|
List Of Largest Known Cosmic Structures
This is a list of the largest cosmic structures so far discovered. The unit of measurement used is the light-year (distance traveled by light in one Julian year; approximately 9.46 trillion kilometres). This list includes superclusters, galaxy filaments and large quasar groups (LQGs). The list characterizes each structure based on its longest dimension. Note that this list refers only to coupling of matter with defined limits, and not the coupling of matter in general (as per example the cosmic microwave background, which fills the entire universe). All structures in this list are defined as to whether their presiding limits have been identified. There are some speculations about this list: *The Zone of Avoidance, or the part of the sky occupied by the Milky Way, blocks out light to several structures, making their limits imprecisely identified. *Some structures are far too distant to be seen even with the most powerful telescopes. Some factors are included to explain the str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quasar
A quasar is an extremely luminous active galactic nucleus (AGN). It is pronounced , and sometimes known as a quasi-stellar object, abbreviated QSO. This emission from a galaxy nucleus is powered by a supermassive black hole with a mass ranging from millions to tens of billions of solar masses, surrounded by a gaseous accretion disc. Gas in the disc falling towards the black hole heats up because of friction and releases energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation. The radiant energy of quasars is enormous; the most powerful quasars have luminosities thousands of times greater than that of a galaxy such as the Milky Way. Usually, quasars are categorized as a subclass of the more general category of AGN. The redshifts of quasars are of cosmological origin. The term originated as a contraction of "quasi-stellar '' tar-like' radio source"—because quasars were first identified during the 1950s as sources of radio-wave emission of unknown physical origin—and when ident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
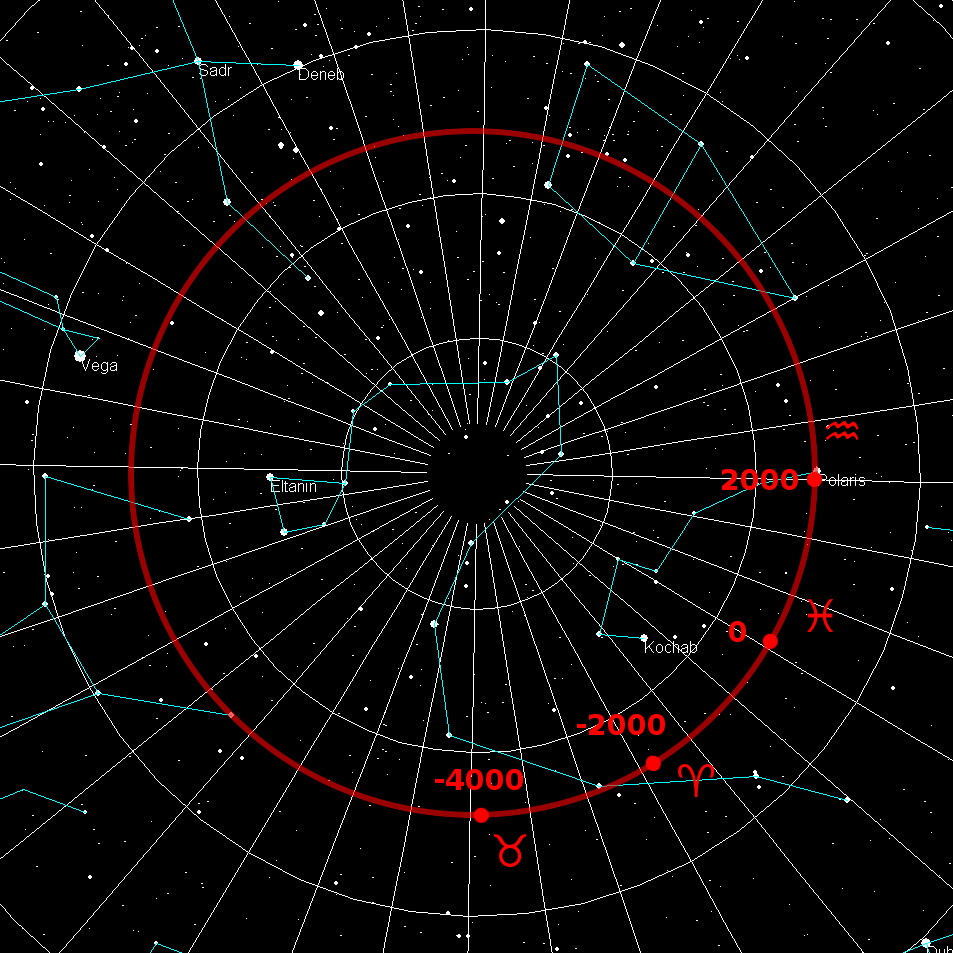
Celestial Pole
The north and south celestial poles are the two points in the sky where Earth's axis of rotation, indefinitely extended, intersects the celestial sphere. The north and south celestial poles appear permanently directly overhead to observers at Earth's North Pole and South Pole, respectively. As Earth spins on its axis, the two celestial poles remain fixed in the sky, and all other celestial points appear to rotate around them, completing one circuit per day (strictly, per sidereal day). The celestial poles are also the poles of the celestial equatorial coordinate system, meaning they have declinations of +90 degrees and −90 degrees (for the north and south celestial poles, respectively). Despite their apparently fixed positions, the celestial poles in the long term do not actually remain permanently fixed against the background of the stars. Because of a phenomenon known as the precession of the equinoxes, the poles trace out circles on the celestial sphere, with a per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Live Science
Live Science is a science news website run by Future via Purch, which it purchased from Imaginova in 2009. Stories and editorial commentary are typically syndicated to major news outlets, such as Yahoo!, MSNBC, AOL, and Fox News.{{fact, date=March 2020 Live Science was originally launched in 2004, but was subsequently shut down and re-launched in 2007. Live Science covers scientific breakthroughs, research ventures and odd facts from around the world in an online newsmagazine format. Purch consumer brands (including Live Science) were acquired by Future in 2018.{{Cite web , url=https://www.futureplc.com/brand/live-science/ , title=Live Science , work=Future plc Future plc is an international multimedia company established in the United Kingdom in 1985. The company has over 220 brands that span magazines, newsletters, websites, and events in fields such as video games, technology, films, music, photogr ... , access-date=18 December 2018 References {{reflist External li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid digital subscribers. It also is a producer of popular podcasts such as '' The Daily''. Founded in 1851 by Henry Jarvis Raymond and George Jones, it was initially published by Raymond, Jones & Company. The ''Times'' has won 132 Pulitzer Prizes, the most of any newspaper, and has long been regarded as a national "newspaper of record". For print it is ranked 18th in the world by circulation and 3rd in the U.S. The paper is owned by the New York Times Company, which is publicly traded. It has been governed by the Sulzberger family since 1896, through a dual-class share structure after its shares became publicly traded. A. G. Sulzberger, the paper's publisher and the company's chairman, is the fifth generation of the family to head the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Hawaii
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. The first universities in Europe were established by Catholic Church monks. The University of Bologna (), Italy, which was founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *being a high degree-awarding institute. *using the word ''universitas'' (which was coined at its foundation). *having independence from the ecclesiastic schools and issuing secular as well as non-secular degrees (with teaching conducted by both clergy and non-clergy): grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law, notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university in medieval life, 1179–1499", McFarland, 2008, , p. 55f.de Ridder-Symoens, Hil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States and one of the most prestigious and highly ranked universities in the world. The university is composed of ten academic faculties plus Harvard Radcliffe Institute. The Faculty of Arts and Sciences offers study in a wide range of undergraduate and graduate academic disciplines, and other faculties offer only graduate degrees, including professional degrees. Harvard has three main campuses: the Cambridge campus centered on Harvard Yard; an adjoining campus immediately across Charles River in the Allston neighborhood of Boston; and the medical campus in Boston's Longwood Medical Area. Harvard's endowment is valued at $50.9 billion, making it the wealthiest academic institution in the world. Endo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Astrophysical Journal
''The Astrophysical Journal'', often abbreviated ''ApJ'' (pronounced "ap jay") in references and speech, is a peer-reviewed scientific journal of astrophysics and astronomy, established in 1895 by American astronomers George Ellery Hale and James Edward Keeler. The journal discontinued its print edition and became an electronic-only journal in 2015. Since 1953 ''The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series'' (''ApJS'') has been published in conjunction with ''The Astrophysical Journal'', with generally longer articles to supplement the material in the journal. It publishes six volumes per year, with two 280-page issues per volume. ''The Astrophysical Journal Letters'' (''ApJL''), established in 1967 by Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar as Part 2 of ''The Astrophysical Journal'', is now a separate journal focusing on the rapid publication of high-impact astronomical research. The three journals were published by the University of Chicago Press for the American Astronomical Society u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Pole Wall
The South Pole Wall (SPW or The South Pole Wall) is a massive cosmic structure formed by a giant wall of galaxies (a galaxy filament) that extends across at least 1.37 billion light-years of space, the nearest light (and consequently part) of which is aged about half a billion light-years. The structure, in its astronomical angle, is dense in five known places including one very near to the celestial South Pole and is, according to the international team of astronomers that discovered the South Pole Wall, "...the largest contiguous feature in the local volume and comparable to the Sloan Great Wall at half the distance ...". Its discovery was announced by Daniel Pomarède of Paris-Saclay University and R. Brent Tully and colleagues of the University of Hawaiʻi in July 2020. Pomarède explained, "One might wonder how such a large and not-so distant structure remained unnoticed. This is due to its location in a region of the sky that has not been completely surveyed, and where di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sloan Digital Sky Survey
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey or SDSS is a major multi-spectral imaging and spectroscopic redshift survey using a dedicated 2.5-m wide-angle optical telescope at Apache Point Observatory in New Mexico, United States. The project began in 2000 and was named after the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation, which contributed significant funding. A consortium of the University of Washington and Princeton University was established to conduct a redshift survey. The Astrophysical Research Consortium (ARC) was established in 1984 with the additional participation of New Mexico State University and Washington State University to manage activities at Apache Point. In 1991 the Sloan Foundation granted the ARC funding for survey efforts and the construction of equipment to carry out the work.. Background At the time of its design, the SDSS was a pioneering combination of novel instrumentation as well as data reduction and storage techniques that drove major advances in astronomical observations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2dF Galaxy Redshift Survey
In astronomy, the 2dF Galaxy Redshift Survey (Two-degree-Field Galaxy Redshift Survey), 2dF or 2dFGRS is a redshift survey conducted by the Australian Astronomical Observatory (AAO) with the 3.9m Anglo-Australian Telescope between 1997 and 11 April 2002. The data from this survey were made public on 30 June 2003. The survey determined the large-scale structure in two large slices of the Universe to a depth of around 2.5 billion light years ( redshift ~ 0.2). It was the world's largest redshift survey between 1998 (overtaking Las Campanas Redshift Survey) and 2003 (overtaken by the Sloan Digital Sky Survey). Matthew Colless, Richard Ellis, Steve Maddox and John Peacock were in charge of the project. Team members Shaun Cole and John Peacock were awarded a share of the 2014 Shaw Prize in astronomy for results from the 2dFGRS. Description The 2dF survey covered an area of about 1500 square degrees, surveying regions in both the north and the south galactic poles. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sloan Great Wall
The Sloan Great Wall (SGW) is a cosmic structure formed by a giant wall of galaxies (a galaxy filament). Its discovery was announced from Princeton University on October 20, 2003, by J. Richard Gott III, Mario Jurić, and their colleagues, based on data from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. Size The wall measures in length, located approximately one billion light-years away. In the sky, it is located within the region of the constellations Corvus, Hydra and Centaurus. It is approximately 1/60 of the diameter of the observable universe, making it the sixth largest known object after the large quasar groups Clowes-Campusano LQG, U1.11, Huge-LQG, the Giant GRB Ring and the galaxy filament Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall (Her-CrB GW), respectively. The Sloan Great Wall is between 1.8–2.7 times longer than the CfA2 Great Wall of galaxies (discovered by Margaret Geller and John Huchra of Harvard in 1989). It also contains several galactic supercluster A supercluster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)



