|
List Of Urban Rail Systems In Japan
The list of urban rail systems in Japan lists urban rail transit systems in Japan, organized by , including number of stations, length (km), and average daily and annual ridership volume. Data is shown only for those areas designated as by the Statistics Bureau of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications. Considerations There are several considerations for the data presented in this list. Station count Data is broken down at the line level, then rolled up for each specific railway operator. The total station count for each operator is a "unique station" count—an interchange or transfer station between two lines operated by the same company is counted as a single station. As a result, summing together the station counts for all of the lines under a single railway operator will generally yield a value greater than the total station count cited for the operator. Some station pairs are officially considered interchanges by their respective railway operators despit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keihan Electric Railway 012
In Japanese, Keihan may refer to: * , the Kyoto-Osaka area, part of the larger area. * , a Kyoto-Osaka train line, often abbreviated to Keihan. * , a local dish of the Amami Islands, Kagoshima Prefecture in the south of Japan. {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Branch Line
A branch line is a phrase used in railway terminology to denote a secondary railway line which branches off a more important through route, usually a main line. A very short branch line may be called a spur line. Industrial spur An industrial spur is a type of secondary track used by railroads to allow customers at a location to load and unload railcars without interfering with other railroad operations. Industrial spurs can vary greatly in length and railcar capacity depending on the requirements of the customer the spur is serving. In heavily industrialized areas, it is not uncommon for one industrial spur to have multiple sidings to several different customers. Typically, spurs are serviced by local trains responsible for collecting small numbers of railcars and delivering them to a larger yard, where these railcars are sorted and dispatched in larger trains with other cars destined to similar locations. Because industrial spurs generally have less capacity and traffic t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chūō Rapid Line
may refer to: Places *Chūō-ku (other), city wards named Chūō **Chūō, Tokyo, a special ward in Tokyo *Chūō, Yamanashi, a city in Yamanashi Prefecture *Chūō, Kumamoto, a former town in Kumamoto Prefecture *Chūō, Okayama, a former town in Okayama Prefecture Transport *Chūō Line (other), railway lines connecting Tokyo to Nagoya *Chūō Shinkansen, a maglev line under construction between Tokyo and Osaka *Chūō Expressway, a toll road connecting Tokyo and Nagoya Other *Chuo University, Tokyo *CHUO-FM, a Canadian community-based campus radio station * (Korean: 중앙 (Hanja: 中央)) *Zhongyang (other) ( cmn, 中央, links=no) {{DEFAULTSORT:Chuo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Japan Railway Company
The is a major passenger railway company in Japan and is the largest of the seven Japan Railways Group companies. The company name is officially abbreviated as JR-EAST or JR East in English, and as in Japanese. The company's headquarters are in Yoyogi, Shibuya, Tokyo, and next to the Shinjuku Station. It is listed in the Tokyo Stock Exchange (it formerly had secondary listings in the Nagoya Stock Exchange, Nagoya and Osaka Exchange, Osaka stock exchanges), is a constituent of the TOPIX Large70 index, and is also one of the three only Japan Railways Group constituents of the Nikkei 225 index, the other being Central Japan Railway Company, JR Central and West Japan Railway Company, JR West. History JR East was incorporated on 1 April 1987 after being spun off from the government-run Japanese National Railways (JNR). The spin-off was nominally "privatization", as the company was actually a wholly owned subsidiary of the government-owned Japanese National Railway Settlement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hiroshima Electric Railway
is a Japanese transportation company established on June 18, 1910, that operates streetcars and buses in and around Hiroshima Prefecture. It is known as for short. The company's rolling stock includes an eclectic range of trams manufactured from across Japan and Europe, earning it the nickname "The Moving Streetcar Museum". From January 2008 the company has accepted PASPY, a smart card ticket system. This is the longest tram network in Japan, with . The atomic bombing of Hiroshima took place on 6 August 1945. 185 employees of the company were killed as a result of the bomb and 108 of its 123 cars were damaged or destroyed. Within three days, the system started running again. Three trams that survived or were rebuilt after the bombing continue to run 75 years afterwards. Railway and streetcar *One Railway line with one route for 16.1 km. ( Miyajima Line) **between Hiroden-nishi-hiroshima Station and Hiroden-miyajima-guchi Station. **trains(trams) link up with other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saikyō Line
The Saikyō Line ( ja, 埼京線, ) is a Japanese railway line operated by the East Japan Railway Company (JR East). It connects Ōsaki Station in Shinagawa, Tokyo, and Ōmiya Station in Saitama Prefecture. The line's name is an abbreviation of the two areas the line connects: Saitama ( ja, 埼玉, links=no) and Tōkyō ( ja, 東京, links=no). At the northern end of the line, some trains continue beyond Ōmiya as far as on the Kawagoe Line; at the southern end of the line, many Saikyō Line trains continue onward beyond Ōsaki to either on the Rinkai Line (operated by Tokyo Waterfront Area Rapid Transit) or on the Sotetsu Main Line (via the Sōtetsu Shin-Yokohama Line). Beside the link that connects the Saikyō and Rinkai lines is the JR East Tokyo General Rolling Stock Centre that stores the rolling stock for the Yamanote Line and other types of rolling stock; and the Hinkaku Line which links Saikyo Line to the Tokaido Freight Line and Sotetsu-JR Link Line. Basic data *O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ōsaki Station
is a railway station in Shinagawa, Tokyo, Japan, jointly operated by East Japan Railway Company (JR East) and Tokyo Waterfront Area Rapid Transit (TWR). Lines Ōsaki Station is served by the following JR East lines. * Saikyō Line * Shōnan-Shinjuku Line * Yamanote Line It also forms the western starting point of the TWR Rinkai Line to . Most Saikyō Line trains operate through to Shin-Kiba on the Rinkai Line. Station layout The station has four island platforms serving eight tracks. Platforms 1 to 4 are for the Yamanote Line, and 5 to 8 are shared by the Saikyō Line, the Shōnan-Shinjuku Line, and the Rinkai Line. Ōsaki is one of the stations on the Yamanote Line loop where trains are put into and taken out of service. It therefore has four tracks (two in each direction) for the Yamanote Line so as not to interfere with continuing trains (trains go several rounds before being taken out). Chest-high platform edge doors were introduced on the Yamanote Line platforms from 22 D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ikebukuro Station
Ikebukuro Station ( ja, 池袋駅, ) is a major railway station located in the Ikebukuro district of Toshima, Tokyo, Japan, shared by the East Japan Railway Company (JR East), Tokyo subway operator Tokyo Metro, and the two private railway operators Seibu Railway and Tobu Railway. With 2.71 million passengers on an average daily in 2007, it is the second-busiest railway station in the world (after Shinjuku Station), and the busiest station in the Tobu, Seibu, and Tokyo Metro networks. It primarily serves commuters from Saitama Prefecture and other residential areas northwest of the city center. It is the Tokyo terminal of the Seibu Ikebukuro Line and the Tobu Tojo Line. Lines JR East Seibu Railway Seibu Ikebukuro Line (Ikebukuro to Agano) - limited through service to Seibu Chichibu Line Tobu Railway Tōbu Tōjō Line (Ikebukuro to Yorii) Tokyo Metro Station layout In Ikebukuro Station, there are two main entrances; the East exit and the West exit. There are a number o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
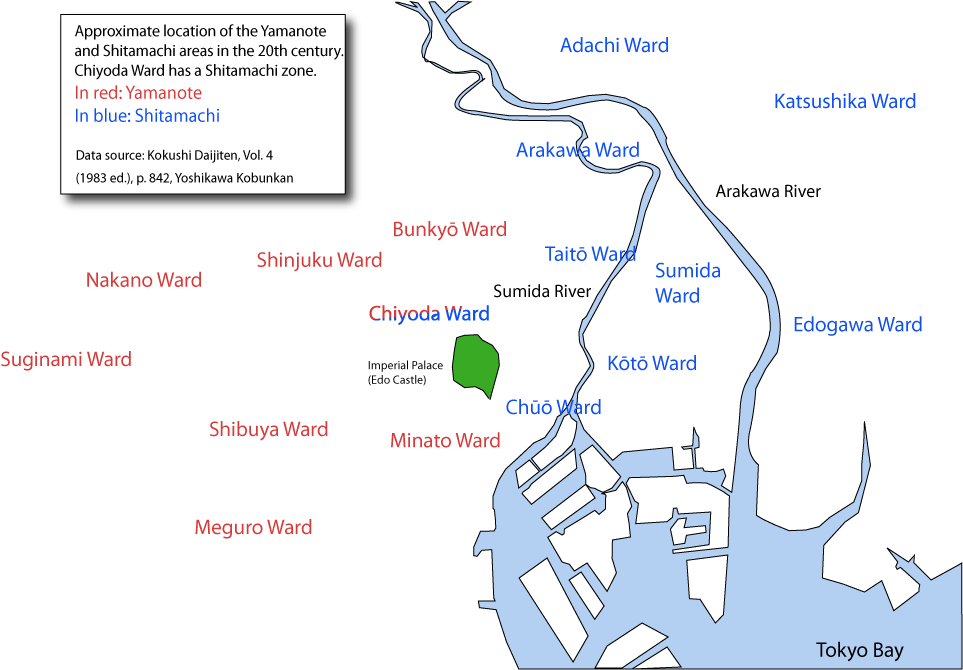
Yamanote Freight Line
and are traditional names for two areas of Tokyo, Japan. Yamanote refers to the affluent, upper-class areas of Tokyo west of the Imperial Palace.Iwanami Japanese dictionary, 6th Edition (2008), DVD version While citizens once considered it as consisting of Hongo, Kōjimachi, Koishikawa, Ushigome, Yotsuya, Akasaka, Aoyama and Azabu in the Bunkyō, Chiyoda (in part), Shinjuku, and Minato wards, its size has grown to include the Nakano, Suginami and Meguro wards. Shitamachi is the traditional name for the area of Tokyo including today the Adachi, Arakawa, Chiyoda (in part), Chūō, Edogawa, Katsushika, Kōtō, Sumida, and Taitō wards, the physically low part of the city along and east of the Sumida River. The two regions have always been vaguely defined, as their identity was more based on culture and caste than on geography. While Tokugawa vassals of the warrior caste (hatamoto and gokenin) lived in the hilly Yamanote, lower castes (merchants and artisans) lived in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hashimoto Station (Kanagawa)
is a major passenger interchange railway station located in the city of Sagamihara, Kanagawa, Japan and operated by the East Japan Railway Company (JR East) and the private railway operator Keio Corporation. Lines Hashimoto Station is served by the Yokohama Line and Sagami Line operated by JR East, as well as the Keio Sagamihara Line. It is from , from , and from . Station layout The JR East station has two island platforms and one side platform. The station building is built above the platforms and tracks, and the station has a "Midori no Madoguchi" staffed ticket office. The Keio station has one elevated island platform, with the station building underneath. Interconnecting from platform 5 is impossible (as of 2022). There are platform screen doors on platforms 1, 2, and 3 for Yokohama Line. Beyond platform 4, the tracks of the Sagami Line connect with the Yokohama Line (towards Hachiōji Station). Until March 2022, the Sagami Line provided through service onto the Yokoh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keiō Line
The is a 37.9-km railway line in western Tokyo, Japan, owned by the private railway operator Keiō Corporation. It connects Shinjuku, Tokyo, with the suburban city of Hachiōji. The Keiō Line is part of a network with interchanges and through running to other lines of Keiō Corporation: the Keiō New Line, Keiō Sagamihara Line, the Keiō Keibajō Line, the Keiō Dōbutsuen Line, the Keiō Takao Line, and the gauge Keiō Inokashira Line. Services Six different types of limited-stop services are operated on the Keiō Line, along with local trains. Destinations are from Shinjuku unless otherwise indicated. English abbreviations are tentative for this article. ; : Also known as for short. Until 2001 it was called . ; (R) : Most services for Hashimoto and Keiō-Tama-Center on the Sagamihara Line, and Takaosanguchi on the Takao Line ; (SeE) : Most bound for on the Sagamihara Line. Until 2013, these were weekday-only services called . ; (E) :Most services run from the Toe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |