|
List Of Viverrids
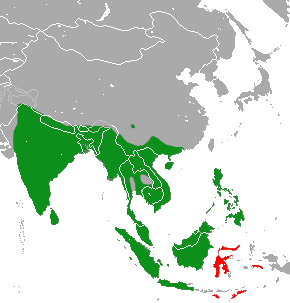
Viverridae is a family of mammals in the order Carnivora, composed mainly of the civets and genets. A member of this family is called a viverrid. They are widespread primarily throughout Africa, India, and southeast Asia, and are found primarily in forests, shrublands, and grasslands, though some species can be found in savannas or wetlands. Most viverrids are 40–65 cm (16–26 in) long, plus a 35–60 cm (14–24 in) tail, though the West African oyan can be as small as 30 cm (12 in) plus a 35 cm (14 in) tail, and some binturongs can be up to 96 cm (38 in) plus a 89 cm (35 in) tail. Most species do not have population estimates, though three viverrids are classified as endangered, and one, the Malabar large-spotted civet, is classified as critically endangered with a population size of around 200. No viverrid species have been domesticated. The 33 species of Viverridae are split into 14 genera within 4 subfamilies: the 3 civet subfamilies Viverrinae, Hemigalinae, and Paradoxu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
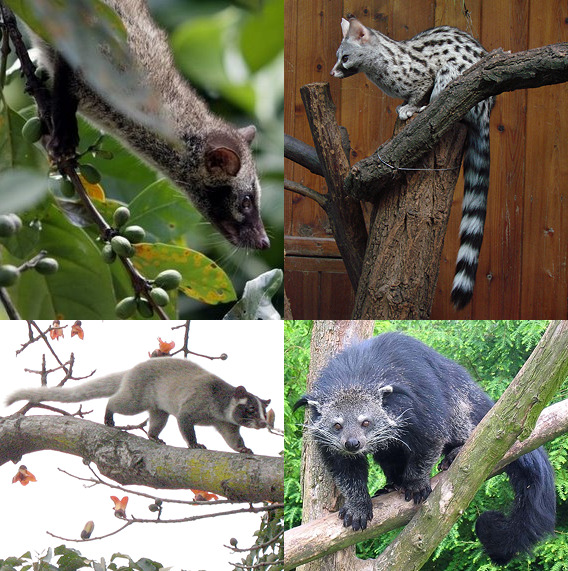
Viverrids Mosaic
Viverridae is a family of small to medium-sized, feliform mammals. The viverrids () comprise 33 species placed in 14 genera. This family was named and first described by John Edward Gray in 1821. Viverrids occur all over Africa, southern Europe, and South and Southeast Asia, across the Wallace Line. Their occurrence in Sulawesi and in some of the adjoining islands shows them to be ancient inhabitants of the Old World tropics. Characteristics Viverrids have four or five toes on each foot and half-retractile claws. They have six incisors in each jaw and molars with two tubercular grinders behind in the upper jaw, and one in the lower jaw. The tongue is rough with sharp prickles. A pouch or gland occurs beneath the anus, but there is no cecum. Viverrids are the most primitive of all the families of feliform Carnivora and clearly less specialized than the Felidae. In external characteristics, they are distinguished from the Felidae by the longer muzzle and tuft of facial vibri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paradoxurinae
Paradoxurinae is a subfamily of the feliform viverrids that was denominated and first described by John Edward Gray in 1864. Pocock subordinated the genera ''Paradoxurus'', ''Paguma'' and ''Arctictis'' to this subfamily. Classification Living species Phylogenetic tree The phylogenetic relationships of Paradoxurinae are shown in the following cladogram: Extinct genera *'' Kichechia'' *'' Tugenictis'' *''Kanuites ''Kanuites'' is an extinct genus of Paradoxurinae, paradoxurine viverrid carnivore. It lived in Africa, during the Miocene epoch. Description ''Kanuites'' was about long, and looked remarkably similar to modern Genet (animal), genets. ''Kanuite ...'' *'' Siamictis'' References Viverrids Taxa named by John Edward Gray {{carnivora-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctogalidia
The small-toothed palm civet (''Arctogalidia trivirgata''), also known as the three-striped palm civet, is a palm civet native to dense forests of Southeast Asia, from the Assam district of India to Indochina and the Malay Peninsula and on Sumatra, Bangka, Java, Borneo, and numerous small nearby islands of Indonesia. The first scientific description by John Edward Gray in 1832 was based on a zoological specimen from the Maluku Islands in the collection of the Rijksmuseum van Natuurlijke Historie in Leiden, Netherlands. It is blackish grey, has black paws and three black longitudinal stripes on the back. A monotypic genus, ''Arctogalidia'' means ‘bear-weasel’ (from ancient Greek '' arkto-'' ‘bear’ + ''galidia'' ‘little weasel’). The specific epithet ''trivirgata'' means ‘three-striped’ in Latin. The small-toothed palm civet is mid-sized by the standards of its family, weighing 2.4 kg (5.3 lbs) and measuring 53 cm (21 in) long along the body, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
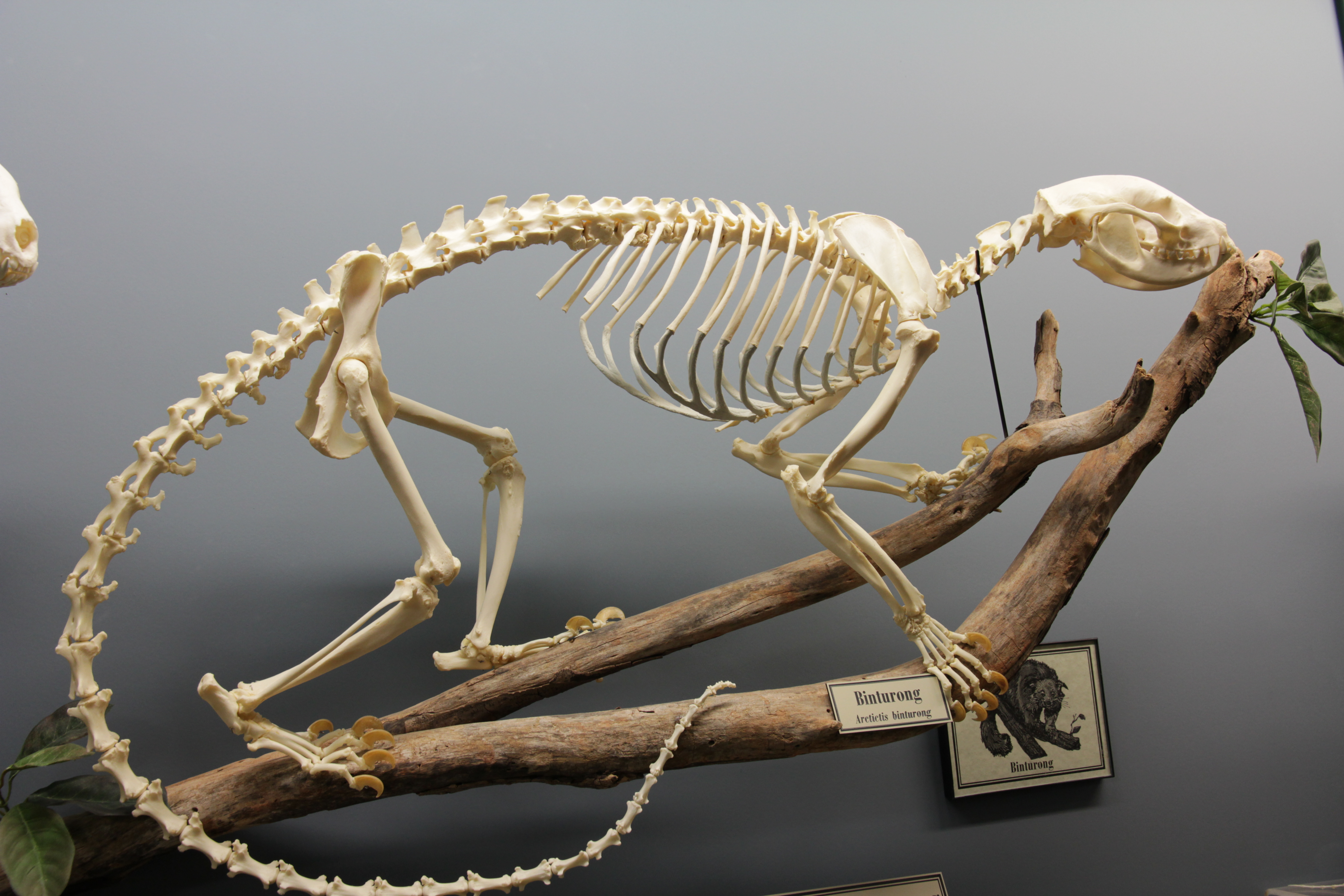
Arctictis
The binturong (''Arctictis binturong'') (, ), also known as the bearcat, is a viverrid native to South and Southeast Asia. It is uncommon in much of its range, and has been assessed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List because of a declining population trend that is estimated at more than 30% since the mid-1980s. The binturong is the only living species in the genus ''Arctictis''. Etymology The name ''Arctictis'' means 'bear-weasel', from Greek '' arkt-'' 'bear' + '' iktis'' 'weasel'. In Riau, Indonesia it is called 'benturong' and 'tenturun'. Its common name in Borneo is "binturong", which is related to the Western Malayo-Polynesian root "ma-tuRun". Taxonomy ''Viverra binturong'' was the scientific name proposed by Thomas Stamford Raffles in 1822 for a specimen from Malacca. The generic name ''Arctictis'' was proposed by Coenraad Jacob Temminck in 1824. ''Arctictis'' is a monotypic taxon; its morphology is similar to that of members of the genera ''Paradoxurus'' and ''Paguma'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemigalus
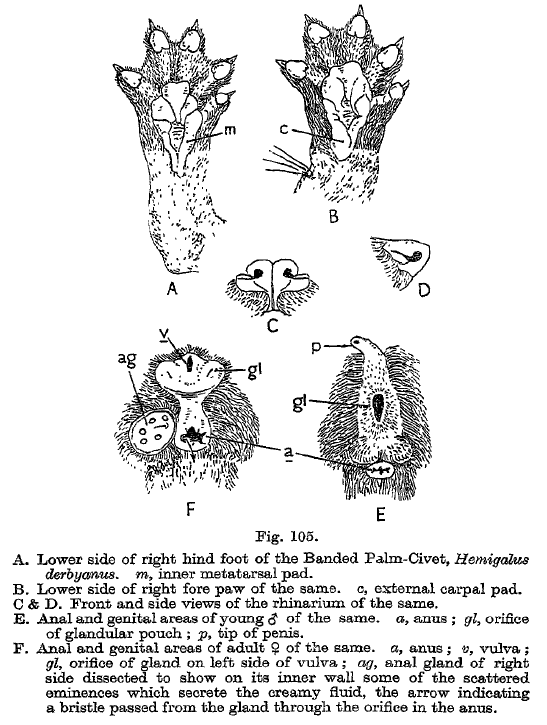
The banded palm civet (''Hemigalus derbyanus''), also called banded civet, is a viverrid native to Myanmar, Peninsular Malaysia, peninsular Thailand and the Sunda Islands of Sipura, Sumatra and Borneo. It is listed as Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List because of its large geographic and elevation range and tolerance to some habitat disturbance. ''Hemigalus'' is a monospecific genus that was first named and described by Claude Jourdan in 1837. Characteristics The banded palm civet has a long pointed face, reminiscent of insectivorous mammals. It has a long body set on short legs, and five toes on each foot with retractable claws. It looks very similar to Owston's palm civet (''Chrotogale owstoni''), except that it lacks spots on its body, and the hair on its neck points upwards instead of down along the neck. It is also similar to the rare Hose's palm civet (''Diplogale hosei''), an endemic of northern Borneo - they only differ in shape of muzzle and teeth and Hose's civet do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplogale
Hose's palm civet (''Diplogale hosei''), also known as Hose's civet, is a viverrid species endemic to the island of Borneo. It is listed on the IUCN Red List as Vulnerable because of an ongoing population decline, estimated to be more than 30% over the last three generations (inferred to be 15 years) and suspected to be more than 30% in the next three generations due to declines in population inferred from habitat destruction and degradation. ''Diplogale'' is a monospecific genus. Hose's palm civet was named after the zoologist Charles Hose by Oldfield Thomas in 1892. Hose collected the first specimen in Sarawak in 1891. What little is known of the species comes primarily from 17 museum specimens worldwide. Only in 1997, the first living specimen was obtained and released after two months. Hose's civet is not kept in captivity anywhere in the world. Characteristics The upperparts (from nose to tail tip, including outer surfaces of the four limbs) are dark brown to blackish brow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cynogale
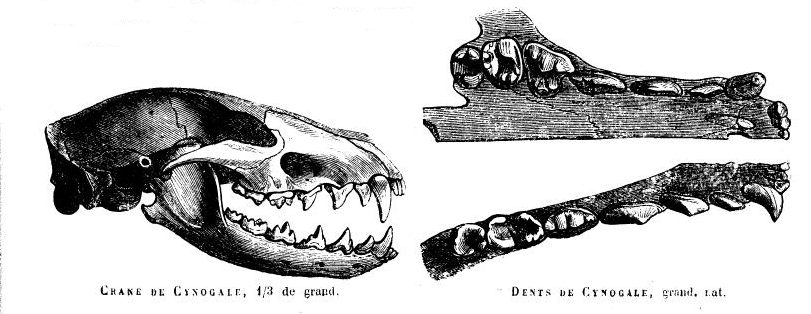
The otter civet (''Cynogale bennettii'') is a semiaquatic viverrid native to Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia and Brunei. It is listed as Endangered because of a serious ongoing population decline, estimated to be more than 50% over the past three generations (estimated to be 15 years), inferred from direct habitat destruction, and indirect inferred declines due to pollutants. ''Cynogale'' is a monospecific genus. Characteristics The otter civet possesses several adaptations to its habitat, including a broad mouth and webbed feet with naked soles and long claws. Its muzzle is long with numerous long whiskers. It is in many ways similar to the Hose's palm civet (''Diplogale hosei'') but has a shorter tail and no whitish underparts. Distribution and habitat Otter civets are distributed in Sumatra, Borneo and peninsular Thailand. Preferred habitat appears to be lowland primary forest, but they have also been recorded in secondary forest, bamboo and logged forest. The supposed ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrotogale
Owston's palm civet (''Chrotogale owstoni'') is a civet native to Vietnam, Laos and southern China. It is listed as Endangered by IUCN because of an ongoing population decline, estimated to be more than 50% over the last three generations, inferred from over-exploitation, habitat destruction and degradation. ''Chrotogale'' is a monospecific genus. Owston's palm civet is named after the wildlife collector Alan Owston. Characteristics The Owston's palm civet is a mid-sized palm civet at 57 cm (23 in), plus a tail of 43 cm (17 in). With its pointed face, it is sometimes thought to resemble a large insectivore, such as a shrew. It has a tawny buff-grey body with highly contrasted black markings on its back and tail. They usually only have 4 bands on their back. The last two-thirds of the tail is completely black. They look somewhat like the banded palm civet, ''Hemigalus derbyanus'', except for that the hair on the back of their neck are not reversed, and the Ow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poiana (genus)
The African linsangs also known as oyans are two species classified in the mammalian subfamily Viverrinae, in the family Viverridae. There is one genus, ''Poiana''. The name ''linsang'' is from Javanese ''linsang'' or ''wlinsang'', which used to be wrongly translated as "otter" in English dictionaries. Linsangs are nocturnal, generally solitary tree dwellers. They are carnivorous, eating squirrels and other rodents, small birds, lizards and insects. Typical size is a little over 30 cm (1 foot), with a tail that more than doubles that length. Bodies are long, with short legs, giving a low appearance. Both species have yellowish bodies with black markings (stripes, blotches and spots), though the distribution and nature of the markings varies between the two species. Taxonomy The genus ''Poiana'' was erected by John Edward Gray in a paper read at the 8 November 1864 meeting of the Zoological Society of London and published the following year, in the ''Proceedings of the Zool ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hybrid (biology)
In biology, a hybrid is the offspring resulting from combining the qualities of two organisms of different breeds, varieties, species or genera through sexual reproduction. Hybrids are not always intermediates between their parents (such as in blending inheritance), but can show hybrid vigor, sometimes growing larger or taller than either parent. The concept of a hybrid is interpreted differently in animal and plant breeding, where there is interest in the individual parentage. In genetics, attention is focused on the numbers of chromosomes. In taxonomy, a key question is how closely related the parent species are. Species are reproductively isolated by strong barriers to hybridisation, which include genetic and morphological differences, differing times of fertility, mating behaviors and cues, and physiological rejection of sperm cells or the developing embryo. Some act before fertilization and others after it. Similar barriers exist in plants, with differences in flowering tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IUCN Red List
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of biological species. It uses a set of precise criteria to evaluate the extinction risk of thousands of species and subspecies. These criteria are relevant to all species and all regions of the world. With its strong scientific base, the IUCN Red List is recognized as the most authoritative guide to the status of biological diversity. A series of Regional Red Lists are produced by countries or organizations, which assess the risk of extinction to species within a political management unit. The aim of the IUCN Red List is to convey the urgency of conservation issues to the public and policy makers, as well as help the international community to reduce species extinction. According to IUCN the formally stated goals of the Red List are to provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |