|
List Of Wartime Orders Of Battle For The British 1st Division (1809–1945)
An order of battle is a list of the various elements of a military formation organised within a hierarchical command structure. It can provide information on the strength of that formation and the equipment used. An order of battle is not necessarily a set structure, and it can change depending on tactical or strategic developments, or the evolution of military doctrine. For example, a division could be altered radically from one campaign to another through the adding or removing of subunits but retain its identity and prior history. The size of a division can vary dramatically as a result of what forces are assigned and the doctrine employed at that time. The 1st Division was an infantry division of the British Army, which was formed numerous times from 1809 to present. Several formations bore the name "1st Division", from 1809 through to the end of the 19th century. Per the 1st Division's official website, its lineage is described as including the Peninsular War, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divisional Insignia Of The British Army
Formation signs at the division level were first introduced in the British Army in the First World War. They were intended (initially) as a security measure to avoid displaying the division's designation in the clear. They were used on vehicles, sign posts and notice boards and were increasingly, but not universally, worn on uniform as the War progressed. Discontinued by the regular army after 1918, only a few Territorial divisions continued to wear them before 1939. Reintroduced officially in late 1940 in the Second World War, divisional formation signs were much more prevalent on uniforms and were taken up by many other formations, independent brigades, corps, armies, overseas and home commands, military districts and lines of communication areas. The sign could be based on many things, geometry (simple or more complex), heraldry, regional or historical associations, a pun, the role of the division or a combination. First World War Until 1916, unit names were written on vehicl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Defence (United Kingdom)
The Ministry of Defence (MOD or MoD) is the department responsible for implementing the defence policy set by His Majesty's Government, and is the headquarters of the British Armed Forces. The MOD states that its principal objectives are to defend the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and its interests and to strengthen international peace and stability. The MOD also manages day-to-day running of the armed forces, contingency planning and defence procurement. The expenditure, administration and policy of the MOD are scrutinised by the Defence Select Committee, except for Defence Intelligence which instead falls under the Intelligence and Security Committee of Parliament. History During the 1920s and 1930s, British civil servants and politicians, looking back at the performance of the state during the First World War, concluded that there was a need for greater co-ordination between the three services that made up the armed forces of the United Kingdom: t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coldstream Guards
The Coldstream Guards is the oldest continuously serving regular regiment in the British Army. As part of the Household Division, one of its principal roles is the protection of the monarchy; due to this, it often participates in state ceremonial occasions. The Regiment has consistently provided formations on deployments around the world and has fought in the majority of the major conflicts in which the British Army has been engaged. The Regiment has been in continuous service and has never been amalgamated. It was formed in 1650 as 'Monck's Regiment of Foot' and was then renamed 'The Lord General's Regiment of Foot Guards' after the restoration in 1660. With Monck's death in 1670 it was again renamed 'The Coldstream Regiment of Foot Guards' after the location in Scotland from which it marched to help restore the monarchy in 1660. Its name was again changed to 'The Coldstream Guards' in 1855 and this is still its present title. Today, the Regiment consists of: Regimental Headq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bourbon Restoration In France
The Bourbon Restoration was the period of French history during which the House of Bourbon returned to power after the first fall of Napoleon on 3 May 1814. Briefly interrupted by the Hundred Days War in 1815, the Restoration lasted until the July Revolution of 26 July 1830. Louis XVIII and Charles X, brothers of the executed king Louis XVI, successively mounted the throne and instituted a conservative government intended to restore the proprieties, if not all the institutions, of the Ancien Régime. Exiled supporters of the monarchy returned to France but were unable to reverse most of the changes made by the French Revolution. Exhausted by decades of war, the nation experienced a period of internal and external peace, stable economic prosperity and the preliminaries of industrialization. Background Following the French Revolution (1789–1799), Napoleon Bonaparte became ruler of France. After years of expansion of his French Empire by successive military victories, a coaliti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First French Empire
The First French Empire, officially the French Republic, then the French Empire (; Latin: ) after 1809, also known as Napoleonic France, was the empire ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, who established French hegemony over much of continental Europe at the beginning of the 19th century. It lasted from 18 May 1804 to 11 April 1814 and again briefly from 20 March 1815 to 7 July 1815. Although France had already established a colonial empire overseas since the early 17th century, the French state had remained a kingdom under the Bourbons and a republic after the French Revolution. Historians refer to Napoleon's regime as the ''First Empire'' to distinguish it from the restorationist ''Second Empire'' (1852–1870) ruled by his nephew Napoleon III. The First French Empire is considered by some to be a " Republican empire." On 18 May 1804, Napoleon was granted the title Emperor of the French (', ) by the French and was crowned on 2 December 1804, signifying the end of the French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to the southwest, and the North Sea to the northwest. It covers an area of and has a population of more than 11.5 million, making it the 22nd most densely populated country in the world and the 6th most densely populated country in Europe, with a density of . Belgium is part of an area known as the Low Countries, historically a somewhat larger region than the Benelux group of states, as it also included parts of northern France. The capital and largest city is Brussels; other major cities are Antwerp, Ghent, Charleroi, Liège, Bruges, Namur, and Leuven. Belgium is a sovereign state and a federal constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary system. Its institutional organization is complex and is structured on both regional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
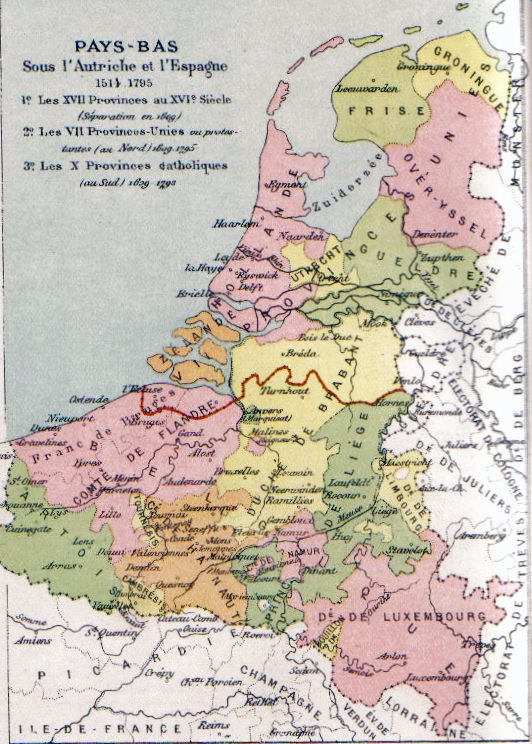
Southern Netherlands
The Southern Netherlands, also called the Catholic Netherlands, were the parts of the Low Countries belonging to the Holy Roman Empire which were at first largely controlled by Habsburg Spain (Spanish Netherlands, 1556–1714) and later by the Austrian Habsburgs (Austrian Netherlands, 1714–1794) until occupied and annexed by Revolutionary France (1794–1815). The region also included a number of smaller states that were never ruled by Spain or Austria: the Prince-Bishopric of Liège, the Imperial Abbey of Stavelot-Malmedy, the County of Bouillon, the County of Horne and the Princely Abbey of Thorn. The Southern Netherlands comprised most of modern-day Belgium and Luxembourg, small parts of the modern Netherlands and Germany (the Upper Guelders region, as well as the Bitburg area in Germany, then part of Luxembourg), in addition to (until 1678) most of the present Nord-Pas-de-Calais region, and Longwy area in northern France. The (southern) Upper Guelders region consisted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Vittoria
At the Battle of Vitoria (21 June 1813) a British, Portuguese and Spanish army under the Marquess of Wellington broke the French army under King Joseph Bonaparte and Marshal Jean-Baptiste Jourdan near Vitoria in Spain, eventually leading to victory in the Peninsular War. Background In July 1812, after the Battle of Salamanca, the French had evacuated Madrid, which Wellington's army entered on 12 August 1812. Deploying three divisions to guard its southern approaches, Wellington marched north with the rest of his army to lay siege to the fortress of Burgos, away, but he had miscalculated the enemy's strength, and on 21 October he had to abandon the Siege of Burgos and retreat. By 31 October he had abandoned Madrid too and retreated first to Salamanca then to Ciudad Rodrigo, near the Portuguese frontier, to avoid encirclement by French armies from the north-east and south-east. Wellington spent the winter reorganizing and reinforcing his forces to attack King Joseph in Madr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Talavera
The Battle of Talavera (27–28 July 1809) was fought just outside the town of Talavera de la Reina, Spain some southwest of Madrid, during the Peninsular War. At Talavera, a British army under Sir Arthur Wellesley combined with a Spanish army under General Cuesta in operations against French-occupied Madrid. The French army withdrew at night after several of its attacks had been repulsed. After Marshal Soult's French army had retreated from Portugal, General Wellesley's 20,000 British troops advanced into Spain to join 33,000 Spanish troops under General Cuesta. They marched up the Tagus valley to Talavera, some southwest of Madrid. There they encountered 46,000 French under Marshal Claude Victor and Major-General Horace Sébastiani, with the French king of Spain, Joseph Bonaparte in nominal command. The French crossed the Alberche in the middle of the afternoon on 27July. A few hours later, the French attacked the right of the Spaniards and the British left. A strate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Portugal
The Kingdom of Portugal ( la, Regnum Portugalliae, pt, Reino de Portugal) was a monarchy in the western Iberian Peninsula and the predecessor of the modern Portuguese Republic. Existing to various extents between 1139 and 1910, it was also known as the Kingdom of Portugal and the Algarves after 1415, and as the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves between 1815 and 1822. The name is also often applied to the Portuguese Empire, the realm's overseas colonies. The nucleus of the Portuguese state was the County of Portugal, established in the 9th century as part of the ''Reconquista'', by Vímara Peres, a vassal of the King of Asturias. The county became part of the Kingdom of León in 1097, and the Counts of Portugal established themselves as rulers of an independent kingdom in the 12th century, following the battle of São Mamede. The kingdom was ruled by the Alfonsine Dynasty until the 1383–85 Crisis, after which the monarchy passed to the House of Aviz. Dur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Spain (1810–73)
The history of Spain dates to contact the pre-Roman peoples of the Mediterranean coast of the Iberian Peninsula made with the Greeks and Phoenicians and the first writing systems known as Paleohispanic scripts were developed. During Classical Antiquity, the peninsula was the site of multiple successive colonizations of Greeks, Carthaginians, and Romans. Native peoples of the peninsula, such as the Tartessos people, intermingled with the colonizers to create a uniquely Iberian culture. The Romans referred to the entire Peninsula as Hispania, from where the modern name of Spain originates. The region was divided up, at various times, into different Roman provinces. As was the rest of the Western Roman Empire, Spain was subject to the numerous invasions of Germanic tribes during the 4th and 5th centuries CE, resulting in the loss of Roman rule and the establishment of Germanic kingdoms, most notably the Visigoths and the Suebi, marking the beginning of the Middle Ages in Spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke Of Wellington
Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, (1 May 1769 – 14 September 1852) was an Anglo-Irish soldier and Tory statesman who was one of the leading military and political figures of 19th-century Britain, serving twice as prime minister of the United Kingdom. He is among the commanders who won and ended the Napoleonic Wars when the coalition defeated Napoleon at the Battle of Waterloo in 1815. Wellesley was born in Dublin into the Protestant Ascendancy in Ireland. He was commissioned as an ensign in the British Army in 1787, serving in Ireland as aide-de-camp to two successive lords lieutenant of Ireland. He was also elected as a member of Parliament in the Irish House of Commons. He was a colonel by 1796 and saw action in the Netherlands and in India, where he fought in the Fourth Anglo-Mysore War at the Battle of Seringapatam. He was appointed governor of Seringapatam and Mysore in 1799 and, as a newly appointed major-general, won a decisive victory over the Maratha Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(Tony_Radakin_cropped).jpg)