|
List Of Mammals Of Gabon
This is a list of the mammal species recorded in Gabon. Of the mammal species in Gabon, four are endangered, nine are vulnerable, and seven are near threatened. The following tags are used to highlight each species' conservation status as assessed by the International Union for Conservation of Nature: Some species were assessed using an earlier set of criteria. Species assessed using this system have the following instead of near threatened and least concern categories: Order: Afrosoricida (tenrecs and golden moles) The order Afrosoricida contains the golden moles of southern Africa and the tenrecs of Madagascar and Africa, two families of small mammals that were traditionally part of the order Insectivora. *Family: Tenrecidae (tenrecs) **Subfamily: Potamogalinae ***Genus: ''Potamogale'' **** Giant otter shrew, ''Potamogale velox'' LC Order: Hyracoidea (hyraxes) The hyraxes are any of four species of fairly small, thickset, herbivorous mammals in the order Hyracoidea. Ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gabon
Gabon (; ; snq, Ngabu), officially the Gabonese Republic (french: République gabonaise), is a country on the west coast of Central Africa. Located on the equator, it is bordered by Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the north, the Republic of the Congo on the east and south, and the Gulf of Guinea to the west. It has an area of nearly and its population is estimated at million people. There are coastal plains, mountains (the Cristal Mountains and the Chaillu Massif in the centre), and a savanna in the east. Since its independence from France in 1960, the sovereign state of Gabon has had three presidents. In the 1990s, it introduced a multi-party system and a democratic constitution that aimed for a more transparent electoral process and reformed some governmental institutions. With petroleum and foreign private investment, it has the fourth highest HDI in the region (after Mauritius, Seychelles and South Africa) and the fifth highest GDP per capita (PPP) i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Forest Elephant
The African forest elephant (''Loxodonta cyclotis'') is one of the two living African elephant species. It is native to humid forests in West Africa and the Congo Basin. It is the smallest of the three living elephant species, reaching a shoulder height of . Both sexes have straight, down-pointing tusks, which erupt when they are 1–3 years old. It lives in family groups of up to 20 individuals. Since it forages on leaves, seeds, fruit, and tree bark, it has been referred to as the 'megagardener of the forest'. It contributes significantly to maintain the composition and structure of the Guinean Forests of West Africa and the Congolese rainforests. The first scientific description of the species was published in 1900. During the 20th century, overhunting caused a sharp decline in population, and by 2013 it was estimated that less than 30,000 individuals remained. It is threatened by habitat loss, fragmentation, and poaching. The conservation status of populations varies across ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
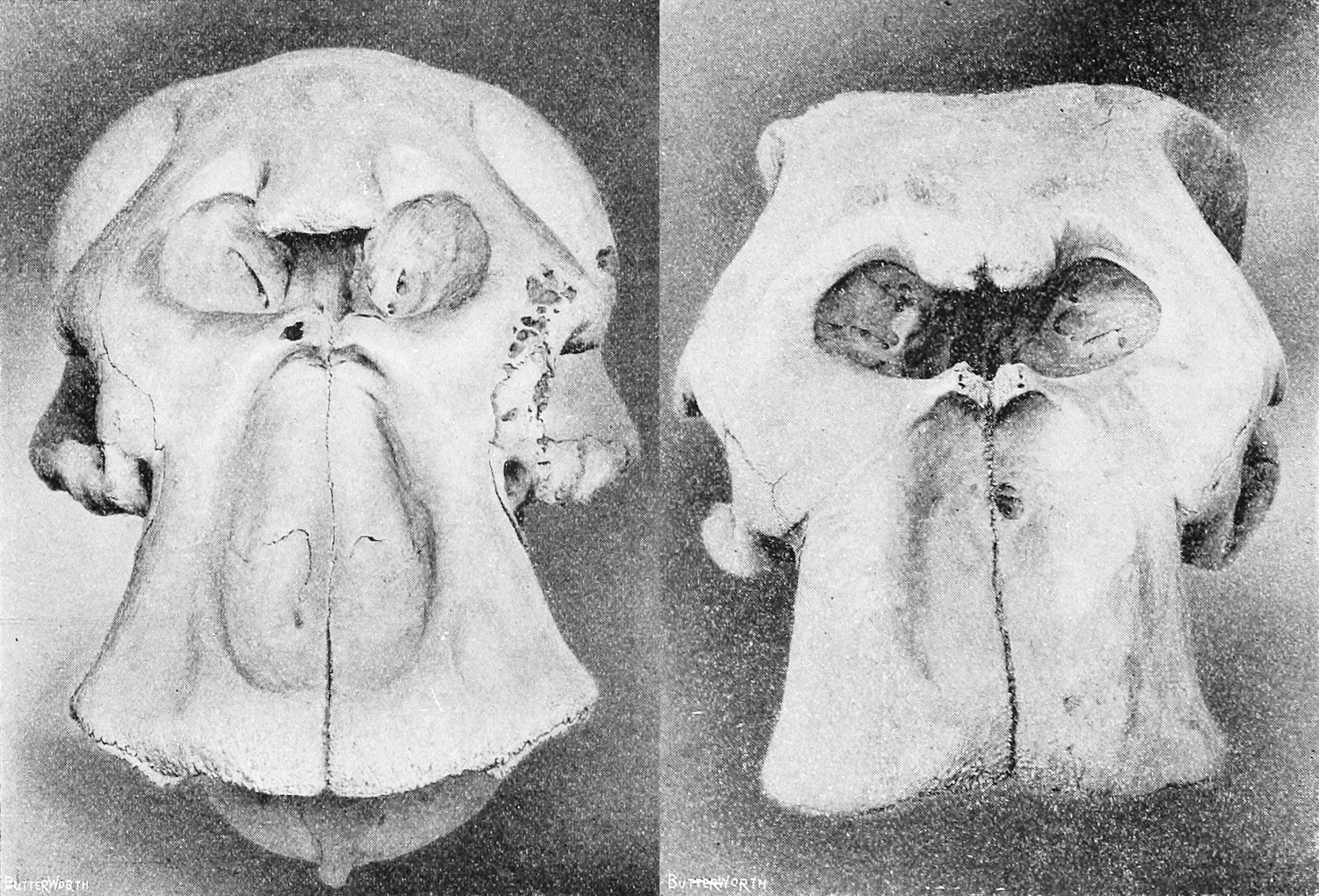
Tarsier
Tarsiers ( ) are haplorhine primates of the family Tarsiidae, which is itself the lone extant family within the infraorder Tarsiiformes. Although the group was once more widespread, all of its species living today are found in Maritime Southeast Asia, specifically the Philippines, Malaysia, Indonesia, and Brunei.They are found primarily in forested habitats, especially forests that have liana, since the vine gives tarsiers vertical support when climbing trees. Evolutionary history Fossil record Fossils of tarsiiform primates are found in Asia, Europe, and North America, with disputed fossils from Africa, but extant tarsiers are restricted to several Southeast Asian islands in Indonesia, Philippines, and Malaysia. The fossil record indicates that their dentition has not changed much, except in size, in the past 45 million years. Within the family Tarsiidae, there are two extinct genera, '' Xanthorhysis'' and ''Afrotarsius''. However, the placement of ''Afrotarsius'' is not ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorisoidea
Lorisoidea is a superfamily of nocturnal primates found throughout Africa and Asia. Members include the galagos and the lorisids. As strepsirrhines, lorisoids are related to the lemurs of Madagascar and are sometimes included in the infraorder Lemuriformes, although they are also sometimes placed in their own infraorder, Lorisiformes Gregory, 1915. Classification * Order Primates ** Suborder Strepsirrhini *** Infraorder †Adapiformes *** Infraorder Lemuriformes **** Superfamily Lemuroidea: lemurs **** Superfamily Lorisoidea ***** Family Lorisidae: lorises, pottos, and angwantibos ***** Family Galagidae: galagos ** Suborder Haplorhini Haplorhini (), the haplorhines (Greek for "simple-nosed") or the "dry-nosed" primates, is a suborder of primates containing the tarsiers and the simians (Simiiformes or anthropoids), as sister of the Strepsirrhini ("moist-nosed"). The name is some ...: tarsiers, monkeys, and apes Notes References * . Mammal superfamilies Taxa na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lemur
Lemurs ( ) (from Latin ''lemures'' – ghosts or spirits) are Strepsirrhini, wet-nosed primates of the Superfamily (biology), superfamily Lemuroidea (), divided into 8 Family (biology), families and consisting of 15 genera and around 100 existing species. They are endemic to the island of Madagascar. Most existing lemurs are small, have a pointed snout, large eyes, and a long tail. They arboreal, chiefly live in trees and nocturnal, are active at night. Lemurs share resemblance with other primates, but evolved independently from monkeys and apes. Due to Madagascar's highly seasonal climate, Evolution of lemurs, lemur evolution has produced a level of species diversity rivaling that of any other primate group. Until shortly after humans arrived on the island around 2,000 years ago, there were lemurs as large as a male gorilla. Most species have been discovered or promoted to full species status since the 1990s; however, lemur Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic classification is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, and language. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structures composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from families and kinship networks to political states. Social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, and rituals, which bolster human society. Its intelligence and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate phenomena have motivated humanity's development of science, philosophy, mythology, religion, and other fields of study. Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus ''Homo'', in common usage, it generally refers to ''Homo sapiens'', the only extant member. Anatomically moder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandrill At San Francisco Zoo
The mandrill (''Mandrillus sphinx'') is a large Old World monkey native to west central Africa. It is one of the most colorful mammals in the world, with red and blue skin on its face and posterior. The species is sexually dimorphic, as males have a larger body, longer canine teeth and brighter coloring. Its closest living relative is the drill with which it shares the genus '' Mandrillus''. Both species were traditionally thought to be baboons, but further evidence has shown that they are more closely related to white-eyelid mangabeys. Mandrills mainly live in tropical rainforests but will also travel across savannas. They are active during the day and spend most of their time on the ground. Their preferred foods are fruit and seeds, but mandrills will consume leaves, piths, mushrooms, and animals from insects to juvenile antelope. Mandrills live in large, stable groups known as "hordes" which can number in the hundreds. Females form the core of these groups, while a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorilla Gorilla04
Gorillas are herbivorous, predominantly ground-dwelling great apes that inhabit the tropical forests of equatorial Africa. The genus ''Gorilla'' is divided into two species: the eastern gorilla and the western gorilla, and either four or five subspecies. The DNA of gorillas is highly similar to that of humans, from 95 to 99% depending on what is included, and they are the next closest living relatives to humans after chimpanzees and bonobos. Gorillas are the largest living primates, reaching heights between 1.25 and 1.8 metres, weights between 100 and 270 kg, and arm spans up to 2.6 metres, depending on species and sex. They tend to live in troops, with the leader being called a silverback. The Eastern gorilla is distinguished from the Western by darker fur colour and some other minor morphological differences. Gorillas tend to live 35–40 years in the wild. The oldest gorilla known is Fatou (b. 1957), who is still alive at the advanced age of 65 years. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primate
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians (monkeys and apes, the latter including humans). Primates arose 85–55 million years ago first from small terrestrial mammals, which adapted to living in the trees of tropical forests: many primate characteristics represent adaptations to life in this challenging environment, including large brains, visual acuity, color vision, a shoulder girdle allowing a large degree of movement in the shoulder joint, and dextrous hands. Primates range in size from Madame Berthe's mouse lemur, which weighs , to the eastern gorilla, weighing over . There are 376–524 species of living primates, depending on which classification is used. New primate species continue to be discovered: over 25 species were described in the 2000s, 36 in the 2010s, and three in the 2020s. Primates have large bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Manatee
The African manatee (''Trichechus senegalensis''), also known as the West African manatee, is a species of manatee that inhabits much of the western region of Africa – from Senegal to Angola. It is the only manatee species to be found in the Old World. Not a great deal is known about ''T. senegalensis.'' Taxonomy The African manatee was officially declared a species under the ''Trichechus senegalensis'' taxon in 1795 by naturalist Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link. No subspecies of this taxon are known. Although African manatees live in both coastal areas and isolated inland areas, genetic evidence suggests no significant differences between the two populations. The African manatee falls under the genus ''Trichechus'' with only two other species, the Amazonian manatee and the West Indian manatee, which are also sirenians. Range and habitat African manatees inhabit the widest ranges of habitats of any sirenian species, ranging from offshore islands in the Atlantic, rivers in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)





.jpg)
