|
List Of Works By George Webster
George Webster (1797–1864) was an English architect who practised in Kendal, Westmorland. He worked mainly in domestic architecture, designing new houses, and remodelling older houses. His early designs were mainly in Neoclassical (Greek Revival) style. He later pioneered the use of the Tudor Revival style, and in some of his latest designs he incorporated Italianate The Italianate style was a distinct 19th-century phase in the history of Classical architecture. Like Palladianism and Neoclassicism, the Italianate style drew its inspiration from the models and architectural vocabulary of 16th-century Italian ... features. He also designed some churches, all in Gothic Revival style, plus some public and commercial buildings. () Key Buildings References Citations Sources * * * {{refend Webster, George ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Webster (architect)
George Webster (3 May 1797 – 16 April 1864) was an English architect who practised in Kendal, which was at the time in Westmorland, and later in Cumbria. All of his works were executed near his practice, and were located in Cumbria, in north Lancashire, and in the adjacent parts of Yorkshire. Most of his work was carried out on domestic buildings, but he also designed churches, and public and commercial buildings. Early life George Webster came from a family of builders who later became architects, his father Francis (1767–1827) being described as a " mason, builder, and architect" whose speciality was the production of marble chimney-pieces and funerary monuments. It is not known how George received his architectural training, but he joined his father's business as a partner, and in 1818, he designed for the country house of Read Hall in Lancashire. Works Webster's works were geographically confined to the area around his office in Kendal, in what is now Cumbria, the nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lancashire
Lancashire ( , ; abbreviated Lancs) is the name of a historic county, ceremonial county, and non-metropolitan county in North West England. The boundaries of these three areas differ significantly. The non-metropolitan county of Lancashire was created by the Local Government Act 1972. It is administered by Lancashire County Council, based in Preston, and twelve district councils. Although Lancaster is still considered the county town, Preston is the administrative centre of the non-metropolitan county. The ceremonial county has the same boundaries except that it also includes Blackpool and Blackburn with Darwen, which are unitary authorities. The historic county of Lancashire is larger and includes the cities of Manchester and Liverpool as well as the Furness and Cartmel peninsulas, but excludes Bowland area of the West Riding of Yorkshire transferred to the non-metropolitan county in 1974 History Before the county During Roman times the area was part of the Bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rydal, Cumbria
Rydal is a village in Cumbria, England. It is a small cluster of houses, a hotel, and St Mary's Church, on the A591 road midway between Ambleside and Grasmere. Historically part of Westmorland, Rydal is significant in the history of English Romantic literature. William Wordsworth lived at Rydal Mount from 1813 to 1850. Dr Thomas Arnold, notable headmaster of Rugby School, had a summer home at Fox How in nearby Under Loughrigg. Arnold's son, the poet Matthew Arnold, was a frequent visitor and a close friend of Wordsworth. At the northern end of Rydal Water is White Moss House, believed to be the only house owned by Wordsworth, which he bought for his son, Willie and which remained in the Wordsworth family until the 1930s. Rydal is often a starting point for the Fairfield horseshoe, a hillwalking ridge hike. See also *Rydal Mount *Rydal Water Rydal Water is a small body of water in the central part of the English Lake District, in the county of Cumbria. It is located ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Mary's Church, Rydal
St Mary's Church is in the village of Rydal in the Lake District, Cumbria, England. It is an active Anglican parish church in the deanery of Windermere, the archdeaconry of Westmorland and Furness, and the diocese of Carlisle. The church, built in the Gothic revival style, is situated off the A591 road between Ambleside and Grasmere and is recorded in the National Heritage List for England as a designated Grade II* listed building. History The church was built by Lady le Fleming of Rydal Hall, at a cost of £1,500. The foundation stone was laid in 1823 with the chapel opened in 1824, and consecrated in 1825. The architect was George Webster. Poet William Wordsworth helped to choose the site, which was originally an orchard. See also *Rydal, Cumbria *Listed buildings in Lakes, Cumbria References {{Reflist Diocese of Carlisle Windermere Windermere Windermere (sometimes tautology (language), tautologically called Windermere Lake to distinguish it from the nearby town o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgian Houses, Thorney Hill, Kendal - Geograph
Georgian may refer to: Common meanings * Anything related to, or originating from Georgia (country) **Georgians, an indigenous Caucasian ethnic group **Georgian language, a Kartvelian language spoken by Georgians **Georgian scripts, three scripts used to write the language **Georgian (Unicode block), a Unicode block containing the Mkhedruli and Asomtavruli scripts **Georgian cuisine, cooking styles and dishes with origins in the nation of Georgia and prepared by Georgian people around the world * Someone from Georgia (U.S. state) * Georgian era, a period of British history (1714–1837) **Georgian architecture, the set of architectural styles current between 1714 and 1837 Places *Georgian Bay, a bay of Lake Huron *Georgian Cliff, a cliff on Alexander Island, Antarctica Airlines *Georgian Airways, an airline based in Tbilisi, Georgia *Georgian International Airlines, an airline based in Tbilisi, Georgia *Air Georgian, an airline based in Ontario, Canada *Sky Georgia, an airlin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Alcock Beck
Thomas Alcock Beck (1795–1846) was an English author known for writing ''Annales Furnesienses'' (1844), a history of Furness Abbey, which was dedicated by permission to Her Majesty Queen Victoria, and which contained twenty-six steel engravings and several woodcuts. Beck was a long-term resident of Hawkshead in Lancashire, where his parents had lived at The Grove. He used a wheelchair for much of his life, being unable to walk due to a spinal complaint. At one time he had attended Hawkshead Grammar School and he matriculated at Trinity College, Cambridge in 1814, but left without taking a degree. Around 1819, he commenced the building of his regency mansion Esthwaite Lodge (subsequently a youth hostel), to the design of George Webster. The grounds were specially laid out with easy gradients for his wheelchair. Besides other antiquarian interests, he also edited Dr. William Close's unfinished work ''An Itinerary of Furness''. Marriage On 25 April 1838 he married Elizabeth Fell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doric Order
The Doric order was one of the three orders of ancient Greek and later Roman architecture; the other two canonical orders were the Ionic and the Corinthian. The Doric is most easily recognized by the simple circular capitals at the top of columns. Originating in the western Doric region of Greece, it is the earliest and, in its essence, the simplest of the orders, though still with complex details in the entablature above. The Greek Doric column was fluted or smooth-surfaced, and had no base, dropping straight into the stylobate or platform on which the temple or other building stood. The capital was a simple circular form, with some mouldings, under a square cushion that is very wide in early versions, but later more restrained. Above a plain architrave, the complexity comes in the frieze, where the two features originally unique to the Doric, the triglyph and gutta, are skeuomorphic memories of the beams and retaining pegs of the wooden constructions that preceded stone Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawkshead Youth Hostel - Geograph
Hawkshead is a village and civil parish in Cumbria, England, which attracts tourists to the South Lakeland area. The parish includes the hamlets of Hawkshead Hill, to the north west, and Outgate, a similar distance north. Hawkshead contains one primary school but no secondary school and four public houses. Geography Hawkshead is just north of Esthwaite Water, in a valley to the west of Windermere and east of Coniston Water. It is part of Furness, making it a part of the ancient county of Lancashire. History The township of Hawkshead was originally owned by the monks of Furness Abbey; nearby Colthouse derives its name from the stables owned by the Abbey. Hawkshead grew to be an important wool market in medieval times and later as a market town after the Dissolution of the Monasteries in 1532. It was granted its first market charter by King James I in 1608. In 1585, Hawkshead Grammar School was established by Archbishop Edwin Sandys of York after he successfully petitioned Qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawkshead
Hawkshead is a village and civil parish in Cumbria, England, which attracts tourists to the South Lakeland area. The parish includes the hamlets of Hawkshead Hill, to the north west, and Outgate, a similar distance north. Hawkshead contains one primary school but no secondary school and four public houses. Geography Hawkshead is just north of Esthwaite Water, in a valley to the west of Windermere and east of Coniston Water. It is part of Furness, making it a part of the ancient county of Lancashire. History The township of Hawkshead was originally owned by the monks of Furness Abbey; nearby Colthouse derives its name from the stables owned by the Abbey. Hawkshead grew to be an important wool market in medieval times and later as a market town after the Dissolution of the Monasteries in 1532. It was granted its first market charter by King James I in 1608. In 1585, Hawkshead Grammar School was established by Archbishop Edwin Sandys of York after he successfully petitioned Qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esthwaite Lodge
Esthwaite Lodge is a 19th-century house in Hawkshead, Cumbria, England; it is a Grade II listed building. The house was commissioned by Thomas Alcock Beck, a local resident and antiquarian. He employed Kendal-based architect George Webster to design a property for him. Webster's design was a stuccoed villa of two storeys and three bays with a slate hipped roof. Completed in 1821 the house is in the Neoclassical Greek Revival style a Doric porch was added. Beck died in 1846 but his widow and his descendants continued to live in the house until the early 20th century. The 1911 census for England, however, records the property as being unoccupied. Ownership of the house passed to the Brocklebank family who leased the house to a number of tenants. One of these, between 1929 and 1932 was the novelist Francis Brett Young until he decided that the weather was too wet for him. With the outbreak of the Second World War the house was used for accommodating volunteers involved w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
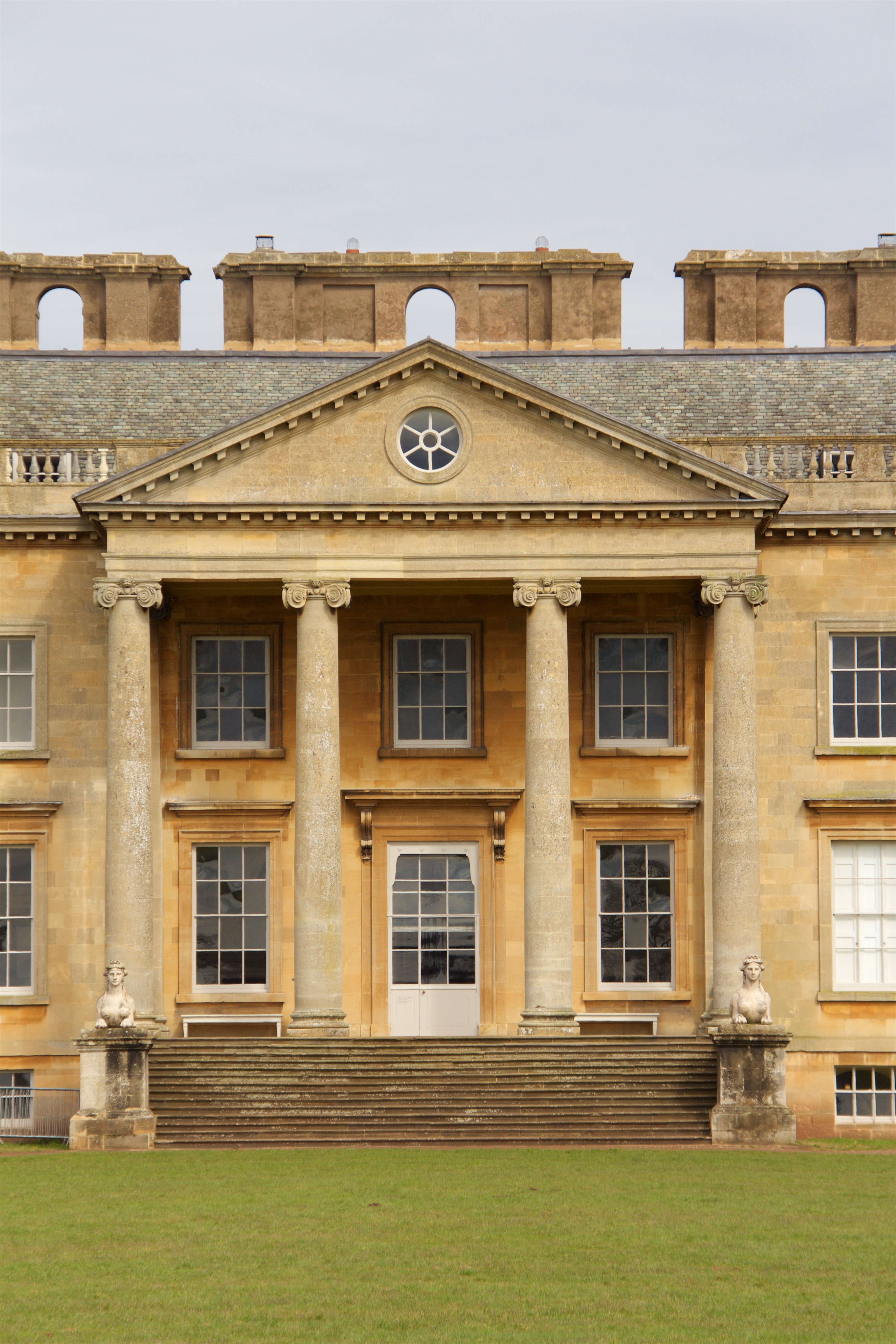
Portico
A portico is a porch leading to the entrance of a building, or extended as a colonnade, with a roof structure over a walkway, supported by columns or enclosed by walls. This idea was widely used in ancient Greece and has influenced many cultures, including most Western cultures. Some noteworthy examples of porticos are the East Portico of the United States Capitol, the portico adorning the Pantheon in Rome and the portico of University College London. Porticos are sometimes topped with pediments. Palladio was a pioneer of using temple-fronts for secular buildings. In the UK, the temple-front applied to The Vyne, Hampshire, was the first portico applied to an English country house. A pronaos ( or ) is the inner area of the portico of a Greek or Roman temple, situated between the portico's colonnade or walls and the entrance to the ''cella'', or shrine. Roman temples commonly had an open pronaos, usually with only columns and no walls, and the pronaos could be as long as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
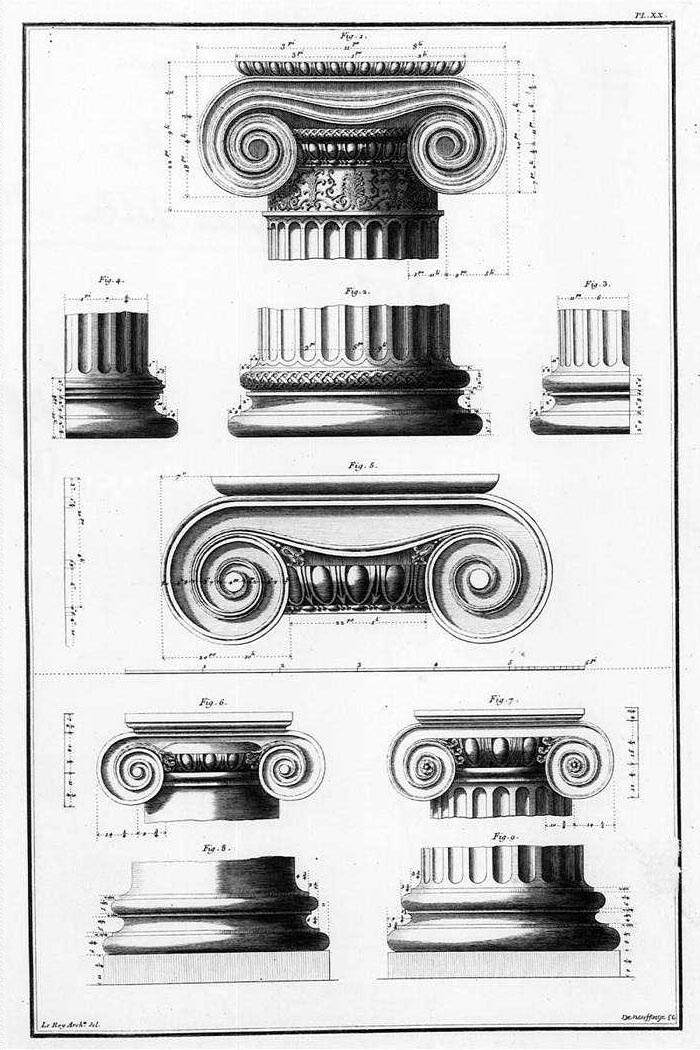
Ionic Order
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric and the Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan (a plainer Doric), and the rich variant of Corinthian called the composite order. Of the three classical canonic orders, the Corinthian order has the narrowest columns, followed by the Ionic order, with the Doric order having the widest columns. The Ionic capital is characterized by the use of volutes. The Ionic columns normally stand on a base which separates the shaft of the column from the stylobate or platform while the cap is usually enriched with egg-and-dart. The ancient architect and architectural historian Vitruvius associates the Ionic with feminine proportions (the Doric representing the masculine). Description Capital The major features of the Ionic order are the volutes of its capital, which have been the subject of much theoretical and practical discourse, based on a brief and obscure passage i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |