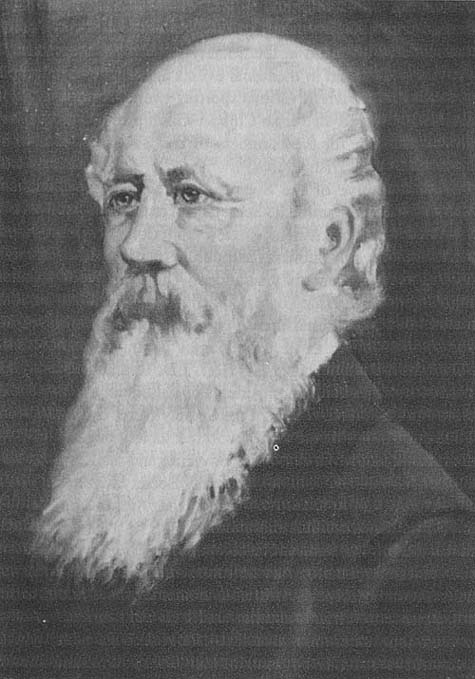|
List Of Premiers Of Newfoundland And Labrador
The premier of Newfoundland and Labrador is current title of the first minister for the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador, which was at certain points in its history a colony, dominion, and province. The province had a system of responsible government from 1855 to 1934, and again since 1949. Newfoundland became a British crown colony in 1855, in 1907 it became a dominion, and in 1949, it became a province and joined Canadian Confederation. Since then, the province has been a part of the Canadian federation and has kept its own legislature to deal with provincial matters. The province was named Newfoundland and Labrador on April 1, 1949 . The province has a unicameral Westminster-style parliamentary government, in which the premier is the leader of the party that controls the most seats in the House of Assembly. The premier is Newfoundland and Labrador's head of government, and the king of Canada is its head of state and is represented by the lieutenant governor of Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of Newfoundland And Labrador
The flag of Newfoundland and Labrador was introduced in 1980 and was designed by Newfoundland artist Christopher Pratt. The flag design was approved by the Newfoundland and Labrador House of Assembly, House of Assembly of the province of Newfoundland and Labrador, Newfoundland, Canada, on May 28, 1980. It was flown for the first time on Discovery Day#Canada, Discovery Day, June 24, 1980. The name of the province was changed to Newfoundland and Labrador by an amendment to the constitution of Canada in December 2001 at the request of the provincial legislature. Design Symbolism The design was chosen due to its broad symbolism. The blue (pantone 2955C) represents the waters of the sea, lakes and rivers; the white represents snow and ice; the red (pantone 200C) represents human effort, and the yellow gold (pantone 137C) symbolizes the confidence the people of Newfoundland and Labrador have in themselves and for the future. The flag design is that of etchings on Beothuk and Innu decor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Newfoundland And Labrador General Elections
This article provides a summary of results for the general elections to the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador's unicameral legislative body, the Newfoundland and Labrador House of Assembly. The number of seats has varied over time, from a low of twenty-seven for the first election in 1949, to a high of fifty-two during the 1980s and early 1990s. There are currently 40 seats in the house. The chart on the right shows the information graphically, with the most recent elections on the right. It shows that politics in Newfoundland and Labrador have been dominated by two parties: the Liberal party (red) and the Conservative party (blue). The Liberal party have won ten out of the seventeen elections held. This article only covers elections since the province became part of the Canadian Confederation in 1949. It was then named ''Newfoundland'', and its official name changed to ''Newfoundland and Labrador'' in 2001. Prior to becoming part of Canada, Newfoundland was a Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Washington (1871)
The Treaty of Washington was a treaty signed and ratified by the United Kingdom and the United States in 1871 during the first premiership of William Gladstone and the presidency of Ulysses S. Grant. It settled various disputes between the countries, including the ''Alabama'' Claims for damages to American shipping caused by British-built warships, as well as illegal fishing in Canadian waters and British civilian losses in the American Civil War. It inaugurated permanent peaceful relations between the United States and Canada, and United States and Britain. After the arbitrators endorsed the American position in 1872, Britain settled the matter by paying the United States $15.5 million (approximately $ million in ), ending the dispute and leading to a treaty that restored friendly relations between Britain and the United States. That international arbitration established a precedent, and the case aroused interest in codifying public international law. Background In early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Newfoundland Constabulary
The Royal Newfoundland Constabulary (RNC) is the provincial police service for the province of Newfoundland and Labrador. The Royal Newfoundland Constabulary is one of three provincial police forces in Canada, alongside the Ontario Provincial Police and the Sûreté du Québec. Uniquely, the responsibility policing in Newfoundland and Labrador is not granted to municipalities — in Ontario and Quebec, the provincial police provide frontline police services only to extraordinarily small communities or at the request of a municipal council; in Newfoundland and Labrador, the Constabulary operates in all communities by default. Since 1949, the Royal Canadian Mounted Police have provided police services in the province's rural interior, in place of the RNC. History The first police constables in Newfoundland and Labrador were appointed by Governor Henry Osborn to six separate judicial districts in 1729. In the 19th century, the RNC was modeled after the Royal Irish Constabulary wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Fox Bennett
Charles James Fox Bennett (11 June 1793 in Shaftesbury, England – 5 December 1883) was a merchant and politician who successfully fought attempts to take Newfoundland into Canadian confederation. Bennett was a successful businessman and one of the colony's richest residents with interests in the fisheries, distillery and brewery industry and shipbuilding. His brother Thomas Bennett, a magistrate and member of Newfoundland's first House of Assembly, was a partner in the business. Bennett became involved in politics in the 1840s as a leader of the colony's Anglican community and an opponent of responsible government, an argument he lost when an alliance of Catholics and non-Anglican Protestants persuaded the Colonial Office to grant Newfoundland self-government. In the 1860s, he led the Anti-Confederation Party opposing the proposals by Sir Frederick Carter to join Canada. Bennett's party defeated Carter's Conservatives on the Confederation issue in the 1869 elections, all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick Carter
Sir Frederick Bowker Terrington Carter, (February 12, 1819 – March 1, 1900) was a lawyer and Premier of Newfoundland from 1865 to 1870 and from 1874 to 1878. Career Carter was the son of Peter Weston Carter''Volume one, p. 363, Encyclopedia of Newfoundland and Labrador'', . grandson of William Carter and great-grandson of Robert Carter, who was appointed justice of the peace at Ferryland in 1750. In 1855, he was elected to the House of Assembly as a Conservative and was Speaker from 1861 to 1865. In 1865 he succeeded Sir Hugh Hoyles as Prime Minister. Carter was a supporter of Canadian confederation having been a delegate to the 1864 Quebec conference. However, the Conservatives were defeated on the Confederation issue in the November 1869 election by the Anti-Confederation Party led by Charles Fox Bennett. Even though Newfoundland did not join the confederation until 1949, Carter is considered one of the Fathers of Confederation. Carter became Premier a second time in 187 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burin, Newfoundland And Labrador
Burin ( ) is a town on the Burin Peninsula in Placentia Bay, Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. The Burin Peninsula is often affectionately nicknamed "The Boot" due to its resemblance to the footwear when seen on a map, with the town of Burin located near the "heel". Burin is approximately 318 km from the capital of St. John's. Settlement in Burin dates to the early 18th century, although documentary evidence indicates that French fishermen had been fishing and exploring the area even earlier. History Burin was settled as a fishing community, with the earliest known evidence of settlement being in 1718. The town was incorporated in 1950, and included Burin North, Ship Cove and Burin Bay. In 1970, the town limits were expanded and now include Collin's Cove, Path End, Bull's Cove, Black Duck Cove, Long Cove, Green Hill, Little Salmonier, Hollett's Farm, Burin Bay Arm, and Salt Pond. Demographics In the 2021 Census of Population conducted by Statistics Canada, Burin had a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugh Hoyles
Sir Hugh Hoyles (October 17, 1814 – February 1, 1888) was a politician and lawyer who served as the third premier of the colony of Newfoundland. Hoyles was the first premier of Newfoundland to have been born in the colony, and served from 1861 to 1865. Born in St. John's, he was the son of Newman Hoyles, the first leader of the Tory Party. Educated in Nova Scotia Hoyles trained as a lawyer and returned to St John's in 1842, quickly establishing a large and lucrative legal practice. He was eminent in the Natives' Society and the Newfoundland Church Society. Hoyles was elected to the Assembly in 1848. He rapidly became the Conservative leader, opposing responsible government, on the grounds that the colony was not ready for it, and throwing his weight behind Bishop Feild's campaign to divide the Protestant educational grant and put Anglicans on the same footing as Catholics. This proposal alienated Methodists who thereupon voted for the Catholic Liberal Party so that, in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Kent (Newfoundland Politician)
John Kent (1805 – 1 September 1872) arrived in Newfoundland in 1820 and started working for his uncle, Patrick Morris, a successful businessman and entrepreneur. He was elected to the first House of Assembly in 1832 as a Liberal. Kent was a champion of Catholic rights on an island that was then deeply divided along religious lines, which his actions directly exacerbated. He was described in the ''Dictionary of Canadian Biography'' (DCB) as a demagogue who "enjoyed the storm and rode it to his own advantage", a style of politicking later followed in similar fashion by, among others, Edward Murphy Jr. (of Troy, New York) and Richard J. Daley (of Chicago). The DCB states, "Kent's electioneering was a compound of his own strident vitality, intimidation, and clerical influence. Newfoundland in 1832 had virtually universal suffrage under a household franchise, and it was not difficult to secure election by turbulent, and very effective means. Kent was of the school of Reform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip Francis Little
Philip Francis Little (1824 – October 21, 1897) was the first Premier of Newfoundland between 1855 and 1858. He was born in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island. Little studied law there with Charles Young and was admitted to the bar in 1844. He came to Newfoundland in 1846 and articled in law, the first Roman Catholic to practise law in St. John's. His strong views on responsible government, his connections in St. John's Catholic society, and his ability to unite disparate elements of the Liberal Party propelled him to a leadership role in politics. He helped lead the charge for responsible government along with John Kent. After it was granted in 1854, he went on to run a successful campaign as leader of the predominantly Roman Catholic Liberal Party. He became Newfoundland's first Premier in 1855 and served concurrently as the colony's Attorney-General. D.W. Prowse would record that it was, "as near to perfection as possible". With the period of 1855-1857 described ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progressive Conservative Party Of Newfoundland And Labrador
The Progressive Conservative Party of Newfoundland and Labrador is a provincial political party in Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. The party was founded in 1949 and most recently formed the Government of Newfoundland and Labrador from the 2003 general election until the 2015 general election. The party has served as the official opposition to the government of Newfoundland and Labrador since 14 December 2015. On 31 March 2021, MHA David Brazil was appointed interim leader. History Origins The party originated before Newfoundland's confederation with Canada as the Responsible Government League (RGL). The RGL campaigned for responsible government to return to Newfoundland, after being suspended in 1934. In the 1948 referendum, Newfoundland narrowly voted to join Canada as its tenth province. Following the referendum, federal parties started organizing in Newfoundland and most members of the RGL decided to align themselves with the Progressive Conservative Party of Canada, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)