|
List Of Mir Spacewalks
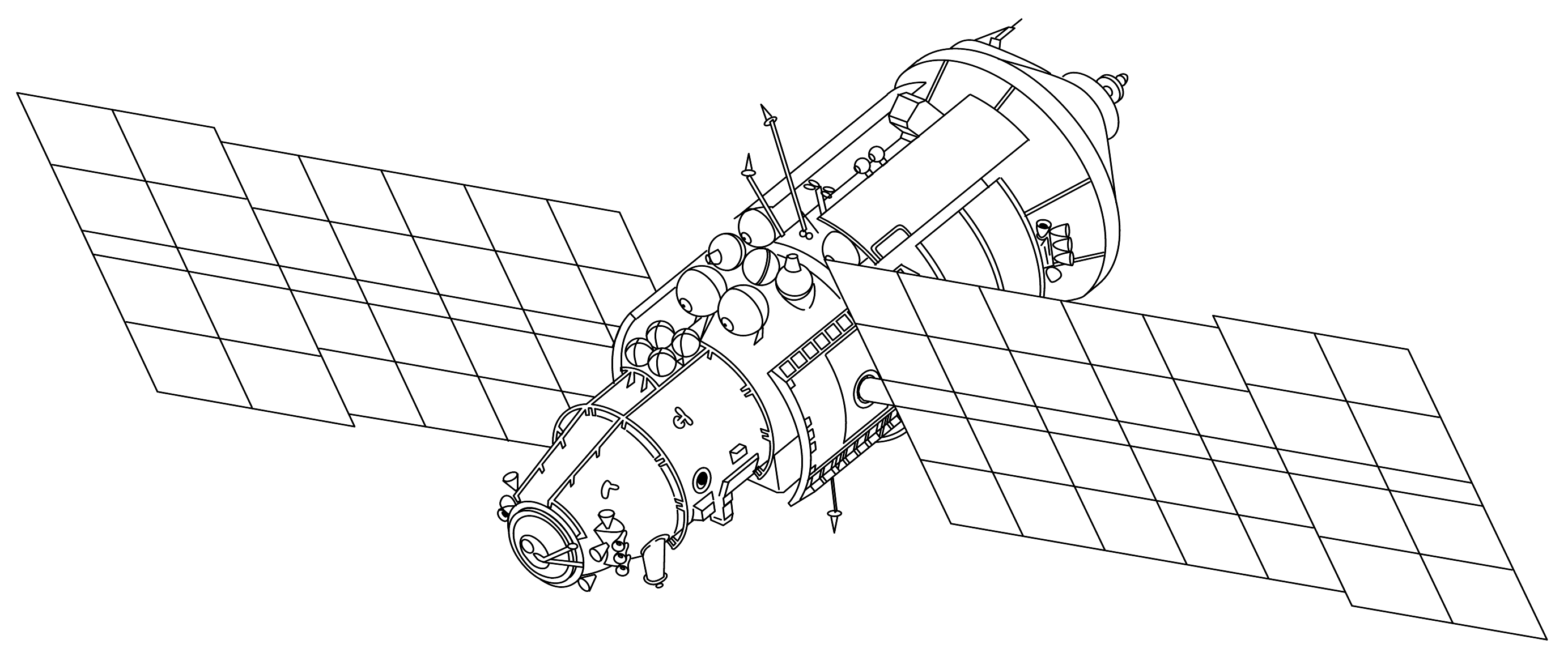
''Mir'' (russian: Мир, ; lit. ''Peace'' or ''World'') was a Soviet and later Russian space station, operational in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001. With a mass greater than that of any previous space station, ''Mir'' was constructed from 1986 to 1996 with a modular design, the first to be assembled in this way. The station was the largest artificial satellite orbiting the Earth until its deorbit on 21 March 2001, a record now surpassed by the International Space Station (ISS). ''Mir'' served as a microgravity research laboratory in which crews conducted experiments in biology, human biology, physics, astronomy, meteorology and spacecraft systems in order to develop technologies required for the permanent occupation of space. Following the success of the Salyut programme, ''Mir'' represented the next stage in the Soviet Union's space station programme. The first module of the station, known as the core module or base block, was launched in 1986, and was follo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mir On 12 June 1998edit1
''Mir'' (russian: Мир, ; ) was a space station that operated in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001, operated by the Soviet Union and later by Russia. ''Mir'' was the first modular space station and was assembled in orbit from 1986 to 1996. It had a greater mass than any previous spacecraft. At the time it was the largest artificial satellite in orbit, succeeded by the International Space Station (ISS) after ''Mir'''s orbital decay, orbit decayed. The station served as a microgravity research laboratory in which crews conducted experiments in biology, human biology, physics, astronomy, meteorology, and spacecraft systems with a goal of developing technologies required for permanent occupation of Outer space, space. ''Mir'' was the first continuously inhabited long-term research station in orbit and held the record for the longest continuous human presence in space at 3,644 days, until it was surpassed by the ISS on 23 October 2010. It holds the record for the longes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outer Space
Outer space, commonly shortened to space, is the expanse that exists beyond Earth and its atmosphere and between celestial bodies. Outer space is not completely empty—it is a near-perfect vacuum containing a low density of particles, predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium, as well as electromagnetic radiation, magnetic fields, neutrinos, dust, and cosmic rays. The baseline temperature of outer space, as set by the background radiation from the Big Bang, is . The plasma between galaxies is thought to account for about half of the baryonic (ordinary) matter in the universe, having a number density of less than one hydrogen atom per cubic metre and a kinetic temperature of millions of kelvins. Local concentrations of matter have condensed into stars and galaxies. Studies indicate that 90% of the mass in most galaxies is in an unknown form, called dark matter, which interacts with other matter through gravitational but not electromagnetic forces. Observations s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extra-vehicular Activity
Extravehicular activity (EVA) is any activity done by an astronaut in outer space outside a spacecraft. In the absence of a breathable Earthlike atmosphere, the astronaut is completely reliant on a space suit for environmental support. EVA includes ''spacewalks'' and lunar or planetary surface exploration (commonly known from 1969 to 1972 as ''moonwalks''). In a stand-up EVA (SEVA), an astronaut stands through an open hatch but does not fully leave the spacecraft. EVA has been conducted by the Soviet Union/Russia, the United States, Canada, the European Space Agency and China. On March 18, 1965, Alexei Leonov became the first human to perform a spacewalk, exiting the Voskhod 2 capsule for 12 minutes and 9 seconds. On July 20, 1969, Neil Armstrong became the first human to perform a moonwalk, outside his lunar lander on Apollo 11 for 2 hours and 31 minutes. On the last three Moon missions, astronauts also performed deep-space EVAs on the return to Earth, to retrieve film canis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Interplanetary Society
The British Interplanetary Society (BIS), founded in Liverpool in 1933 by Philip E. Cleator, is the oldest existing space advocacy organisation in the world. Its aim is exclusively to support and promote astronautics and space exploration. Structure It is a non-profit organisation with headquarters in London and is financed by members' contributions. It is situated on South Lambeth Road ( A203) near Vauxhall station. History The BIS was only preceded in astronautics by the American Interplanetary Society (founded 1930), the German VfR (founded 1927), and Soviet Society for Studies of Interplanetary Travel (founded 1924), but unlike those it never became absorbed into a national industry. Thus it is now the world's oldest existing space advocacy body. When originally formed in October 1933, the BIS aimed not only to promote and raise the public profile of astronautics, but also to undertake practical experimentation into rocketry along similar lines to the organisations above ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Station-keeping
In astrodynamics, orbital station-keeping is keeping a spacecraft at a fixed distance from another spacecraft or celestial body. It requires a series of orbital maneuvers made with thruster burns to keep the active craft in the same orbit as its target. For many low Earth orbit satellites, the effects of non-Keplerian forces, i.e. the deviations of the gravitational force of the Earth from that of a homogeneous sphere, gravitational forces from Sun/Moon, solar radiation pressure and air drag, must be counteracted. The deviation of Earth's gravity field from that of a homogeneous sphere and gravitational forces from the Sun and Moon will in general perturb the orbital plane. For a sun-synchronous orbit, the precession of the orbital plane caused by the oblateness of the Earth is a desirable feature that is part of mission design but the inclination change caused by the gravitational forces of the Sun and Moon is undesirable. For geostationary spacecraft, the inclination change ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Array
A photovoltaic system, also PV system or solar power system, is an electric power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and convert sunlight into electricity, a solar inverter to convert the output from direct to alternating current, as well as mounting, cabling, and other electrical accessories to set up a working system. It may also use a solar tracking system to improve the system's overall performance and include an integrated battery. PV systems convert light directly into electricity, and are not to be confused with other solar technologies, such as concentrated solar power or solar thermal, used for heating and cooling. A solar array only encompasses the ensemble of solar panels, the visible part of the PV system, and does not include all the other hardware, often summarized as balance of system (BOS). PV systems range from small, rooftop-mounted or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton (rocket)
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' elementary charge. Its mass is slightly less than that of a neutron and 1,836 times the mass of an electron (the proton–electron mass ratio). Protons and neutrons, each with masses of approximately one atomic mass unit, are jointly referred to as "nucleons" (particles present in atomic nuclei). One or more protons are present in the Atomic nucleus, nucleus of every atom. They provide the attractive electrostatic central force which binds the atomic electrons. The number of protons in the nucleus is the defining property of an element, and is referred to as the atomic number (represented by the symbol ''Z''). Since each chemical element, element has a unique number of protons, each element has its own unique atomic number, which determines the number of atomic electrons and consequently the chemical characteristics of the element. The word ''proton'' is Greek language, G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priroda
The Priroda (russian: Природа; en, Nature) (TsM-I, 77KSI, 11F77I) module was the seventh and final module of the Mir Space Station. Its primary purpose was to conduct Earth resource experiments through remote sensing and to develop and verify remote sensing methods. The control system of Priroda was developed by the Khartron (Kharkov, Ukraine). Description Priroda was originally designed to carry a deployable solar array. However, due to delays, and the fact that solar arrays were planned for other parts of Mir, a solar array was not included in the launch configuration. Instead, during free flight, Priroda was powered by two redundant sets of batteries totaling 168. Priroda had an unpressurized instrument compartment and a habitable instrument/payload compartment. The unpressurized compartment contained propulsion system components, EVA handrails, and scientific equipment. The instrument/payload compartment was divided into two sections: an outer instrument section an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mir Docking Module
The Stykovochnyy Otsek (russian: стыковочный отсек, en, Docking compartment), GRAU index 316GK, otherwise known as the ''Mir'' docking module or SO, was the sixth module of the Russian space station ''Mir'', launched in November 1995 aboard the . The module, built by RKK Energia, was designed to help simplify space shuttle dockings to ''Mir'' during the Shuttle-''Mir'' programme, preventing the need for the periodic relocation of the ''Kristall'' module necessary for dockings prior to the compartment's arrival. The module was also used to transport two new photovoltaic arrays to the station, as a mounting point for external experiments, and as a storage module when not in use for dockings. Development The docking module originated in the 1992 design version of the cancelled ''Mir''-2 space station, which featured a combined docking compartment and airlock to facilitate docking missions during the Soviet ''Buran'' space shuttle programme (this module, SO-1, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spektr
Spektr (russian: Спектр; en, Spectrum) (TKM-O, 77KSO, 11F77O) was the fifth module of the Mir Space Station. The module was designed for remote observation of Earth's environment containing atmospheric and surface research equipment. Spektr also had four solar arrays which generated about half of the station's electrical power. Development The Spektr module was originally developed as part of a top-secret military program code-named " Oktant". It was planned to carry experiments with space-borne surveillance and test antimissile defense. The surveillance instruments were mounted on the exterior of the module opposite the docking port. Also in this location were two launchers for artificial targets. The heart of the Spektr payload was an experimental optical telescope code-named "Pion” (Peony). Instrument list: * 286K binocular radiometer * Astra 2 – monitored atmospheric trace constituents, Mir environment * Balkan 1 lidar – measures upper cloud altitude. Used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kristall
The Kristall (russian: Кристалл, , Crystal) (77KST, TsM-T, 11F77T) module was the fourth module and the third major addition to ''Mir''. As with previous modules, its configuration was based on the 77K (TKS) module, and was originally named "Kvant 3". It was launched on May 31, 1990 on Proton-K. It docked to Mir autonomously on June 10, 1990. Description Kristall had several materials processing furnaces. They were called Krater 5, Optizon 1, Zona 2, and Zona 3. It also had a biotechnology experiment called the Aniur electrophoresis unit. These experiments were capable of generating 100 kg of raw materials for use on Earth. Located in the docking node was the Priroda 5 camera which was used for Earth resources experiments. Kristall also had several astronomy and astrophysics experiments which were designed to augment experiments that were already located in Kvant-1. Kristall's solar panels were also different from others on Mir. They were designed to be "collapsible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kvant-2
Kvant-2 (russian: Квант-2; English: Quantum-II/2) (77KSD, TsM-D, 11F77D) was the third module and second major addition to the Mir space station. Its primary purpose was to deliver new science experiments, better life support systems, and an airlock to Mir. It was launched on November 26, 1989 on a Proton rocket. It docked to Mir on December 6. Its control system was designed by the NPO "Electropribor" (Kharkiv, Ukraine). Description Kvant-2 was the first Mir module based on the TKS spacecraft (77k module). Kvant-2 was divided into three compartments. They were the EVA airlock, the instrument/cargo compartment, and the instrument/experiment compartment. The instrument/cargo compartment could be sealed off and act as an extension or a back-up to the airlock. Before Kvant-2 docked to the station, EVAs had to be carried by depressurizing the docking node on the Core Module. Kvant-2 also carried the Soviet version of the Manned Maneuvering Unit for the Orlan space suit. It de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |