|
List Of MeSH Codes (D12.776)
The following is a partial list of the "D" codes for Medical Subject Headings (MeSH), as defined by the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM). This list continues the information at List of MeSH codes (D12.644). Codes following these are found at List of MeSH codes (D13). For other MeSH codes, see List of MeSH codes. The source for this content is the set o2006 MeSH Treesfrom the NLM. – proteins – albumins – c-reactive protein – conalbumin – lactalbumin – ovalbumin – avidin – parvalbumins – ricin – serum albumin – methemalbumin – prealbumin – serum albumin, bovine – serum albumin, radio-iodinated – technetium tc 99m aggregated albumin – algal proteins – amphibian proteins – xenopus proteins – amyloid – amyloid beta-protein – amyloid beta-protein precursor – serum amyloid a protein – serum amyloid p-component – antifreeze proteins – antifreeze proteins, type i � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Subject Headings
Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) is a comprehensive controlled vocabulary for the purpose of indexing journal articles and books in the life sciences. It serves as a thesaurus that facilitates searching. Created and updated by the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), it is used by the MEDLINE/PubMed article database and by NLM's catalog of book holdings. MeSH is also used by ClinicalTrials.gov registry to classify which diseases are studied by trials registered in ClinicalTrials. MeSH was introduced in the 1960s, with the NLM's own index catalogue and the subject headings of the Quarterly Cumulative Index Medicus (1940 edition) as precursors. The yearly printed version of MeSH was discontinued in 2007; MeSH is now available only online. It can be browsed and downloaded free of charge through PubMed. Originally in English, MeSH has been translated into numerous other languages and allows retrieval of documents from different origins. Structure MeSH vocabulary is divi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serum Albumin, Bovine
Bovine serum albumin (BSA or "Fraction V") is a serum albumin protein derived from cows. It is often used as a protein concentration standard in lab experiments. The nickname "Fraction V" refers to albumin being the fifth fraction of the original Edwin Cohn purification methodology that made use of differential solubility characteristics of plasma proteins. By manipulating solvent concentrations, pH, salt levels, and temperature, Cohn was able to pull out successive "fractions" of blood plasma. The process was first commercialized with human albumin for medical use and later adopted for production of BSA. Properties The full-length BSA precursor polypeptide is 607 amino acids (AAs) in length. An N-terminal 18-residue signal peptide is cut off from the precursor protein upon secretion, hence the initial protein product contains 589 amino acid residues. An additional six amino acids are cleaved to yield the mature BSA protein that contains 583 amino acids. BSA has thre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
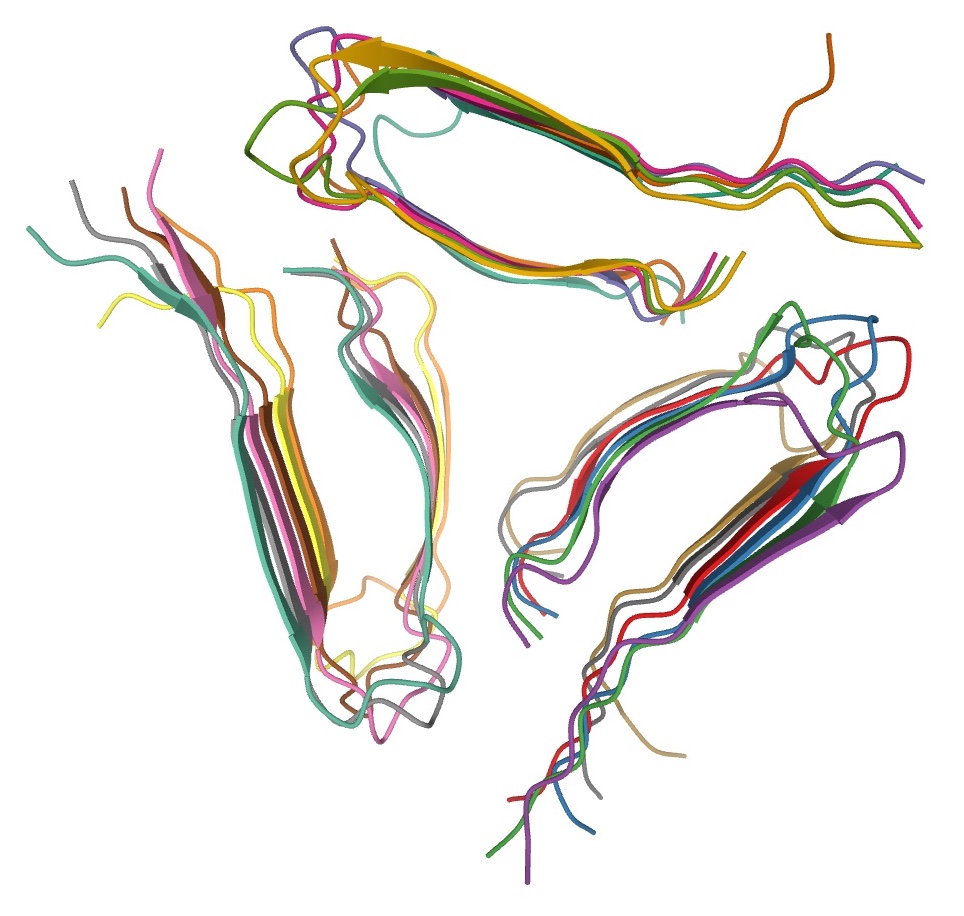
Antifreeze Proteins, Type Ii
An antifreeze is an additive which lowers the freezing point of a water-based liquid. An antifreeze mixture is used to achieve freezing-point depression for cold environments. Common antifreezes also increase the boiling point of the liquid, allowing higher coolant temperature. However, all common antifreeze additives also have lower heat capacities than water, and do reduce water's ability to act as a coolant when added to it. Because water has good properties as a coolant, water plus antifreeze is used in internal combustion engines and other heat transfer applications, such as HVAC chillers and solar water heaters. The purpose of antifreeze is to prevent a rigid enclosure from bursting due to expansion when water freezes. Commercially, both the ''additive'' (pure concentrate) and the ''mixture'' (diluted solution) are called antifreeze, depending on the context. Careful selection of an antifreeze can enable a wide temperature range in which the mixture remains in the liquid p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antifreeze Proteins, Type I
An antifreeze is an additive which lowers the freezing point of a water-based liquid. An antifreeze mixture is used to achieve freezing-point depression for cold environments. Common antifreezes also increase the boiling point of the liquid, allowing higher coolant temperature. However, all common antifreeze additives also have lower heat capacities than water, and do reduce water's ability to act as a coolant when added to it. Because water has good properties as a coolant, water plus antifreeze is used in internal combustion engines and other heat transfer applications, such as HVAC chillers and solar water heaters. The purpose of antifreeze is to prevent a rigid enclosure from bursting due to expansion when water freezes. Commercially, both the ''additive'' (pure concentrate) and the ''mixture'' (diluted solution) are called antifreeze, depending on the context. Careful selection of an antifreeze can enable a wide temperature range in which the mixture remains in the liquid p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antifreeze Proteins
Antifreeze proteins (AFPs) or ice structuring proteins refer to a class of polypeptides produced by certain animals, plants, fungi and bacteria that permit their survival in temperatures below the freezing point of water. AFPs bind to small ice crystals to inhibit the growth and recrystallization of ice that would otherwise be fatal. There is also increasing evidence that AFPs interact with mammalian cell membranes to protect them from cold damage. This work suggests the involvement of AFPs in cold acclimatization. Non-colligative properties Unlike the widely used automotive antifreeze, ethylene glycol, AFPs do not lower freezing point in proportion to concentration. Rather, they work in a noncolligative manner. This phenomenon allows them to act as an antifreeze at concentrations 1/300th to 1/500th of those of other dissolved solutes. Their low concentration minimizes their effect on osmotic pressure. The unusual properties of AFPs are attributed to their selective af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serum Amyloid P-component
The serum amyloid P component (SAP) is the identical serum form of amyloid P component (AP), a 25kDa pentameric protein first identified as the pentagonal constituent of in vivo pathological deposits called "amyloid". APCS is its human gene. In amyloidosis AP makes up 14% of the dry mass of amyloid deposits and is thought to be an important contributor to the pathogenesis of a related group of diseases called the Amyloidoses. These conditions are characterised by the ordered aggregation of normal globular proteins and peptides into insoluble fibres which disrupt tissue architecture and are associated with cell death. AP is thought to decorate and stabilise aggregates by preventing proteolytic cleavage and hence inhibiting fibril removal via the normal protein scavenging mechanisms. This association is utilised in the routine clinical diagnostic technique of SAP scintigraphy whereby radio-labelled protein is injected into patients to locate areas of amyloid deposition. The SAP-a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serum Amyloid A Protein
Serum amyloid A (SAA) proteins are a family of apolipoproteins associated with high-density lipoprotein (HDL) in plasma. Different isoforms of SAA are expressed constitutively (constitutive SAAs) at different levels or in response to inflammatory stimuli (acute phase SAAs). These proteins are produced predominantly by the liver. Acute-phase serum amyloid A proteins Acute-phase serum amyloid A proteins (A-SAAs) are secreted during the acute phase of inflammation. These proteins have several roles, including the transport of cholesterol to the liver for secretion into the bile, the recruitment of immune cells to inflammatory sites, and the induction of enzymes that degrade extracellular matrix. A-SAAs are implicated in several chronic inflammatory diseases, such as amyloidosis, atherosclerosis, and rheumatoid arthritis. Three acute-phase SAA isoforms have been reported in mice, called SAA1, SAA2, and SAA3. During inflammation, SAA1 and SAA2 are expressed and induced principally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amyloid Beta-protein Precursor
Amyloid-beta precursor protein (APP) is an integral membrane protein expressed in many biological tissue, tissues and concentrated in the synapses of neurons. It functions as a cell surface receptor and has been implicated as a regulator of synapse formation, neural plasticity, antimicrobial activity, and iron export. It is coded for by the gene ''APP'' and regulated by substrate presentation. APP is best known as the precursor molecule whose proteolysis generates amyloid beta (Aβ), a polypeptide containing 37 to 49 amino acid residues, whose Amyloid#Structure, amyloid fibrillar form is the primary component of amyloid plaques found in the brains of Alzheimer's disease patients. Genetics Amyloid-beta precursor protein is an ancient and highly Conserved sequence, conserved protein. In humans, the gene ''APP'' is located on chromosome 21 and contains 18 exons spanning 290 kilobases. Several alternative splicing isoforms of APP have been observed in humans, ranging in len ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amyloid Beta-protein
Amyloids are aggregates of proteins characterised by a fibrillar morphology of 7–13 nm in diameter, a beta sheet (β-sheet) secondary structure (known as cross-β) and ability to be stained by particular dyes, such as Congo red. In the human body, amyloids have been linked to the development of various diseases. Pathogenic amyloids form when previously healthy proteins lose their normal structure and physiological functions (misfolding) and form fibrous deposits in amyloid plaques around cells which can disrupt the healthy function of tissues and organs. Such amyloids have been associated with (but not necessarily as the cause of) more than 50 human diseases, known as amyloidosis, and may play a role in some neurodegenerative diseases. Some of these diseases are mainly sporadic and only a few cases are familial. Others are only familial. Some are iatrogenic as they result from medical treatment. Prions are an infectious form of amyloids that can act as a template to convert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amyloid
Amyloids are aggregates of proteins characterised by a Fibril, fibrillar morphology of 7–13 Nanometer, nm in diameter, a beta sheet (β-sheet) Secondary structure of proteins, secondary structure (known as cross-β) and ability to be Staining, stained by particular dyes, such as Congo red. In the human body, amyloids have been linked to the development of various diseases. Pathogenic amyloids form when previously healthy proteins lose their normal Protein structure, structure and physiology, physiological functions (Protein misfolding, misfolding) and form fibrous deposits in amyloid plaques around cells which can disrupt the healthy function of tissues and organs. Such amyloids have been associated with (but not necessarily as the cause of) more than 50 human diseases, known as amyloidosis, and may play a role in some neurodegenerative diseases. Some of these diseases are mainly sporadic and only a few cases are Genetic disorder, familial. Others are only Genetic disorder, fam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenopus Proteins
''Xenopus'' () (Gk., ξενος, ''xenos''=strange, πους, ''pous''=foot, commonly known as the clawed frog) is a genus of highly aquatic frogs native to sub-Saharan Africa. Twenty species are currently described within it. The two best-known species of this genus are ''Xenopus laevis'' and ''Xenopus tropicalis'', which are commonly studied as model organisms for developmental biology, cell biology, toxicology, neuroscience and for modelling human disease and birth defects. The genus is also known for its polyploidy, with some species having up to 12 sets of chromosomes. Characteristics ''Xenopus laevis'' is a rather inactive creature. It is incredibly hardy and can live up to 15 years. At times the ponds that ''Xenopus laevis'' is found in dry up, compelling it, in the dry season, to burrow into the mud, leaving a tunnel for air. It may lie dormant for up to a year. If the pond dries up in the rainy season, ''Xenopus laevis'' may migrate long distances to another pond, main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibian Proteins
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arboreal or freshwater aquatic ecosystems. Thus amphibians typically start out as larvae living in water, but some species have developed behavioural adaptations to bypass this. The young generally undergo metamorphosis from larva with gills to an adult air-breathing form with lungs. Amphibians use their skin as a secondary respiratory surface and some small terrestrial salamanders and frogs lack lungs and rely entirely on their skin. They are superficially similar to reptiles like lizards but, along with mammals and birds, reptiles are amniotes and do not require water bodies in which to breed. With their complex reproductive needs and permeable skins, amphibians are often ecological indicators; in recent decades there has been a dramatic decline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.png)