz Roth, and named "Roth spots" six years later by Moritz Litten. They are typically observed via fundoscopy (using an ophthalmoscope to view inside the eye) or slit lamp exam. The original retinal spots identified in 1872 were attributed to nerve-fibres that had burst. Present-day analysis shows that they can be composed of coagulated fibrin including platelets, focal ischaemia, inflammatory infiltrate, infectious organisms, or neoplastic cells. Cause Roth's spots occur in conditions that predispose to endothelial damage of retinal capillaries, that is when there is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Signs
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showing on a medical scan. A symptom is something out of the ordinary that is experienced by an individual such as feeling feverish, a headache or other pain or pains in the body. Signs and symptoms Signs A medical sign is an objective observable indication of a disease, injury, or abnormal physiological state that may be detected during a physical examination, examining the patient history, or diagnostic procedure. These signs are visible or otherwise detectable such as a rash or bruise. Medical signs, along with symptoms, assist in formulating diagnostic hypothesis. Examples of signs include elevated blood pressure, nail clubbing of the fingernails or toenails, staggering gait, and arcus senilis and arcus juvenilis of the eyes. Indicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |