|
List Of Basic Information Technology Topics
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to information technology: Information technology (IT) – microelectronics based combination of computing and telecommunications technology to treat information, including in the acquisition, processing, storage and dissemination of vocal, pictorial, textual and numerical information. It is defined by the Information Technology Association of America (ITAA) as "the study, design, development, implementation, support or management of computer-based information systems, particularly toward software applications and computer hardware." Different names There are different names for this at different periods or through fields. Some of these names are: * ICT – Information and communication technologies * IT – Information technology * DCT – Data Communication & technology * CDT – Creative digital technology * DT – Design & technology * Communication technology Underlying technolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss", ) is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSFETs for logic functions. CMOS technology is used for constructing integrated circuit (IC) chips, including microprocessors, microcontrollers, memory chips (including CMOS BIOS), and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for analog circuits such as image sensors ( CMOS sensors), data converters, RF circuits ( RF CMOS), and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. The CMOS process was originally conceived by Frank Wanlass at Fairchild Semiconductor and presented by Wanlass and Chih-Tang Sah at the International Solid-State Circuits Conference in 1963. Wanlass later filed US patent 3,356,858 for CMOS circuitry and it was granted in 1967. commercialized the technology with the trademar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor Memory
Semiconductor memory is a digital electronic semiconductor device used for digital data storage, such as computer memory. It typically refers to devices in which data is stored within metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) memory cells on a silicon integrated circuit memory chip. There are numerous different types using different semiconductor technologies. The two main types of random-access memory (RAM) are static RAM (SRAM), which uses several transistors per memory cell, and dynamic RAM (DRAM), which uses a transistor and a MOS capacitor per cell. Non-volatile memory (such as EPROM, EEPROM and flash memory) uses floating-gate memory cells, which consist of a single floating-gate transistor per cell. Most types of semiconductor memory have the property of random access, which means that it takes the same amount of time to access any memory location, so data can be efficiently accessed in any random order. This contrasts with data storage media such as hard disks and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Memory
In computing, memory is a device or system that is used to store information for immediate use in a computer or related computer hardware and digital electronic devices. The term ''memory'' is often synonymous with the term '' primary storage'' or ''main memory''. An archaic synonym for memory is store. Computer memory operates at a high speed compared to storage that is slower but less expensive and higher in capacity. Besides storing opened programs, computer memory serves as disk cache and write buffer to improve both reading and writing performance. Operating systems borrow RAM capacity for caching so long as not needed by running software. If needed, contents of the computer memory can be transferred to storage; a common way of doing this is through a memory management technique called '' virtual memory''. Modern memory is implemented as semiconductor memory, where data is stored within memory cells built from MOS transistors and other components on an integrated circ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three-dimensional Integrated Circuit
A three-dimensional integrated circuit (3D IC) is a MOS (metal-oxide semiconductor) integrated circuit (IC) manufactured by stacking as many as 16 or more ICs and interconnecting them vertically using, for instance, through-silicon vias (TSVs) or Cu-Cu connections, so that they behave as a single device to achieve performance improvements at reduced power and smaller footprint than conventional two dimensional processes. The 3D IC is one of several 3D integration schemes that exploit the z-direction to achieve electrical performance benefits in microelectronics and nanoelectronics. 3D integrated circuits can be classified by their level of interconnect hierarchy at the global ( package), intermediate (bond pad) and local (transistor) level. In general, 3D integration is a broad term that includes such technologies as 3D wafer-level packaging (3DWLP); 2.5D and 3D interposer-based integration; 3D stacked ICs (3D-SICs); monolithic 3D ICs; 3D heterogeneous integration; and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planar Process
The planar process is a manufacturing process used in the semiconductor industry to build individual components of a transistor, and in turn, connect those transistors together. It is the primary process by which silicon integrated circuit chips are built. The process utilizes the surface passivation and thermal oxidation methods. The planar process was developed at Fairchild Semiconductor in 1959. Overview The key concept is to view a circuit in its two-dimensional projection (a plane), thus allowing the use of photographic processing concepts such as film negatives to mask the projection of light exposed chemicals. This allows the use of a series of exposures on a substrate (silicon) to create silicon oxide (insulators) or doped regions (conductors). Together with the use of metallization, and the concepts of p–n junction isolation and surface passivation, it is possible to create circuits on a single silicon crystal slice (a wafer) from a monocrystalline silicon boule. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monolithic Integrated Circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors) integrate into a small chip. This results in circuits that are orders of magnitude smaller, faster, and less expensive than those constructed of discrete electronic components. The IC's mass production capability, reliability, and building-block approach to integrated circuit design has ensured the rapid adoption of standardized ICs in place of designs using discrete transistors. ICs are now used in virtually all electronic equipment and have revolutionized the world of electronics. Computers, mobile phones and other home appliances are now inextricable parts of the structure of modern societies, made possible by the small size and low cost of ICs such as modern computer proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hybrid Integrated Circuit
A hybrid integrated circuit (HIC), hybrid microcircuit, hybrid circuit or simply hybrid is a miniaturized electronic circuit constructed of individual devices, such as semiconductor devices (e.g. transistors, diodes or monolithic ICs) and passive components (e.g. resistors, inductors, transformers, and capacitors), bonded to a substrate or printed circuit board (PCB). A PCB having components on a Printed Wiring Board (PWB) is not considered a true hybrid circuit according to the definition of MIL-PRF-38534. Overview " Integrated circuit" as the term is currently used refers to a monolithic IC which differs notably from a HIC in that a HIC is fabricated by inter-connecting a number of components on a substrate whereas an IC's (monolithic) components are fabricated in a series of steps entirely on a single wafer which is then diced into chips. Some hybrid circuits may contain monolithic ICs, particularly Multi-chip module (MCM) hybrid circuits. Hybrid circuits could be e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Transistor count, Large numbers of tiny MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors) integrate into a small chip. This results in circuits that are orders of magnitude smaller, faster, and less expensive than those constructed of discrete electronic components. The IC's mass production capability, reliability, and building-block approach to integrated circuit design has ensured the rapid adoption of standardized ICs in place of designs using discrete transistors. ICs are now used in virtually all electronic equipment and have revolutionized the world of electronics. Computers, mobile phones and other home appliances are now inextricable parts of the structure of modern societies, made possible by the small size and low cost of ICs such as mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thin-film Transistor
A thin-film transistor (TFT) is a special type of field-effect transistor (FET) where the transistor is thin relative to the plane of the device. TFTs are grown on a supporting (but non-conducting) substrate. A common substrate is glass, because the traditional application of TFTs is in liquid-crystal displays (LCDs). This differs from the conventional bulk metal oxide field effect transistor ( MOSFET), where the semiconductor material typically ''is'' the substrate, such as a silicon wafer. Design and Manufacture TFTs can be fabricated with a wide variety of semiconductor materials. Because it is naturally abundant and well understood, amorphous or polycrystalline silicon was historically used as the semiconductor layer. However, because of the low mobility of amorphous silicon and the large device-to-device variations found in polycrystalline silicon, other materials have been studied for use in TFTs. These include cadmium selenide, metal oxides such as indium gallium z ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FinFET
A fin field-effect transistor (FinFET) is a multigate device, a MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor) built on a substrate where the gate is placed on two, three, or four sides of the channel or wrapped around the channel, forming a double or even multi gate structure. These devices have been given the generic name "FinFETs" because the source/drain region forms fins on the silicon surface. The FinFET devices have significantly faster switching times and higher current density than planar CMOS (complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor) technology. FinFET is a type of non-planar transistor, or "3D" transistor. It is the basis for modern nanoelectronic semiconductor device fabrication. Microchips utilizing FinFET gates first became commercialized in the first half of the 2010s, and became the dominant gate design at 14 nm, 10 nm and 7 nm process nodes. It is common for a single FinFET transistor to contain several fins, arranged side by side and all cove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
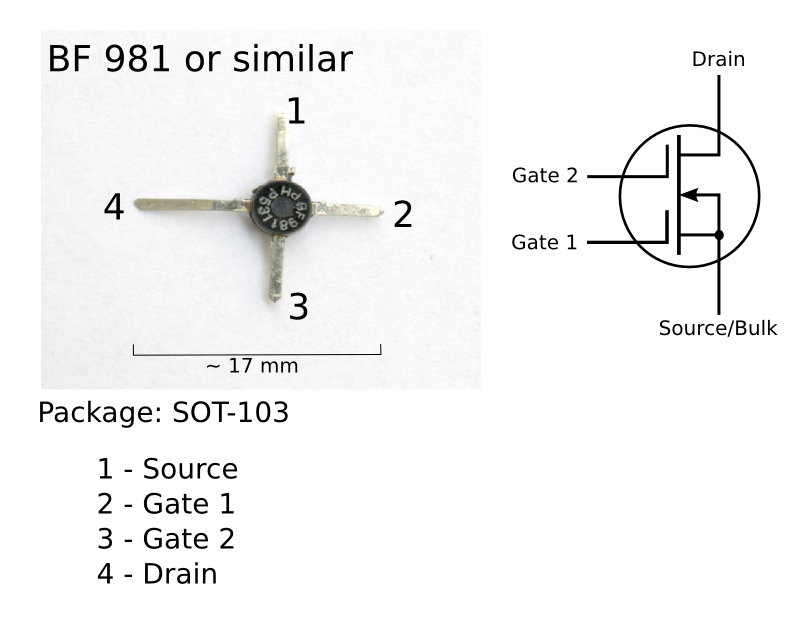
Multi-gate Field-effect Transistor
A multigate device, multi-gate MOSFET or multi-gate field-effect transistor (MuGFET) refers to a metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) that has more than one gate on a single transistor. The multiple gates may be controlled by a single gate electrode, wherein the multiple gate surfaces act electrically as a single gate, or by independent gate electrodes. A multigate device employing independent gate electrodes is sometimes called a multiple-independent-gate field-effect transistor (MIGFET). The most widely used multi-gate devices are the FinFET (fin field-effect transistor) and the GAAFET (gate-all-around field-effect transistor), which are non-planar transistors, or 3D transistors. Multi-gate transistors are one of the several strategies being developed by MOS semiconductor manufacturers to create ever-smaller microprocessors and memory cells, colloquially referred to as extending Moore's law (in its narrow, specific version concerning density scaling, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

.jpg)