|
List Of Languages By Time Of Extinction
An extinct language may be narrowly defined as a language with no native speakers and no Genetic relationship (linguistics), descendant languages. Under this definition, a language becomes extinct upon the death of its last native speaker, the terminal speaker. A language like Latin is not extinct in this sense, because it evolved into the modern Romance languages; it is impossible to state when Latin became extinct because there is a diachronic continuum (compare Dialect continuum, synchronic continuum) between ancestors Late Latin and Vulgar Latin on the one hand and descendants like Old French and Old Italian on the other; any cutoff date for distinguishing ancestor from descendant is arbitrary. For many languages which have become extinct in recent centuries, attestation of usage is datable in the historical record, and sometimes the terminal speaker is identifiable. In other cases, historians and historical linguistics, historical linguists may infer an estimated date of exti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinct Language
An extinct language or dead language is a language with no living native speakers. A dormant language is a dead language that still serves as a symbol of ethnic identity to an ethnic group; these languages are often undergoing a process of revitalisation. Languages that have first-language speakers are known as modern or living languages to contrast them with dead languages, especially in educational contexts. Languages have typically become extinct as a result of the process of cultural assimilation leading to language shift, and the gradual abandonment of a native language in favor of a foreign ''lingua franca''. As of the 2000s, a total of roughly 7,000 natively spoken languages existed worldwide. Most of these are minor languages in danger of extinction; one estimate published in 2004 expected that some 90% of the languages spoken at that time will have become extinct by 2050. Language death Normally the transition from a spoken to an extinct language occurs when a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austronesian Languages
The Austronesian languages ( ) are a language family widely spoken throughout Maritime Southeast Asia, parts of Mainland Southeast Asia, Madagascar, the islands of the Pacific Ocean and Taiwan (by Taiwanese indigenous peoples). They are spoken by about 328 million people (4.4% of the world population). This makes it the fifth-largest language family by number of speakers. Major Austronesian languages include Malay (around 250–270 million in Indonesia alone in its own literary standard named " Indonesian"), Javanese, Sundanese, Tagalog (standardized as Filipino), Malagasy and Cebuano. According to some estimates, the family contains 1,257 languages, which is the second most of any language family. In 1706, the Dutch scholar Adriaan Reland first observed similarities between the languages spoken in the Malay Archipelago and by peoples on islands in the Pacific Ocean. In the 19th century, researchers (e.g. Wilhelm von Humboldt, Herman van der Tuuk) started to apply the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleut Language
Aleut ( ) or is the language spoken by the Aleut living in the Aleutian Islands, Pribilof Islands, Commander Islands, and the Alaska Peninsula (in Aleut , the origin of the state name Alaska). Aleut is the sole language in the Aleut branch of the Eskimo–Aleut languages, Eskimo–Aleut language family. The Aleut language consists of three dialects, including (Eastern Aleut), / (Atka Aleut), and / (Western Aleut, now extinct). Various sources estimate there are fewer than 100 to 150 remaining active Aleut speakers. Because of this, Eastern and Atkan Aleut are classified as "critically endangered and extinct" and have an Expanded Graded Intergenerational Disruption Scale (EGIDS) rating of 7. The task of revitalizing Aleut has largely been left to local government and community organizations. The overwhelming majority of schools in the historically Aleut-speaking regions lack any language/culture courses in their curriculum, and those that do fail to produce fluent or even profi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixed Language
A mixed language, also referred to as a hybrid language or fusion language, is a type of contact language that arises among a bilingual group combining aspects of two or more languages but not clearly deriving primarily from any single language. It differs from a creole language, creole or pidgin, pidgin language in that, whereas creoles/pidgins arise where speakers of many languages acquire a common language, a mixed language typically arises in a population that is fluent in both of the source languages. Because all languages show some degree of mixing by virtue of containing Loanword, loanwords, it is a matter of controversy whether the concept of a mixed language can meaningfully be distinguished from the type of contact and borrowing seen in all languages.Arends et al. 1994 Scholars debate to what extent language mixture can be distinguished from other mechanisms such as code-switching, Stratum (linguistics), substrata, or lexical borrowing. Definitions Other terms used in l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mednyj Aleut Language
Mednyj Aleut (also called Copper Island Creole or Copper Island Aleut) was a mixed language spoken on Bering Island. Mednyj Aleut is characterized by a blending of Russian and Aleut (primarily Attu) elements in most components of the grammar, but most profoundly in the verbal morphology. The Aleut component comprises the majority of the vocabulary, all the derivational morphology, part of the simple sentence syntax, nominal inflection and certain other grammatical means. The Russian components comprise verbal inflection, negation, infinitive forms, part of the simple sentence syntax and all of the compound sentence syntax. History Originally, the language was spoken by Alaskan Creoles on Copper Island, from where it takes its name. The Alaskan Creoles are the descendants of ''promyshlenniki'' men employed by the Russian-American Company (RAC) and Aleut and Alutiiq women, and formed a small but influential population in Russian Alaska. They were bilingual in Russian and Aleut, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington (state)
Washington, officially the State of Washington, is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is often referred to as Washington State to distinguish it from Washington, D.C., the national capital, both named after George Washington (the first President of the United States, U.S. president). Washington borders the Pacific Ocean to the west, Oregon to the south, Idaho to the east, and shares Canada–United States border, an international border with the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of British Columbia to the north. Olympia, Washington, Olympia is the List of capitals in the United States, state capital, and the most populous city is Seattle. Washington is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 18th-largest state, with an area of , and the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 13th-most populous state, with a population of just less than 8 million. The majority of Washington's residents live ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salishan
The Salishan languages ( ), also known as the Salish languages ( ), are a family of languages found in the Pacific Northwest in North America, namely the Canadian province of British Columbia and the American states of Washington, Oregon, Idaho, and Montana. They are characterised by agglutinativity and syllabic consonants. For instance the Nuxalk word (), meaning 'he had had n his possessiona bunchberry plant', has twelve obstruent consonants in a row with no phonetic or phonemic vowels. The Salishan languages are a geographically contiguous block, with the exception of the Nuxalk (Bella Coola), in the Central Coast of British Columbia, and the extinct Tillamook language, to the south on the central coast of Oregon. The terms ''Salish'' and ''Salishan'' are used interchangeably by linguists and anthropologists. The name ''Salish'' or ''Selisch'' is the endonym of the Flathead Nation. Linguists later applied the name Salish to related languages in the Pacific Northwest. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbia-Moses Language
Moses-Columbia, or Columbia-Wenatchi (in Moses-Columbia: Nxaʔamxcín), is an extinct Southern Interior Salish language, also known as ''Nxaảmxcín''. Speakers traditionally lived in the Colville Indian Reservation. The Columbia people were followers of Chief Moses. There were two dialects, Columbia (Sinkiuse, Columbian) and Wenatchi (Wenatchee, Entiat, Chelan). Wenatchi was the heritage language of the Wenatchi, Chelan, and Entiat tribes The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide use of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. The definition is contested, in part due to conflict ..., Columbian of the Sinkiuse-Columbia. Pauline Stensgar, who died on May 2, 2023 at age 96, is reported to have been the last known fully fluent speaker. Phonology Phonological inventory of the Columbia-Wenatchi dialect: The three vowels in Moses-Columbia are /i/, /a/, /u/. They are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
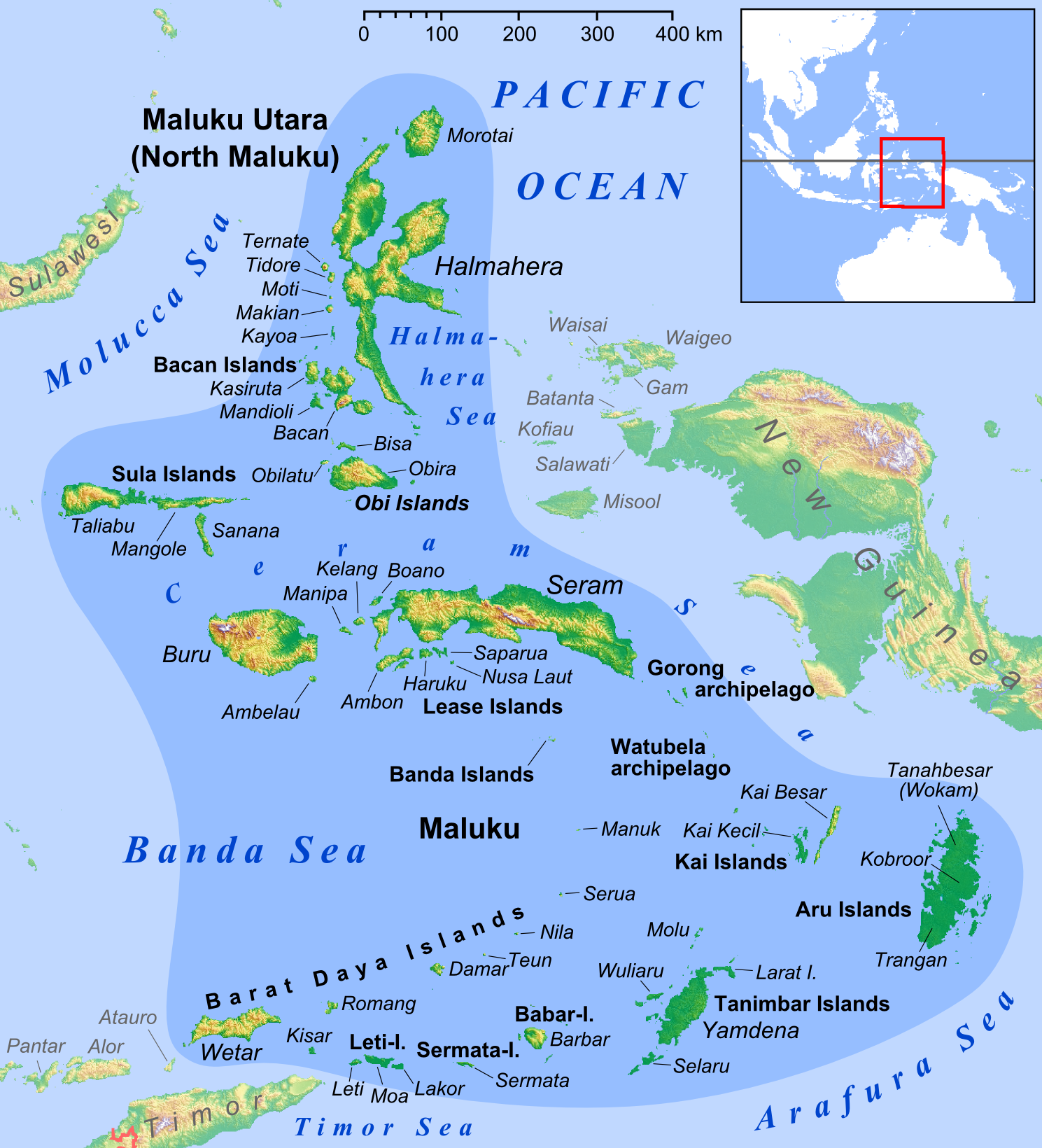
Maluku (province)
Maluku is located in Eastern Indonesia and geographically located in West-Melanesia, between Sulawesi and Western New Guinea, and comprises the central and southern regions of the Maluku Islands. It is directly adjacent to North Maluku, Southwest Papua, and West Papua (province), West Papua in the north, Central Sulawesi, and Southeast Sulawesi in the west, the Banda Sea, Australia, Timor-Leste and East Nusa Tenggara in the south and the Arafura Sea, Central Papua and South Papua in the east. The land area is 46,158.26 km2, and the total population of this province at the 2010 census was 1,533,506 people,Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011. rising to 1,848,923 at the 2020 census,Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2021. the official estimate as at mid 2024 was 1,945,648 (comprising 983,943 males and 961,705 females).Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 28 February 2025, ''Provinsi Maluku Dalam Angka 2025'' (Katalog-BPS 1102001.81) The largest city and capital of Maluku province is A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luhu Language
Luhu was an Austronesian language spoken in the west of Seram Island in eastern Indonesia. It was spoken in Luhu village on Hoamoal Peninsula at the western end of Seram, and in Boano and Kelang islands, off the western tip of Seram Island. The northernmost dialect, Piru, was separated from the rest of the language through colonial depopulation, and was influenced by neighboring languages as it became moribund Moribund refers to a literal or figurative state near death. Moribund may refer to: * ''Moribund'' (album), a 2006 album by the Norwegian black metal band Koldbrann * " Le Moribond", a song by Jacques Brel known in English as "Seasons in the Sun .... In 1989, there were an estimated 3,500 native speakers, but by 2024, the language had gone extinct. References Central Maluku languages Seram Island {{au-lang-stub Extinct languages of Indonesia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwest Papuan Languages
The Northwest Papuan languages are a proposed language family of Papuan languages. Many of the constituent branches of Northwest Papuan were first proposed to be related by H.K.J. Cowan in the 1950s. Voorhoeve (1971) connected the Border and Tor families. Using only pronouns as a diagnostic, Malcolm Ross linked most of the western (Foja Range) branch of the family, which is now fairly secure. The current form of the proposal was worked out by Timothy Usher under the name "North(west) New Guinea" (not to be confused with the proposed North New Guinea branch of the Austronesian language family). It is not yet certain, however, that the similarities in vocabulary between Foja Range and the other constituent families are due to inheritance rather than borrowing. Languages * Fas * Sentani * Border (Upper Tami) * Sko * Foja Range ** Nimboran ** Kwerbic **'' Mawes'' ** Orya–Tor The western branch, Foja Range, is equivalent to Ross's Tor–Kwerba family with the addition of Nimbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mawes Language
Mawes is a recently extinct Papuan language of Indonesia. Usher (2020) proposes that it may be related to the Kwerbic languages. Foley (2018) classifies Mawes as a language isolate A language isolate is a language that has no demonstrable genetic relationship with any other languages. Basque in Europe, Ainu and Burushaski in Asia, Sandawe in Africa, Haida and Zuni in North America, Kanoê in South America, and Tiwi ..., and so does Hammarström (2010). It had 850 native speakers in 2006, but was extinct by 2024. Pronouns Pronouns are: : Basic vocabulary Basic vocabulary of Mawes listed in Foley (2018): : The following basic vocabulary words are from Voorhoeve (1975), as cited in the Trans-New Guinea database: : Sentences Of the few sentences that have been documented for Mawes, some example sentences are: Further reading *Wambaliau, Theresia. 2006. ''Survey Report on the Mawes Language in Papua, Indonesia''. (in Indonesian). Unpublished manuscr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |