|
List Of Semiregular Variable Stars
This is a list of semiregular variable stars. Variability ranges are taken from the General Catalogue of Variable Stars (GCVS) where these are visual magnitudes, otherwise from the International Variable Star Index (VSX). Spectral types are taken from the GCVS, which may differ from more recent MK spectral types but often defines a range. {, class="wikitable sortable" style="font-size:90%;" , - bgcolor="#efefef" ! Star ! Constellation ! Discovery ! Maximum (Apparent magnitude, mV) ! Minimum (Apparent magnitude, mV) ! Range ! Period (days) ! width="8%", Spectral Type ! Semiregular variable star, Type ! width="25%", Comment , --- , Theta Apodis, θ Aps , Apus , , 4m.65 , 6m.20 , , , M7III , SRb , , --- , Beta Andromedae, β And (Mirach) , Andromeda (constellation), Andromeda , , 2m.01 , 2m.10 , , , M0IIIa , SRb , suspected , --- , Z Aquarii, Z Aqr , Aquarius (constellation), Aquarius , , 7m.4 , 10m.2 , , , M1e-M7III , SRa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiregular Variable
In astronomy, a semiregular variable star, a type of variable star, is a giant or supergiant of intermediate and late (cooler) spectral type showing considerable periodicity in its light changes, accompanied or sometimes interrupted by various irregularities. Periods lie in the range from 20 to more than 2000 days, while the shapes of the light curves may be rather different and variable with each cycle. The amplitudes may be from several hundredths to several magnitudes (usually 1-2 magnitudes in the V filter). Classification The semiregular variable stars have been sub-divided into four categories for many decades, with a fifth related group defined more recently. The original definitions of the four main groups were formalised in 1958 at the tenth general assembly of the International Astronomical Union (IAU). The General Catalogue of Variable Stars (GCVS) has updated the definitions with some additional information and provided newer reference stars where old examples such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Superba
La Superba (Y CVn, Y Canum Venaticorum) is a strikingly red giant star in the constellation Canes Venatici. It is a carbon star and semiregular variable. Visibility La Superba is a semiregular variable star, varying by about a magnitude over a roughly 160-day cycle, but with slower variation over a larger range. Periods of 194 and 186 days have been suggested, with a resonance between the periods. Y CVn is one of the reddest stars known, and it is among the brightest of the giant red carbon stars. It is the brightest of known J-stars, which are a very rare category of carbon stars that contain large amounts of carbon-13 (carbon atoms with 7 neutrons instead of the usual 6). The 19th century astronomer Angelo Secchi, impressed with its beauty, gave the star its common name, which is now accepted by the International Astronomical Union. Properties The angular diameter of La Superba has been measured at . It is expected to be pulsating but this has not been seen i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SS Cephei
SS is an abbreviation for ''Schutzstaffel'', a paramilitary organisation in Nazi Germany. SS, Ss, or similar may also refer to: Places *Guangdong Experimental High School (''Sheng Shi'' or ''Saang Sat''), China *Province of Sassari, Italy (vehicle plate code) *South Sudan (ISO 3166-1 code SS) *SS postcode area, UK, around Southend-on-Sea *San Sebastián, Spanish city Arts, entertainment, and media *SS (band), an early Japanese hardcore punk band * ''SS'' (manga), a Japanese comic 2000-2003 *SS Entertainment, a Korean entertainment company *''S.S.'', for Sosthenes Smith, H. G. Wells pseudonym for story ''A Vision of the Past'' *SS, the production code for the 1968 ''Doctor Who'' serial ''The Wheel in Space'' *''Sesame Street'', American kids' TV show Language * Ss (digraph) used in Pinyin * ß or ss, a German-language ligature * switch-reference in linguistics *''Scilicet'', used as a section sign * (''in the strict sense'') in Latin *Swazi language (ISO 639-1 code "ss") Scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Herschel
Frederick William Herschel (; german: Friedrich Wilhelm Herschel; 15 November 1738 – 25 August 1822) was a German-born British astronomer and composer. He frequently collaborated with his younger sister and fellow astronomer Caroline Herschel (1750–1848). Born in the Electorate of Hanover, William Herschel followed his father into the military band of Hanover, before emigrating to Great Britain in 1757 at the age of nineteen. Herschel constructed his first large telescope in 1774, after which he spent nine years carrying out sky surveys to investigate double stars. Herschel published catalogues of nebulae in 1802 (2,500 objects) and in 1820 (5,000 objects). The resolving power of the Herschel telescopes revealed that many objects called nebulae in the Messier catalogue were actually clusters of stars. On 13 March 1781 while making observations he made note of a new object in the constellation of Gemini. This would, after several weeks of verification and consultation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cepheus (constellation)
Cepheus is a constellation in the far northern sky, named after Cepheus, a king of Aethiopia in Greek mythology. It is one of the 48 constellations listed by the second century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 constellations in the modern times. The constellation's brightest star is Alpha Cephei, with an apparent magnitude of 2.5. Delta Cephei is the prototype of an important class of star known as a Cepheid variable. RW Cephei, an orange hypergiant, together with the red supergiants Mu Cephei, MY Cephei, SW Cephei, VV Cephei, and V354 Cephei are among the largest stars known. In addition, Cepheus also has the hyperluminous quasar S5 0014+81, which hosts an ultramassive black hole in its core, reported at 40 billion solar masses, about 10,000 times more massive than the central black hole of the Milky Way, making this among the most massive black holes currently known. This paper does acknowledge the possibility of an optical illusion that would cause an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mu Cephei
Mu Cephei ( Latinized from μ Cephei, abbreviated Mu Cep or μ Cep), also known as Herschel's Garnet Star, Erakis, or HD 206936, is a red supergiant or hypergiant star in the constellation Cepheus. It appears garnet red and is located at the edge of the IC 1396 nebula. Since 1943, the spectrum of this star has served as a spectral standard by which other stars are classified. Mu Cephei is visually nearly 100,000 times brighter than the Sun, with an absolute visual magnitude of −7.6. It is also one of the largest known stars with a radius around or over 1,000 times that of the sun (), and were it placed in the Sun's position it would engulf the orbit of Mars and Jupiter. History The deep red color of Mu Cephei was noted by William Herschel, who described it as "a very fine deep garnet colour, such as the periodical star ο Ceti". It is thus commonly known as Herschel's "Garnet Star". Mu Cephei was called ''Garnet sidus'' by Giuseppe Piazzi in his catalogue. An a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
V810 Centauri
V810 Centauri is a double star consisting of a yellow hypergiant primary (V810 Cen A) and blue giant secondary (V810 Cen B). It is a small amplitude variable star, entirely due to the supergiant primary which is visually over three magnitudes (about 12x) brighter than the secondary. It is the MK spectral standard for class G0 0-Ia. V810 Cen A shows semi-regular variations with several component periods. The dominant mode is around 156 days and corresponds to Cepheid fundamental mode radial pulsation. Without the other stellar pulsation modes it would be considered a Classical Cepheid variable. Other pulsation modes have been detected at 89 to 234 days, with the strongest being a possible non-radial p-mode at 107 days and a possible non-radial g-mode at 185 days. The blue giant secondary has a similar mass and luminosity to the supergiant primary, but is visually much fainter. The primary is expected to have lost around since it was on the main sequence, and has expa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RV Tauri Variable
RV Tauri variables are luminous variable stars that have distinctive light variations with alternating deep and shallow minima. History and discovery German astronomer Friedrich Wilhelm Argelander monitored the distinctive variations in brightness of R Scuti from 1840 to 1850. R Sagittae was noted to be variable in 1859, but it was not until the discovery of RV Tauri by Russian astronomer Lidiya Tseraskaya in 1905 that the class of variable was recognised as distinct. Three spectroscopic groups were identified: * A, ''GK-type'' with spectra unambiguously of type G or K * B, ''Fp(R)'', spectra are inconsistent, with features of F, G, and later classes found together, plus carbon (class R) features * C, ''Fp'', peculiar spectra with generally weak absorption lines and without strong carbon bands RV Tauri stars are further classified into two photometric sub-types based on their light curves: * RVa: these are RV Tauri variables which do not vary in mean brightness * RVb: these a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
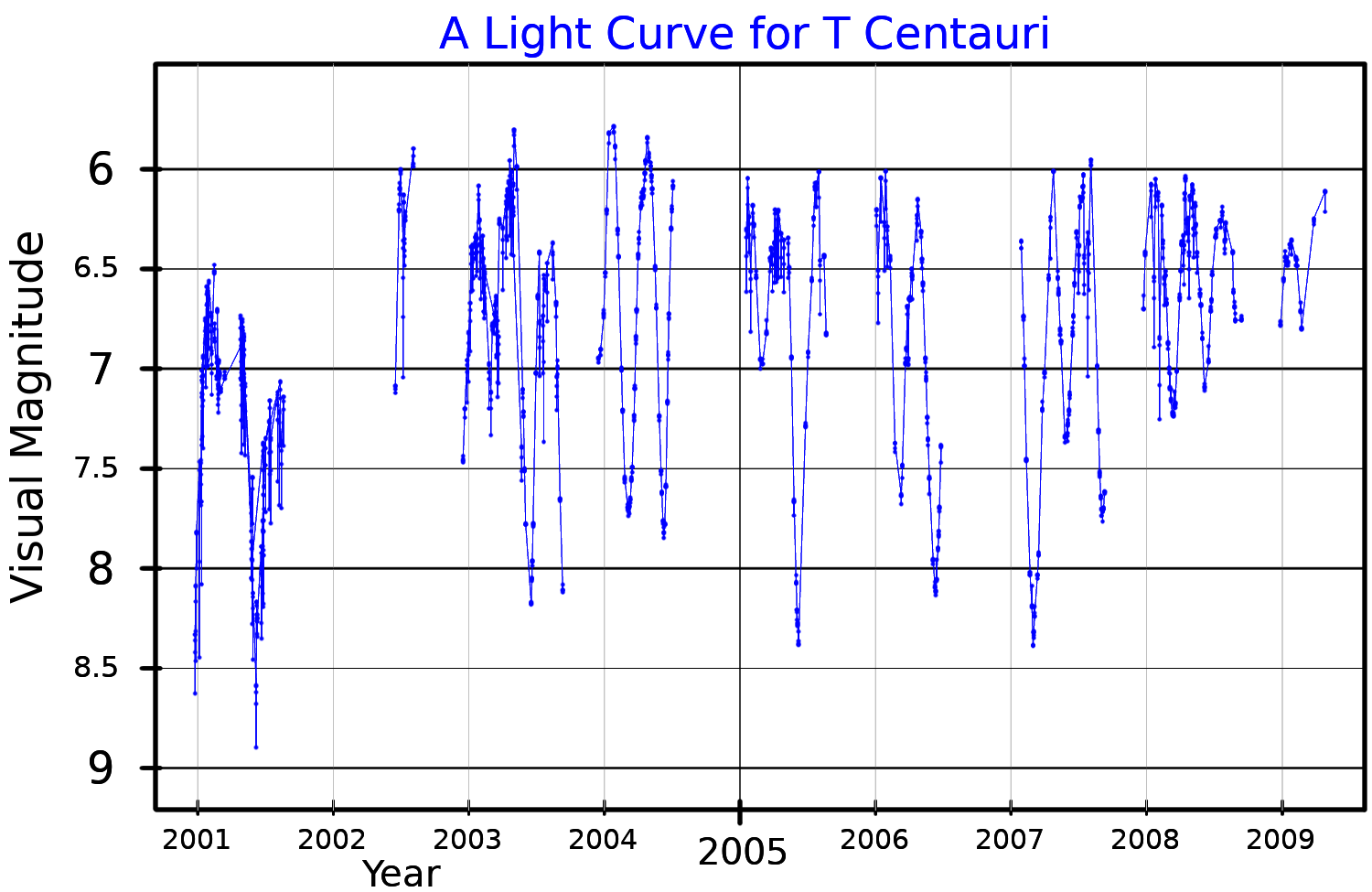
T Centauri
T Centauri is a variable star located in the far southern constellation Centaurus.SIMBADT Centauri(accessed 22 July 2014) It varies between magnitudes 5.56 and 8.44 over 181.4 days, making it intermittently visible to the naked eye. Pulsating between spectral classes K0:e and M4II:e, it has been classed as a semiregular variable, though Sebastian Otero of the American Association of Variable Star Observers has noted its curve more aligned with RV Tauri variable RV Tauri variables are luminous variable stars that have distinctive light variations with alternating deep and shallow minima. History and discovery German astronomer Friedrich Wilhelm Argelander monitored the distinctive variations in brightne ... stars and has classified it as one. References Centaurus (constellation) Semiregular variable stars Centauri, T Durchmusterung objects 119090 066825 K-type giants 5147 M-type bright giants Asymptotic-giant-branch stars RV Tauri variables {{var-star-stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centaurus
Centaurus is a bright constellation in the southern sky. One of the 88 modern constellations by area, largest constellations, Centaurus was included among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. In Greek mythology, Centaurus represents a centaur; a creature that is half human, half horse (another constellation named after a centaur is one from the zodiac: Sagittarius (constellation), Sagittarius). Notable stars include Alpha Centauri, the nearest star system to the Solar System, its neighbour in the sky Beta Centauri, and V766 Centauri, one of the largest stars yet discovered. The constellation also contains Omega Centauri, the brightest globular cluster as visible from Earth and the largest identified in the Milky Way, possibly a remnant of a dwarf galaxy. Notable features Stars Centaurus contains several very bright stars. Its alpha and beta stars are used as "pointer stars" to help observers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2 Centauri
2 Centauri is a single star in the Southern celestial hemisphere, southern constellation of Centaurus, located approximately 183 light-years from Earth. It has the Bayer designation g Centauri; ''2 Centauri'' is the Flamsteed designation. This object is visible to the naked eye as faint, red-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.19. It is moving away from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +41 km/s. The star is a member of the HD 1614 supercluster. This is an stellar evolution, evolved red giant star with a stellar classification of M5 III. It is classified as a semiregular variable star, semiregular variable star and its brightness varies from magnitude +4.16 to +4.26 with a period of 12.57 days. The star has around 70 times the Sun's radius and is radiating 72 times the Sun's luminosity from its enlarged photosphere at an effective temperature of . References {{DEFAULTSORT:2 Centauri M-type giants Asymptotic-giant-branch stars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WZ Cassiopeiae
WZ Cassiopeiae (WZ Cas) is a deep red hued star in the northern constellation of Cassiopeia. It is a variable star with a magnitude that ranges from 6.3 down to 8.8, placing it near the limit of naked eye visibility at peak magnitude. The estimated distance to this star, as determined from its annual parallax shift of , is about 1,540 light years. It is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −34 km/s. This is an aging carbon star on the asymptotic giant branch. Keenan (1993) assigned it a classification of , which indicates it is of the N star subtype in the revised Morgan–Keenan system, with a C2 strength index of 2 (a measure of the excess of carbon over oxygen) and an anomalously strong line of lithium at 6707 Å. It is losing mass at the rate of , which is on the low side for a star of this type. This is a semiregular variable of subtype SRb with periods of 186 and 366 days due to radial pulsations. It has expande ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
