|
List Of Spiritualist Organizations
This is a list of notable Spiritualism, Spiritualist organizations: *Agasha Temple of Wisdom *Arthur Findlay College *Camp Chesterfield *International Spiritualist Federation *National Spiritualist Association of Churches *Spiritualist Association of Great Britain *Spiritualists' National Union See also * Spiritualist church External links Spiritualist Churches Spiritualist.tv * * [http://readersandrootworkers.org/wiki/List_of_Spiritualist_Organizations Historical and contemporary international list of Spiritualist Organizations, Associations, and Camps] The New Christian Spiritualists' Society Website Spiritualist organizations, Organizations Lists of organizations {{org-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiritualism
Spiritualism is the metaphysical school of thought opposing physicalism and also is the category of all spiritual beliefs/views (in monism and dualism) from ancient to modern. In the long nineteenth century, Spiritualism (when not lowercase) became most known as a social religious movement according to which the laws of nature and of God include "the continuity of consciousness after the transition of death" and "the possibility of communication between those living on Earth and those who have made the transition". The afterlife, or the " spirit world", is seen by spiritualists not as a static place, but as one in which spirits continue to evolve. These two beliefs—that contact with spirits is possible, and that spirits are more advanced than humans—lead spiritualists to a third belief: that spirits are capable of providing useful insight regarding moral and ethical issues, as well as about the nature of God. Some spiritualists will speak of a concept which they refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agasha Temple Of Wisdom
The Agasha Temple of Wisdom is a spiritualist group founded in 1943 by Richard Zenor. After the publication of James Crenshaw's book ''Telephone Between Two Worlds'' in 1950, in which both Zenor and the temple were prominently featured, the temple became more popular. Upon Zenor's death in 1978, Geary Salvat was chosen to lead the group. References Sources * Leslie Shepard (Editor) ''Encyclopedia of Occultism and Parapsychology Volume 1 A-L'', The Gale Group, 2001 * J. Gordon Melton ''Religious Bodies in the U.S.: A Dictionary'', Routledge, 1992 (although this is a listing only)LeRoy E. Froom, Professor of Historical Theology, Andrews University, ''Occult Forces of Both East and West,'' Ministry, International Journal for Pastors*Gordon Collier ''Make Your Own World'' (3 volumes), Book of Destiny, 1955 (no ISBN) Further reading *Crenshaw, James. ''Telephone Between Two Worlds''. Los Angeles: DeVorss, 1950. *Eisen, William. ''Agasha, Master of Wisdom''. Marina del Rey, Calif.: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Findlay College
Arthur Findlay College is a college of Spiritualism and psychic sciences at Stansted Hall in Stansted Mountfitchet, Essex, England. Stansted Hall was built in 1871, and the college was founded there in 1964. In accordance with Arthur Findlay's wishes, the college building and grounds are administered by the Spiritualists' National Union (SNU). The head offices of SNU at Redwoods are within the college grounds. Course prices include daily meals, tuition and accommodations. History of Stansted Hall Stansted Hall, built in 1871, was given to the Spiritualists' National Union in by J. Arthur Findlay, MBE, JP, a former honorary president of the SNU, and in accordance with his wishes is administered by the Union as a college for the advancement of psychic science.Richmond, Simon. ''How to be a ghostbuster'', The Independent, 27 February 1996 Findlay bought the estate in 1923 upon his retirement from business and first mooted the idea of a spiritualist college at Stansted to the u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camp Chesterfield
Camp Chesterfield was founded in 1891 and is the home of the Indiana Association of Spiritualists, located in Chesterfield, Indiana. Camp Chesterfield offers Spiritualist Church services, seminary, and mediumship, faith healing, and spiritual development classes, as well as psychic readings for patrons. In 2002, the camp was designated a historic district, the "Chesterfield Spiritualist Camp District," and listed on the National Register of Historic Places. History In August 1925, 14 Camp Chesterfield mediums were arrested on charges of obtaining money under false pretences. The charges were filed by a news service reporter who had spent time investigating the camp. In 1960, psychic investigator Andrija Puharich and Tom O'Neill, publisher of the Spiritualist magazine ''Psychic Observer'', arranged to film two seances at Camp Chesterfield using infrared film, intending to procure scientific proof of spirit materializations. The medium was shown the camera beforehand, and w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
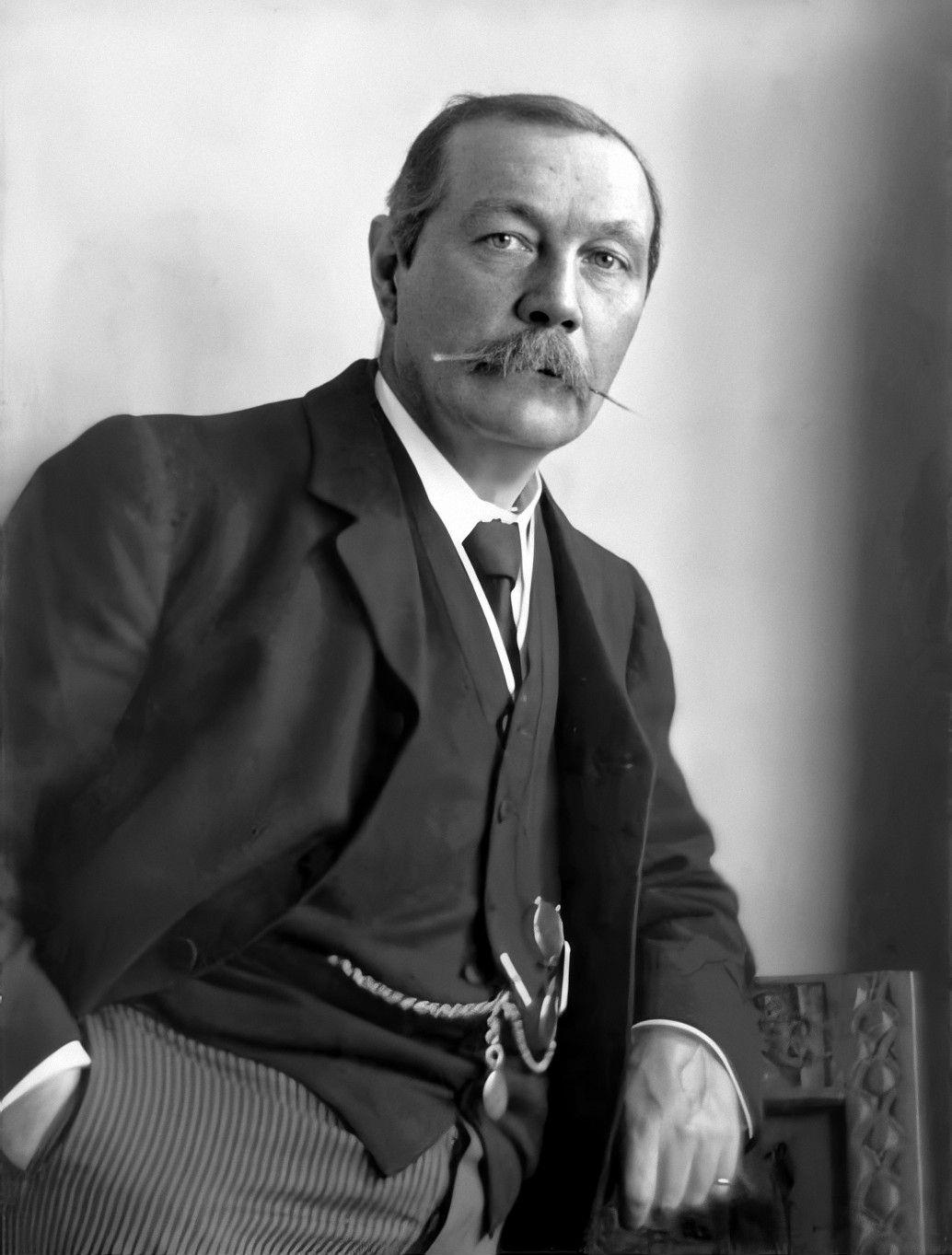
International Spiritualist Federation
The International Spiritualist Federation is a society dedicated to supporting spiritualist churches around the globe, with particular emphasis on those based in countries which do not support spiritualism as a religion. The federation was first proposed at an 1888 conference held in Barcelona, but was officially established in 1923. Every year since then they have run courses and held lectures for one week which attempt to raise awareness of spiritualism. Particularly notable was the 1925 conference attended by then head of the organisation, Sir Arthur Conan Doyle Sir Arthur Ignatius Conan Doyle (22 May 1859 – 7 July 1930) was a British writer and physician. He created the character Sherlock Holmes in 1887 for '' A Study in Scarlet'', the first of four novels and fifty-six short stories about Ho ..., who blamed ectoplasm for his faulty slides during his presentation. References External links * {{Spiritism and Spiritualism Spiritualist organizations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Spiritualist Association Of Churches
The National Spiritualist Association of Churches (NSAC) is one of the oldest and largest of the national Spiritualist church organizations in the United States. The NSAC was formed as the National Spiritualist Association of the United States of America (NSA) in September 1893, during a three-day convention in Chicago, Illinois. Although American Spiritualists had previously tended to resist institutional or denominational organization, early NSA leaders hoped organization would help promote the truths of the religion both spiritually and practically. Organization could help non-Spiritualists distinguish genuine mediumship from the rapidly proliferating varieties of fraudulent mediumship, increase communication among Spiritualists, prevent the legal prosecution of spirit mediums under fortune telling and medical licensing laws, and counterattacks by "orthodox" ministers in the press. To these reasons, early leaders added the material support of spirit mediums and healers, ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiritualist Association Of Great Britain
The Spiritualist Association of Great Britain (the SAGB) is a British spiritualist organisation. It was established ion 10th July 1872. History The SAGB grew out of the Marylebone Spiritualist Association (founded 1872). The story of the association's early struggles "to propagate spiritual truths in the Marylebone area of London" is told in an SAGB publication, "One Hundred Years of Spiritualism", which also states that Queen Victoria allegedly held several séances after the death of the Prince Consort. A famous and outspoken supporter of the SAGB was Arthur Conan Doyle, who (according to his obituary in the ''New York Times'') in later years "often expressed a wish that he should be remembered for his psychic work rather than for his novels". Serving the principles of the Spiritualist movement, and open to members and non-members alike, the SAGB offers rooms where the public, whether Spiritualist or not, may sit for readings with spirit mediums. Sunday services are free a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiritualists' National Union
The Spiritualists' National Union (SNU) is a Spiritualist organisation, founded in the United Kingdom in 1901, and is one of the largest Spiritualist groups in the world. Its motto is ''Light, Nature, Truth''. Over its history, it has organised test cases regarding the legal status of spiritualist mediums, with regard to such matters as exemption from compulsory military National service. In legal terms, Spiritualist mediums were considered to violate such laws as the Vagrancy Act 1824, which outlawed fortune telling, and the Witchcraft Act 1735. The Union campaigned against these laws for many years. They were eventually repealed by the Fraudulent Mediums Act 1951, which legalised the practice of mediums unless it was shown that they were profiting financially from a fraudulent service. This act was repealed in April 2008, and fraudulent mediums are now covered by consumer protection legislation, namely The Consumer Protection from Unfair Trading Regulations 2008. It has also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiritualist Church
A spiritualist church is a church affiliated with the informal spiritualist movement which began in the United States in the 1840s. Spiritualist churches are now found around the world, but are most common in English-speaking countries, while in Latin America, Central America, Caribbean and Sub-Saharan Africa, where a form of spiritualism called spiritism is more popular, meetings are held in spiritist centres, most of which are non-profit organizations rather than ecclesiastical bodies. History The origin of mediumship is usually linked to the seances conducted by the Fox sisters at Hydesville, Arcadia, New York in 1848, but some believers date the unofficial beginning of modern American Spiritualism to the Shakers and similar religious groups. By 1853 the movement had reached San Francisco and London, and by 1860 was worldwide. The Fox family remained very active in Spiritualism for many years. Other notable Spiritualists of that era were Mercy Cadwallader, who became a sort of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiritualist Organizations
Spiritualism is the metaphysical school of thought opposing physicalism and also is the category of all spiritual beliefs/views (in monism and dualism) from ancient to modern. In the long nineteenth century, Spiritualism (when not lowercase) became most known as a social religious movement according to which the laws of nature and of God include "the continuity of consciousness after the transition of death" and "the possibility of communication between those living on Earth and those who have made the transition". The afterlife, or the " spirit world", is seen by spiritualists not as a static place, but as one in which spirits continue to evolve. These two beliefs—that contact with spirits is possible, and that spirits are more advanced than humans—lead spiritualists to a third belief: that spirits are capable of providing useful insight regarding moral and ethical issues, as well as about the nature of God. Some spiritualists will speak of a concept which they refer to as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |