|
List Of Destroyer Classes
This is a list of destroyer classes. Argentina (Armada de la República Argentina) * ''Catamarca'' class — 2 ships * ''La Plata'' class — 2 ships * ''Cervantes'' class — 2 ships, ex- ''Churruca'' class * ''Mendoza'' class — 3 ships * ''Buenos Aires'' class — 7 ships, improved G class * ''Almirante Domecq García'' class — 5 ships, ex- ''Fletcher'' class * ''Seguí'' class — 3 ships, ex- ''Allen M. Sumner'' class * ''Comodoro Py'' class — 1 ship, ex- ''Gearing'' class * ''Hercules'' class — 2 ships (same as UK's Type 42 Batch 1) * ''Almirante Brown'' class — 4 ships, MEKO 360 H2 Australia (Royal Australian Navy) * River class — 6 ships * Anzac class — 1 ship * ''Stalwart'' class — 5 ships * V and W class — 4 ships * ''Scott'' class — 1 ship * ''Nizam'' class — 5 ships * ''Arunta'' class — 3 ships * ''Quadrant'' class — 5 ships * Battle class — 2 ships * ''Daring'' class — 3 ships * ''Perth'' class — 3 ships * ''Hobart'' class — 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Destroyer
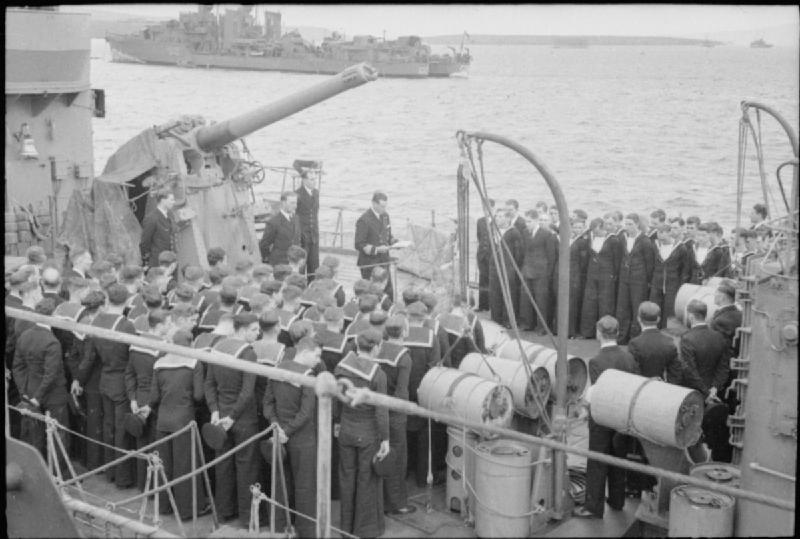
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, manoeuvrable, long-endurance warship intended to escort larger vessels in a fleet, convoy or battle group and defend them against powerful short range attackers. They were originally developed in 1885 by Fernando Villaamil for the Spanish NavySmith, Charles Edgar: ''A short history of naval and marine engineering.'' Babcock & Wilcox, ltd. at the University Press, 1937, page 263 as a defense against torpedo boats, and by the time of the Russo-Japanese War in 1904, these "torpedo boat destroyers" (TBDs) were "large, swift, and powerfully armed torpedo boats designed to destroy other torpedo boats". Although the term "destroyer" had been used interchangeably with "TBD" and "torpedo boat destroyer" by navies since 1892, the term "torpedo boat destroyer" had been generally shortened to simply "destroyer" by nearly all navies by the First World War. Before World War II, destroyers were light vessels with little endurance for unat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
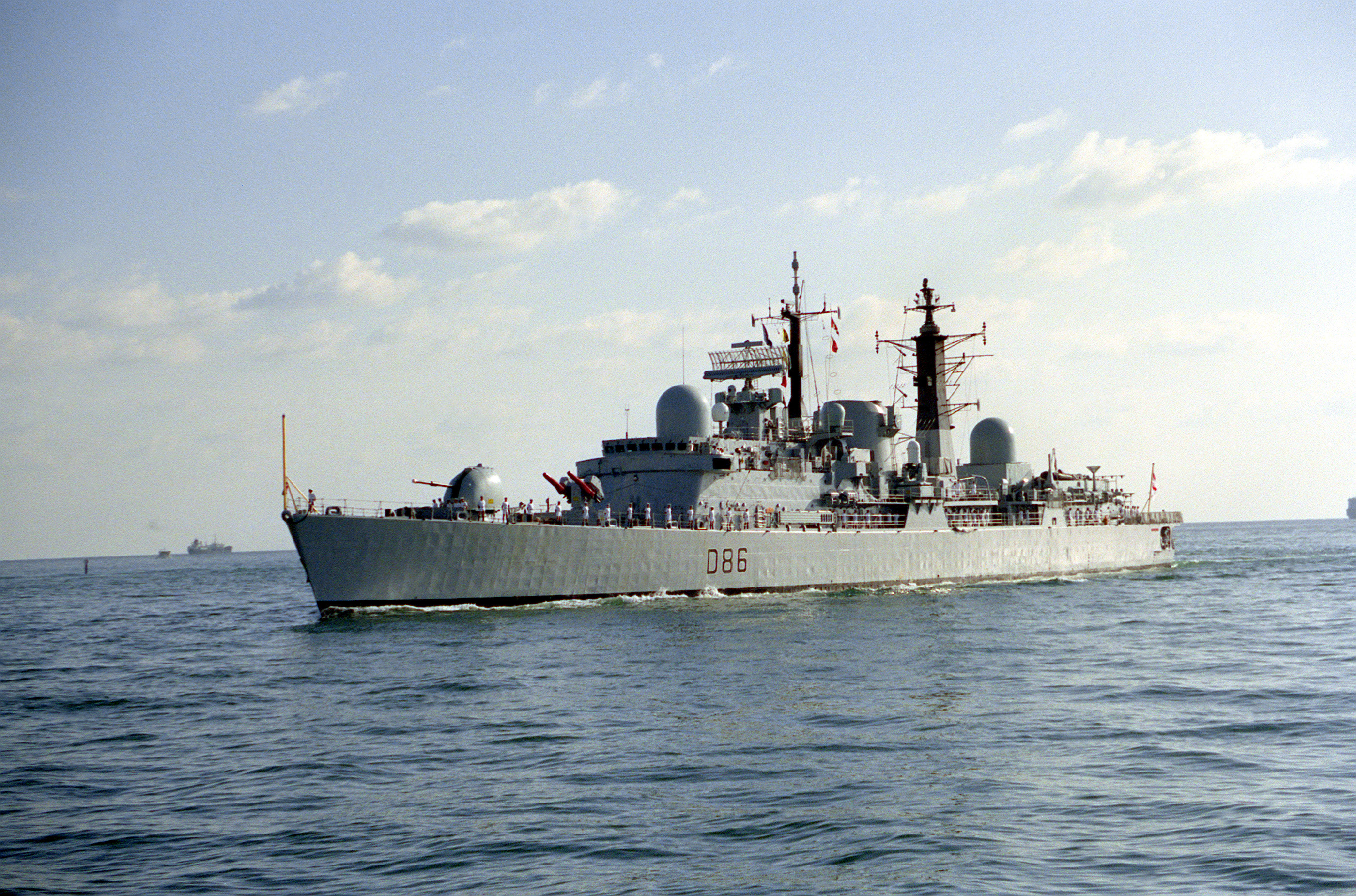
Type 42 Destroyer
The Type 42 or ''Sheffield'' class, was a class of fourteen guided-missile destroyers that served in the Royal Navy.Marriott, Leo: ''Royal Navy Destroyers since 1945'', , Ian Allan Ltd, 1989 A further two ships of this class were built for and served with the Argentine Navy. The first ship of the class was ordered in 1968 and launched in 1971. Two of the class (''Sheffield'' and ''Coventry'') were sunk in action during the Falklands War of 1982. The Royal Navy used this class of destroyer for 38 years between 1975 and 2013. No ships of this class remain active in the Royal Navy and one remains in the Argentine Navy. The Royal Navy has replaced them with Type 45 destroyers. History The class was designed in the late 1960s to provide fleet area air defence. In total fourteen vessels were constructed in three batches. In addition to the Royal Navy ships, two more ships were built to the same specifications as the Batch 1 vessels for the Argentine Navy. ''Hércules'' was built i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daring-class Destroyer (1949)
The ''Daring'' class was a class of eleven destroyers built for the Royal Navy (RN) and Royal Australian Navy (RAN). Constructed after World War II, and entering service during the 1950s, eight ships were constructed for the RN, and three ships for the RAN. Two of the RN destroyers were subsequently sold to and served in the Peruvian Navy (MGP). A further eight ships were planned for the RN but were cancelled before construction commenced, while a fourth RAN vessel was begun but was cancelled before launch and broken up on the slipway. The ''Daring''-class ships were both the largest and most heavily armed ships serving in Commonwealth navies to be classified as destroyers. They were intended to fill some of the duties of cruisers, which post WW2 were considered both expensive and obsolete by naval planners, and were briefly officially considered a hybrid type (Darings) before being rated as destroyers. They were also the last destroyers of the RN and RAN to possess guns as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle-class Destroyer
The Battle class were a class of destroyers of the British Royal Navy (RN) and Royal Australian Navy (RAN), named after naval or other battles fought by British or English forces. Built in three groups, the first group were ordered under the 1942 naval estimates. A modified second and third group, together with two ships of an extended design were planned for the 1943 and 1944 estimates. Most of these ships were cancelled when it became apparent that the war was being won and the ships would not be required, although two ships of the third group, ordered for the RAN, were not cancelled and were subsequently completed in Australia. Seven Battles were commissioned before the end of World War II, but only saw action, with the British Pacific Fleet. "1942" or "Early Battle" class The first years of World War II had shown that British destroyers were ill-equipped to deal with concentrated air attacks, and the Royal Navy suffered heavy losses as a result. In 1941 urgent conside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Q And R-class Destroyer
The Q and R class was a class of sixteen War Emergency Programme destroyers ordered for the British Royal Navy in 1940 as the 3rd and 4th Emergency Flotilla. They served as convoy escorts during World War II. Three Q-class ships were transferred to the Royal Australian Navy upon completion, with two further ships being handed over in 1945. ''Roebuck'' had the dubious honour of being launched prematurely by an air raid at Scotts shipyard in Greenock, her partially complete hulk lying submerged in the dockyard for nine months before it was salvaged and completed. Design The Q and R class were repeats of the preceding , but reverted to the larger J-, K- and N-class hull to allow for the inevitable growth in topweight. As they had fewer main guns than the J, K and Ns, some magazine space was replaced by fuel bunkers, allowing for some to be made at , over the of their ancestors. Like the O and Ps, they were armed with what weapons were available; guns on single mountings t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribal-class Destroyer (1936)
The Tribal class, or ''Afridi'' class, were a ship class, class of destroyers built for the Royal Navy, Royal Canadian Navy and Royal Australian Navy that saw service in World War II. Originally conceived during design studies for a light fleet cruiser, the Tribals evolved into fast, powerful destroyers, with greater emphasis on guns over torpedoes than previous destroyers, in response to new designs by Japan, Italy, and Germany. The Tribals were well admired by their crews and the public when they were in service due to their power, often becoming symbols of prestige while in service. As some of the Royal Navy's most modern and powerful escort ships, the Tribal class served with distinction in nearly all theatres of World War II. Only a handful of Royal Navy Tribals survived the war, all of which were subsequently scrapped from hard use, while Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth Tribals continued to serve into the Cold War, serving with distinction in the Korean War. Only on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
J-, K- And N-class Destroyer
The J, K and N class consisted of 24 destroyers built for the Royal Navy beginning in 1938. They were a return to a smaller vessel, with a heavier torpedo armament, after the that emphasised guns over torpedoes. The ships were built in three flotillas or groups, each consisting of eight ships with names beginning with "J", "K" and "N". The flag superior of the pennant numbers changed from "F" to "G" in 1940. The ships were modified throughout their wartime service, particularly their anti-aircraft (AA) guns; they were also fitted with radar. Design history The design was intended as a smaller follow-on from the preceding Tribal class, and incorporated one radical new idea that was a departure from all previous Royal Navy destroyer designs. That was the adoption of a two boiler room layout. This reduced hull length and allowed for a single funnel, both reducing the profile and increasing the arcs of fire of the light anti-aircraft (AA) weapons. However, this also increased v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Admiralty Type Leader
The Admiralty type leader, sometimes known as the ''Scott'' class, were a class of eight destroyer leaders designed and built for the Royal Navy towards the end of World War I. They were named after Scottish historical leaders. The function of a leader was to carry the flag staff of a destroyer flotilla, therefore they were enlarged to carry additional crew, offices and signalling equipment, allowing a fifth gun to be carried. These ships were contemporary with the Thornycroft type leader, distinguishable by their two narrow funnels of equal height, the Thornycroft designs latter having characteristic broad, slab-sided funnels. All except ''Mackay'' and ''Malcolm'' were completed in time for wartime service, ''Scott'' being a war loss. The two final orders – ''Barrington'' and ''Hughes'' – were cancelled with the end of the War; these two had originally been ordered to the Thornycroft leader design. ''Stuart'' was transferred to Australia in 1933. All the remaining ships ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
V And W-class Destroyer
The V and W class was an amalgam of six similar classes of destroyer built for the Royal Navy under the 9th, 10th, 13th and 14th of fourteen War Emergency Programmes during the First World War and generally treated as one class. For their time they were among the most powerful and advanced ships of their type in the world, and set the trend for future British designs. They arrived in time to see service in the First World War. During the interwar period these ships formed the backbone of the Royal Navy's destroyer flotillas until gradually replaced by new construction; by the mid-1930s most had been displaced to the reserve fleet. Most ships survived to make an extensive contribution to the Second World War effort, in the vital role of convoy escort, freeing up more modern ships for fleet action. History The V and W class were the ultimate evolution of British destroyer design in the First World War, embodying the improvements of their predecessors as well as new techno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-class Destroyer (1917)
The S class (initially known as the Modified ''Trenchant'' classMarch, ''op. cit.'' p.215.) was a class of 67 destroyers ordered for the Royal Navy in 1917 under the 11th and 12th Emergency War Programmes. They saw active service in the last months of the First World War and in the Russian and Irish Civil Wars during the early 1920s. Most were relegated to the reserve by the mid-1920s and subsequently scrapped under the terms of the London Naval Treaty. Eleven survivors saw much action during the Second World War. Background In early 1917, the First World War had been going on for two and a half years. Despite the disappointing outcome of the Battle of Jutland the previous year, the British Grand Fleet, consisting of battleships, cruisers, and destroyers and based in northern Scotland, was successfully confining the German surface navy to the German Bight, while enforcing a blockade of German maritime trade with the wider world. In southern North Sea, the Harwich F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parker-class Flotilla Leader
The ''Parker''-class leaders or improved ''Marksman''-class leaders were a class of six destroyer leaders built for the Royal Navy during 1916–17 for World War I service. They were named after famed historical naval leaders, except for ''Anzac'', which was named to honour the Australian and New Zealand Army Corps, and was later transferred to the Royal Australian Navy. They were the last major Royal Navy warships to be ordered with three propeller shafts, a design that was never widely adopted in British warships. Design The ''Parker''s were based on the design of the preceding leaders and shared the same hull design and dimensions. Operations with the ''Marksman'' class and previous leaders indicated several areas for improvement: more freeboard, increased firepower, and relocation of the bridge to a position further aft. On the ''Parker'' class, the bridge was moved aft by reducing the boiler rooms from three to two; instead of the four funnels on the ''Marksman''s, the '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River-class Torpedo-boat Destroyer
The River class was a class of six torpedo-boat destroyers operated by the Royal Australian Navy (RAN). The design was based on a modified version of the British River-class destroyer, 13 of which were planned under the 1904 Naval Estimates, but were cancelled before orders were placed.Friedman, ''British Destroyers'', p. 96 The first batch of three ships was ordered for the Commonwealth Naval Forces in 1909, followed later by a second batch of three a few years later. All six vessels are named after Australian rivers. The Rivers saw service during World War I. Ships of the class participated in the Australian Naval and Military Expeditionary Force capture of German New Guinea, and performed patrols in Australian and Malayan waters. In 1917, the class was deployed as a single unit to the Mediterranean, and assigned to anti-submarine patrols of the Adriatic. The destroyers returned to Australia in 1919, and were placed in reserve. All six ships of the class were disposed of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)