|
List Of Lessepsian Migrant Species
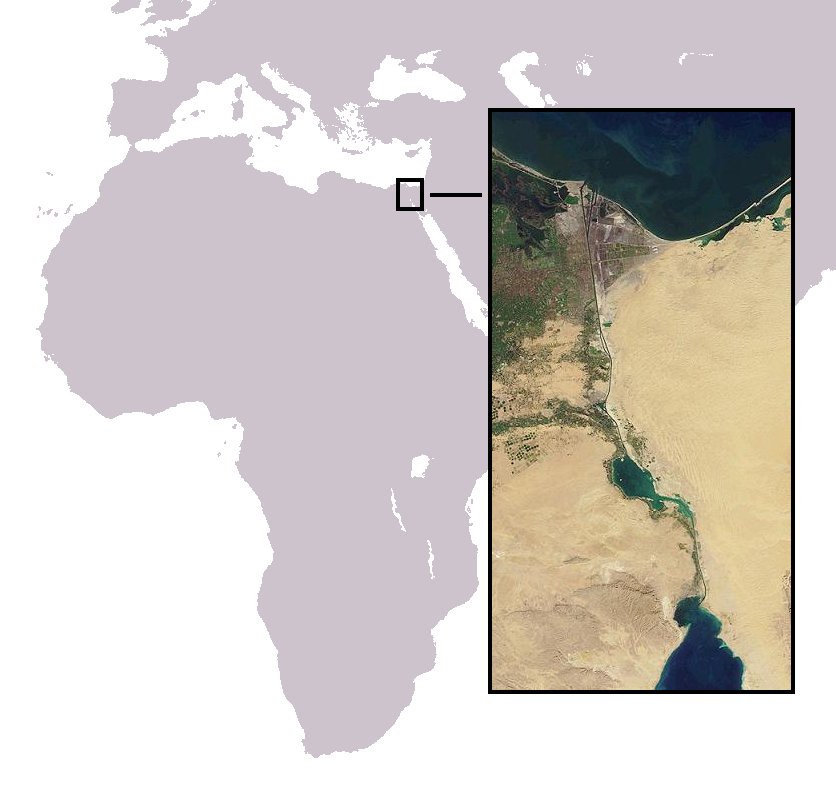
Lessepsian migrants, named after Ferdinand de Lesseps, the French engineer in charge of the Suez Canal's construction, are marine species that are native to the waters on one side of the Suez Canal, and which have been introduced by passage through the canal to the waters on its other side, giving rise to new colonies there and often becoming invasive. Most Lessepsian migrations are of Red Sea species invading the Mediterranean Sea; few occur in the opposite direction. Some examples of Red Sea species to Mediterranean Sea The year given denotes the first record in the Mediterranean (often distinct from the year of publication). Mediterranean species to Red Sea * '' Argyrosomus regius'' * ''Biuve fulvipunctata'' * ''Gobius cobitis'' * ''Gobius paganellus'' * ''Serranus cabrilla'' * ''Solea aegyptiaca'' * ''Umbrina cirrosa ''Umbrina cirrosa'', the shi drum, is a species of marine fish from the warmer waters of the eastern Atlantic Ocean, Mediterranean Sea and the Bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lessepsian Migration
The Lessepsian migration (also called Erythrean invasion) is the migration of marine species across the Suez Canal, usually from the Red Sea to the Mediterranean Sea, and more rarely in the opposite direction. When the canal was completed in 1869, fish, crustaceans, mollusks, and other marine animals and plants were exposed to an artificial passage between the two naturally separate bodies of water, and cross-contamination was made possible between formerly isolated ecosystems. The phenomenon is still occurring today. It is named after Ferdinand de Lesseps, the French diplomat in charge of the canal's construction. The migration of invasive species through the Suez Canal from the Indo-Pacific region has been facilitated by many factors, both abiotic and anthropogenic, and presents significant implications for the ecological health and economic stability of the contaminated areas; of particular concern is the fisheries industry in the Eastern Mediterranean. Despite these threats ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpheus Edwardsii
{{disambig, geo ...
Alpheos or Alpheus may refer to: * Alpheus (mythology), a river god in Greek mythology * Alpheus, West Virginia, a community in the US * Alfeios River, the Greek river which the mythological god refers to * Alphaeus, a father of two of the Twelve Apostles in the New Testament * Alpheus Mytilenaeus, an ancient Greek poet * ''Alpheus'' (crustacean), a genus of shrimps See also * Alphaeus (other) Alphaeus is a man mentioned in the New Testament as the father of two of the Twelve Apostles. Alphaeus may also refer to: * Alphaeus and Zacchaeus, 4th-century Christian martyrs * Alphaeus Philemon Cole (1876–1988), American artist, engraver an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcuatula Perfragilis
''Arcuatula perfragilis'' is a bivalve mollusc of the mussel family, Mytilidae, which has an Indo-Pacific distribution including the Red Sea. It has invaded the eastern Mediterranean from the Red Sea by way of the Suez Canal, a process known as Lessepsian migration. Description ''Arcuatula perfragilis'' has a pale green, equivalve shell with a few yellowish radial lines on the dorsal to posterior portion of the valves. The valves are typical mussel-shaped in that they are narrowly ovoid and transversely elongated. The periostracum is shiny. The surface of the valve has a very weak pattern of radiating lines which is discernible only by the strong ligament along the hinge line typical of the family mytilidae. This hinge has between 1 and 5 small dysodont teeth at the anterior end with a further15 towards the posterior part beyond the ligament. The shell length is normally 20mm. It can be identified from ''Arcuatula senhousia'' in the Mediterranean by its having a darker, less s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israel Journal Of Zoology
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the Eastern Mediterranean, southeastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea and the northern shore of the Red Sea, and Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the northeast, Jordan to the east, and Egypt to the southwest. Israel also is bordered by the Palestinian territories of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip to the east and west, respectively. Tel Aviv is the Economy of Israel, economic and Science and technology in Israel, technological center of the country, while its seat of government is in its proclaimed capital of Jerusalem, although Status of Jerusalem, Israeli sovereignty over East Jerusalem is unrecognized internationally. The land held by present-day Israel witnessed some of the earliest human occup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mytilidae
Mytilidae are a family of small to large marine and brackish-water bivalve molluscs in the order Mytilida. One of the genera, ''Limnoperna'', even inhabits freshwater environments. The order has only this one family which contains some 52 genera.Bouchet, P. (2014Mytilidae Rafinesque, 1815World Register of Marine Species Species in the family Mytilidae are found worldwide, but they are more abundant in colder seas, where they often form uninterrupted beds on rocky shores in the intertidal zone and the shallow subtidal. The subfamily Bathymodiolinae is found in deep-sea habitats. Mytilids include the well-known edible sea mussels. A common feature of the shells of mussels is an asymmetrical shell which has a thick, adherent periostracum. The animals attach themselves to a solid substrate using a byssus. A 2020 study of the phylogeny of Mytilidae recovered two main clades derived from an epifaunal ancestor, with subsequent lineages shifting to other lifestyles, and correlat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mollusca
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000 additional species. The proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. Numerous molluscs also live in freshwater and terrestrial habitats. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat. The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 taxonomic classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurologically advanced of all invertebrates—and either the giant squid or the colossal squid is the largest known invertebrate species. The gastropod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcuatula Arcuatula
''Arcuatula'' is a genus of mussels from the family Mytilidae. Species The following species are currently recognised under the genus ''Arcuatula'': * '' Arcuatula arcuatula'' (Hanley, 1843) * '' Arcuatula capensis'' (Krauss, 1848) * '' Arcuatula elegans'' (Gray, 1828) * '' Arcuatula glaberrima'' (Dunker, 1857) * '' Arcuatula japonica'' (Dunker, 1857) * '' Arcuatula leucosticte'' (Martens, 1897) * '' Arcuatula papyria'' (Conrad, 1846) * ''Arcuatula perfragilis'' (Dunker, 1857) * ''Arcuatula senhousia : ''For the Asian green mussel, see Perna viridis.'' ''Arcuatula senhousia'', commonly known as the Asian date mussel, Asian mussel or bag mussel, is a small saltwater mussel, a Marine (ocean), marine bivalve mollusk species in the family Mytilid ...'' (Benson, 1842) * '' Arcuatula tristis'' (Dunker, 1857) * '' Arcuatula variegate'' (Benson, 1856) References {{Taxonbar, from=Q18583321 Mytilidae Bivalve genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asterinidae
The Asterinidae are a large family of sea stars in the order Valvatida. Description and characteristics These are generally small sea stars, flattened dorsally and bearing very short arms, often giving a pentagonal shape in the body ;example: ''Asterians rubens'' (except in some species possessing more than five arms). The periphery of the body is thin and formed by indistinct, tiny marginal plates. They are characterized by their aborale face formed by plates shaped like crescents, sometimes giving a "knitted" appearance to the skin. The abyssal species can be bigger, like those of the genus '' Anseropoda'', which can exceed 45 cm in diameter. Biology Most of the species are small and relatively cryptic: they are often found hidden under rocks or in crevices, for example. Several species have access to a fissiparous asexual reproduction, multiplying their reproductive potential. For that reason, some species of the genera '' Meridiastra'' and '' Aquilonastra'' can so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echinoderm
An echinoderm () is any member of the phylum Echinodermata (). The adults are recognisable by their (usually five-point) radial symmetry, and include starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars, and sea cucumbers, as well as the sea lilies or "stone lilies". Adult echinoderms are found on the sea bed at every ocean depth, from the intertidal zone to the abyssal zone. The phylum contains about 7,000 living species, making it the second-largest grouping of deuterostomes, after the chordates. Echinoderms are the largest entirely marine phylum. The first definitive echinoderms appeared near the start of the Cambrian. The echinoderms are important both ecologically and geologically. Ecologically, there are few other groupings so abundant in the biotic desert of the deep sea, as well as shallower oceans. Most echinoderms are able to reproduce asexually and regenerate tissue, organs, and limbs; in some cases, they can undergo complete regeneration from a single limb. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquilonastra Burtoni
''Aquilonastra burtoni'' is a species of small sea star from the family Asterinidae from the Red Sea which has colonised the eastern Mediterranean by Lessepsian migration through the Suez Canal, although the Mediterranean populations are clonal reproducing through fissiparous asexual reproduction. It was originally described in 1840 by the English zoologist and philatelist John Edward Gray. Description ''Aquilonastra burtoni'' is a small species of sea star with up to 8 rays, frequently 7, they frequently demonstrate an asymmetrical form after fissiparous division while the form of larger specimens is often symmetrical with 5 equal rays; there is an inconspicuous madreporite in most interradii. The rays narrow basally, tapering to a narrow rounded distal part which is finger-like. Each of the plates on the oral surface has a grouping of 3 crowded mobile tapering spines in their centres, while those of the dorsal surface have a dense group of short tubercles. It is a greenish gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apogonidae
Cardinalfishes are a family, Apogonidae, of ray-finned fishes found in the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans; they are chiefly marine, but some species are found in brackish water and a few (notably ''Glossamia'') are found in fresh water. A handful of species are kept in the aquarium and are popular as small, peaceful, and colourful fish. The family includes about 370 species. They are generally small fish, with most species being less than , and are often brightly coloured. They are distinguished by their large mouths, and the division of the dorsal fin into two separate fins. Most species live in tropical or subtropical waters, where they inhabit coral reefs and lagoons. They are nocturnal, spending the day in dark crevices within the reef. At least some species brood their eggs inside the mouths of the males. Males do not feed during this incubation period. Males incubate the eggs in their mouth due to having longer heads and a larger jaw, which females do not acquire.Hoey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apogonichthyoides Pharaonis
''Apogonichthyoides pharaonis'', the Pharaoh cardinalfish, is a species of cardinalfish from the family Apogonidae which is found the western Indian Ocean and Red Sea. It is one of a group of species which have colonised the eastern Mediterranean Sea from the Red Sea via the Suez Canal, a process known as Lessepsian migration. Description ''Apogonichthyoides pharaonis'' has an oblong, compressed body up to 10 cm in length but more commonly 4–6 cm, with two distinct dorsal fins. The first two spines in the first dorsal fin are very short, the third spine is the longest and there is a single spine on the second dorsal fin and 8–9 soft rays. The anal fin lies directly beneath the second dorsal fin and has 2 spines and 7-8 soft rays and the caudal fin is truncated. The pelvic fin, which has1 spine and 5 soft rays starts beneath the base of the pectoral fins each of which has 15-16 soft rays. The large mouth is oblique and has jaws, pataltne and vomer which bear villifo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_01.jpg)

