|
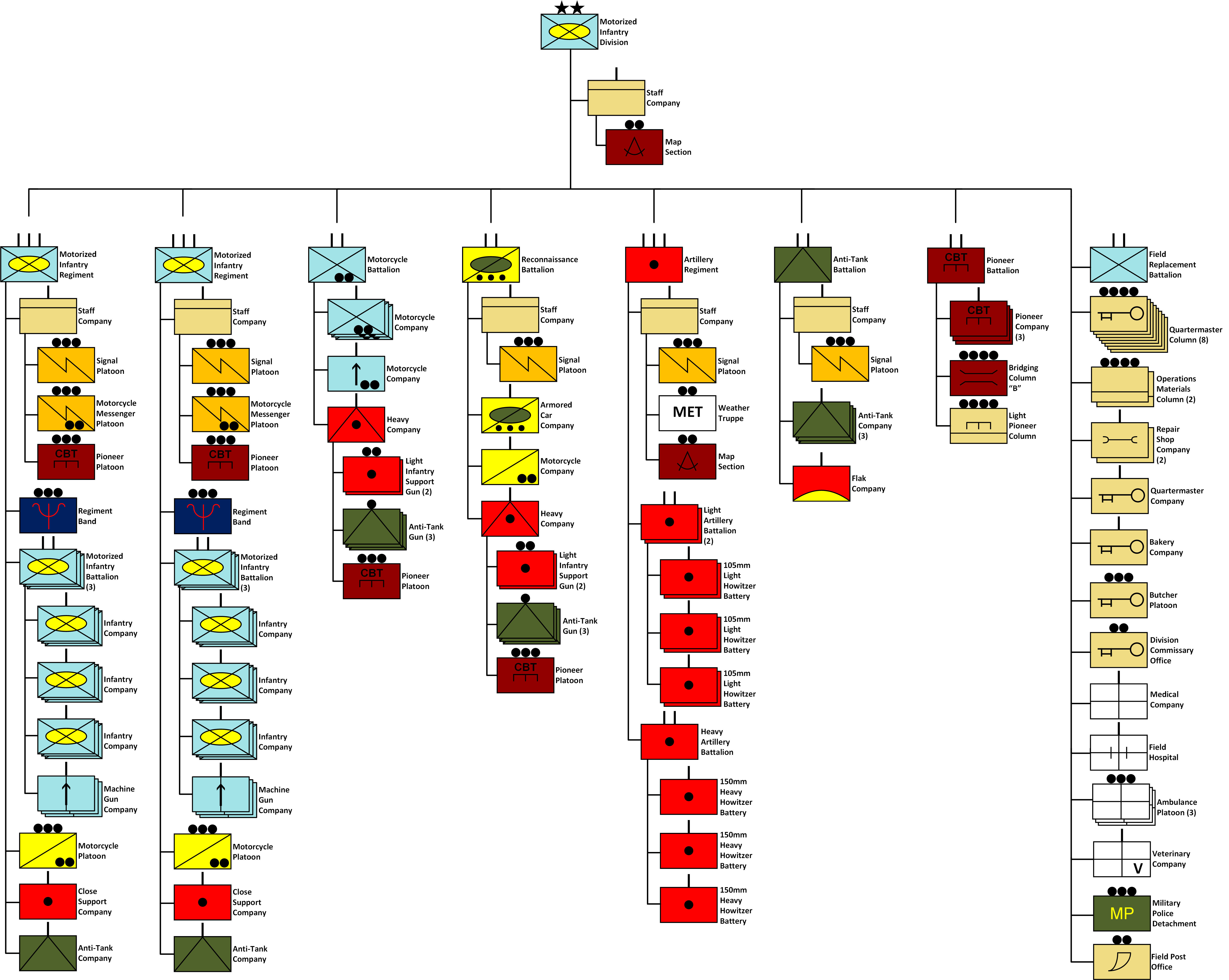
List Of German Divisions In World War II
This article lists divisions of the Wehrmacht (German Armed Forces) and Waffen-SS active during World War II, including divisions of the Heer (army), Luftwaffe (air force), and the Kriegsmarine (navy). Upgrades and reorganizations are shown only to identify the variant names for what is notionally a single unit; other upgrades and reorganizations are deferred to the individual articles. Due to the scope of this list, pre-war changes are not shown. Most of these divisions trained in Berlin, which is also where new military technology was kept and tested. German unit designations These designations are normally not translated and used in the German form in the unit name or description. ;''Bodenständige'': A static unit. Normally assigned to units who were deficient in transport and unable to move their own artillery. Many of these were divisions that had been mauled on the Eastern Front and were sent west to serve as coastal defence garrisons until sufficient resources were avail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Division (military)
A division is a large military unit or Formation (military), formation, usually consisting of between 6,000 and 25,000 soldiers. In most armies, a division is composed of several regiments or brigades; in turn, several divisions typically make up a corps. Historically, the division has been the default combined arms unit capable of independent Military tactics, operations. Smaller combined arms units, such as the American regimental combat team (RCT) during World War II, were used when conditions favored them. In recent times, modern Western militaries have begun adopting the smaller brigade combat team (similar to the RCT) as the default combined arms unit, with the division they belong to being less important. While the focus of this article is on army divisions, in naval usage "division (naval), division" has a completely different meaning, referring to either an administrative/functional sub-unit of a department (e.g., fire control division of the weapons department) aboar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jäger (infantry)
(singular , plural , ; " hunter") is a German military term referring to specific light infantry units. In German-speaking states during the early modern era, the term ''Jäger'' came to denote light infantrymen whose civilian occupations (mostly hunters and foresters) made them well-suited to patrolling and skirmishing, on an individual and independent basis, rather than as part of a large-scale military unit or traditional line infantry. As a consequence, ''Jäger'' was used to describe skirmishers, scouts, sharpshooters and runners. The word's usage and derivatives broadened over time. For instance, was the name given by the Prussian Army to scouts and runners. Conversely, in the modern German army (), is the name given to military police. is usually translated into English as: * "rifleman" (in an infantry role) or "Rifles" (in regimental names); and * "ranger" (especially in North American English; see below). In English is often written as (both pl. and sgl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volksgrenadier
''Volksgrenadier'' was the name given to a type of German Army division formed in the Autumn of 1944 after the double loss of Army Group Center to the Soviets in Operation Bagration and the Fifth Panzer Army to the Allies in Normandy. The name itself was intended to build morale, appealing at once to nationalism (''Volk'') and Germany's older military traditions (''Grenadier''). Germany formed 78 VGDs during the war. ''Volksgrenadier'' divisions were professional military formations with standardized weapons and equipment, unlike the unrelated ''Volkssturm'' militia. History and organisation The strategic emergency and concomitant manpower shortage resulting from the losses in mid-1944 required the creation of infantry divisions that economized on personnel and emphasized defensive strength over offensive strength. The ''Volksgrenadier'' divisions met this need by using only six line infantry battalions instead of the normal nine for infantry divisions – already a common reali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volk
The German noun ''Volk'' () translates to people, both uncountable in the sense of ''people'' as in a crowd, and countable (plural ''Völker'') in the sense of '' a people'' as in an ethnic group or nation (compare the English term ''folk''). Within an English-language context, the German word is of interest primarily for its use in German philosophy, as in ''Volksseele'' ("national soul"), and in German nationalism – notably the derived adjective '' völkisch'' ("national, ethnic"). Etymology The term ''Volk'' in the medieval period (Middle High German ''volc'') had the primary meaning of "large crowd, army", while the more general sense of "population" or "people" was expressed by ''diet'' (adjective '' dietsch, deutsch'' "popular, of the people"). It was only in the early modern period that ''deutsch'' acquired the meaning of an ethnic self-designation. Beginning in 1512, the Holy Roman Empire was named ''Imperium Romanum Sacrum Nationis Germanicæ'', rendered in Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regiment
A regiment is a military unit. Its role and size varies markedly, depending on the country, service and/or a specialisation. In Medieval Europe, the term "regiment" denoted any large body of front-line soldiers, recruited or conscripted in one geographical area, by a leader who was often also the feudal lord ''in capite'' of the soldiers. Lesser barons of knightly rank could be expected to muster or hire a company or battalion from their manorial estate. By the end of the 17th century, infantry regiments in most European armies were permanent units, with approximately 800 men and commanded by a colonel. Definitions During the modern era, the word "regiment" – much like "corps" – may have two somewhat divergent meanings, which refer to two distinct roles: # a front-line military formation; or # an administrative or ceremonial unit. In many armies, the first role has been assumed by independent battalions, battlegroups, task forces, brigades and other, similarly s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Security Division
Security Divisions (German: ''Sicherungs-Divisionen'') were German rear-area military units engaged in Nazi security warfare in occupied Europe during World War II. Almost all divisions were employed in areas on the Eastern front with the exception of the 325th Security Division which operated within Occupied France. The units were tasked with fighting local partisans, intelligience and counter-insurgency against resistance groups, rounding up Jews and other ethnic groups as part of The Holocaust, and conducting punitive actions in civilian areas. These divisions carried out numerous war crimes. Many of their commanders were punished after the war at the Subsequent Nuremberg trials for their conduct during the war. History The Wehrmacht security divisions were set up at the beginning of 1941 and were intended to perform policing, security and counter-insurgency duties in the rear of the main German field armies, under the direction of the respective army rear area command, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Security Division (Wehrmacht)
Security Divisions (German: ''Sicherungs-Divisionen'') were German rear-area military units engaged in Bandenbekämpfung, Nazi security warfare in German-occupied Europe, occupied Europe during World War II. Almost all divisions were employed in areas on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern front with the exception of the 325th Security Division (Wehrmacht), 325th Security Division which operated within Occupied France. The units were tasked with fighting local Partisan (military), partisans, intelligience and counter-insurgency against resistance groups, rounding up Jews and other ethnic groups as part of The Holocaust, and conducting punitive actions in civilian areas. These divisions carried out numerous war crimes. Many of their commanders were punished after the war at the Subsequent Nuremberg trials for their conduct during the war. History The Wehrmacht security divisions were set up at the beginning of 1941 and were intended to perform Bandenbekämpfung, policing, se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armoured Warfare
Armoured warfare or armored warfare (mechanized forces, armoured forces or armored forces) (American English; American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, see spelling differences), is the use of armoured fighting vehicle, armored fighting vehicles in modern warfare. It is a major component of modern Military science, methods of war. The premise of armoured warfare rests on the ability of troops to penetrate conventional Defense (military), defensive lines through use of Maneuver warfare, manoeuvre by armoured units. Much of the application of armoured warfare depends on the use of tanks and related vehicles used by other supporting arms such as infantry fighting vehicles, self-propelled artillery, and other combat vehicles, as well as mounted combat engineers and other support units. The doctrine of armoured warfare was developed to break the static nature of World War I trench warfare on the Western Front (World War I), Western Front, and return to the 19th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panzer Division (Wehrmacht)
A Panzer division was one of the armored (tank) divisions in the army of Nazi Germany during World War II. Panzer divisions were the key element of German success in the blitzkrieg operations of the early years of World War II. Later the Waffen-SS formed its own ''panzer divisions'', and even the Luftwaffe fielded an elite panzer division: the Hermann Göring Division. A panzer division was a combined arms formation, having both tanks (german: Panzerkampfwagen, , usually shortened to ""), mechanized and motorized infantry, along with artillery, anti-aircraft and other integrated support elements. At the start of the war, panzer divisions were more effective than the equivalent Allied armored divisions due to their combined arms doctrine, even though they had fewer and generally less technically-advanced tanks. By mid-war, though German tanks had often become technically superior to Allied tanks, Allied armored warfare and combined arms doctrines generally caught up with the Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ski Warfare
Ski warfare is the use of ski-equipped troops in war. History Early Ski warfare is first recorded by the Danish historian Saxo Grammaticus in the 13th century. During the Battle of Oslo in 1161, Norwegian troops used skis for reconnoitering. They were also used in 1452 in Sweden, and in the 15th to 17th centuries by various other Scandinavian countries. In 1767, military ski competitions began. They evolved into the biathlon. Napoleonic Wars Denmark-Norway (though only Norwegian) ski troops were used against Sweden during the 1807–1814 Napoleonic Wars. World War I During World War I the Italian Army raised 88 Alpini Battalions. Their purpose was to fight summer and winter in the highest regions of the Alpine Arch. Most of the battalions were dissolved after World War I. Only nine Alpini regiments remain in service today, and only four still train every soldier in ski warfare: the 4th Alpini Parachutist Regiment, 5th Alpini Regiment, 6th Alpini Regiment and 7th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Warfare
Mountain warfare (also known as alpine warfare) is warfare in mountains or similarly rough terrain. Mountain ranges are of strategic importance since they often act as a natural border, and may also be the origin of a water source (for example, the Golan Heights). Attacking a prepared enemy position in mountain terrain generally requires a greater ratio of attacking soldiers to defending soldiers than a war conducted on level ground. Mountains present natural hazards such as lightning, strong gusts of wind, rock falls, avalanches, snow packs, ice, extreme cold, and glaciers with their crevasses. The general uneven terrain and the slow pace of troop and material movement are all additional threats to combatants. Movement, reinforcements, and medical evacuation up and down steep slopes and areas where even pack animals cannot reach involves an enormous exertion of energy. History Second Punic War In 218 BC (DXXXVI a.u.c.) the Carthaginian army commander Hannibal marched troop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gebirgsjäger
''Gebirgsjäger'' () are the light infantry part of the alpine or mountain troops (''Gebirgstruppe'') of Germany, Austria and Switzerland. The word '' Jäger'' (meaning "hunter" or "huntsman") is a characteristic term used for light infantry in German speaking countries. Origins The mountain infantry of Austria have their roots in the three ''Landesschützen'' regiments of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. The mountain infantry of modern Germany carry on certain traditions of the German Alpenkorps (Alpine corps) of World War I. Both countries' mountain infantry share the Edelweiß insignia, established in 1907 as a symbol of the Austro-Hungarian ''Landesschützen'' regiments by Emperor Franz Joseph I. These troops wore the edelweiss on the uniform collar. When the ''Alpenkorps'' served alongside the ''Landesschützen'' on Austria's southern frontier against Italian forces from May 1915, the ''Landesschützen'' honoured the men of the ''Alpenkorps'' by awarding them their own insi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


