|
List Of NGC Objects (1–1000)
This is a list of NGC objects 1–1000 from the New General Catalogue (NGC). The astronomical catalogue is composed mainly of star clusters, nebulae, and galaxies. Other objects in the catalogue can be found in the other subpages of the list of NGC objects. The constellation information in these tables is from ''The Complete New General Catalogue and Index Catalogue of Nebulae and Star Clusters by J. L. E. Dreyer'', which was accessed using the VizieR Service. Galaxy morphological types and objects that are members of the Small Magellanic Cloud are identified using the ''NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database''. The other data of these tables are from the SIMBAD Astronomical Database unless otherwise stated. 1–100 101–200 201–300 301–400 401–500 501–600 601–700 701–800 801–900 901–1000 See also * Lists of astronomical objects This is a list of lists, grouped by type of astronomical object. Solar System * List of Solar System obj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New General Catalogue
The ''New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars'' (abbreviated NGC) is an astronomical catalogue of deep-sky objects compiled by John Louis Emil Dreyer in 1888. The NGC contains 7,840 objects, including galaxies, star clusters and emission nebulae. Dreyer published two supplements to the NGC in 1895 and 1908, known as the ''Index Catalogues'' (abbreviated IC), describing a further 5,386 astronomical objects. Thousands of these objects are best known by their NGC or IC numbers, which remain in widespread use. The NGC expanded and consolidated the cataloguing work of William and Caroline Herschel, and John Herschel's ''General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars''. Objects south of the celestial equator are catalogued somewhat less thoroughly, but many were included based on observation by John Herschel or James Dunlop. The NGC contained multiple errors, but attempts to eliminate them were made by the ''Revised New General Catalogue'' (RNGC) by Jack W. Sulent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiral Galaxy
Spiral galaxies form a class of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work ''The Realm of the Nebulae''Alt URL pp. 124–151) and, as such, form part of the . Most spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating containing s, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as the |
NGC 12
NGC 12 is an intermediate spiral galaxy in the Pisces Pisces may refer to: * Pisces, an obsolete (because of land vertebrates) taxonomic superclass including all fish * Pisces (astrology), an astrological sign * Pisces (constellation), a constellation **Pisces Overdensity, an overdensity of stars in ... constellation. It was discovered by William Herschel on December 6, 1790. References External links * * {{DEFAULTSORT:NGC 0012 Galaxies discovered in 1790 Intermediate spiral galaxies Pisces (constellation) 0012 00074 00645 17901206 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGC 10
NGC 10 is a spiral galaxy located in the southern constellation of Sculptor. It was discovered by John Herschel on 25 September 1834. The galaxy is located at a distance of from the Sun. Its morphological classification in the De Vaucouleurs system is SAB(rs)bc, where the 'SAB' denotes a weak- barred spiral, '(rs)' indicates a slight ring-like structure, and 'bc' means the spiral arms are moderately to loosely wound. Paturel et al. (2003) assigned this galaxy a classification of SBbc, indicating a barred spiral galaxy. On December 22, 2011, a Type II supernova A Type II supernova (plural: ''supernovae'' or ''supernovas'') results from the rapid collapse and violent explosion of a massive star. A star must have at least 8 times, but no more than 40 to 50 times, the mass of the Sun () to undergo this ... designated SN 2011jo was discovered in NGC 10 by Stuart Parker of New Zealand. It was located east and north of the galactic nucleus. References External links * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
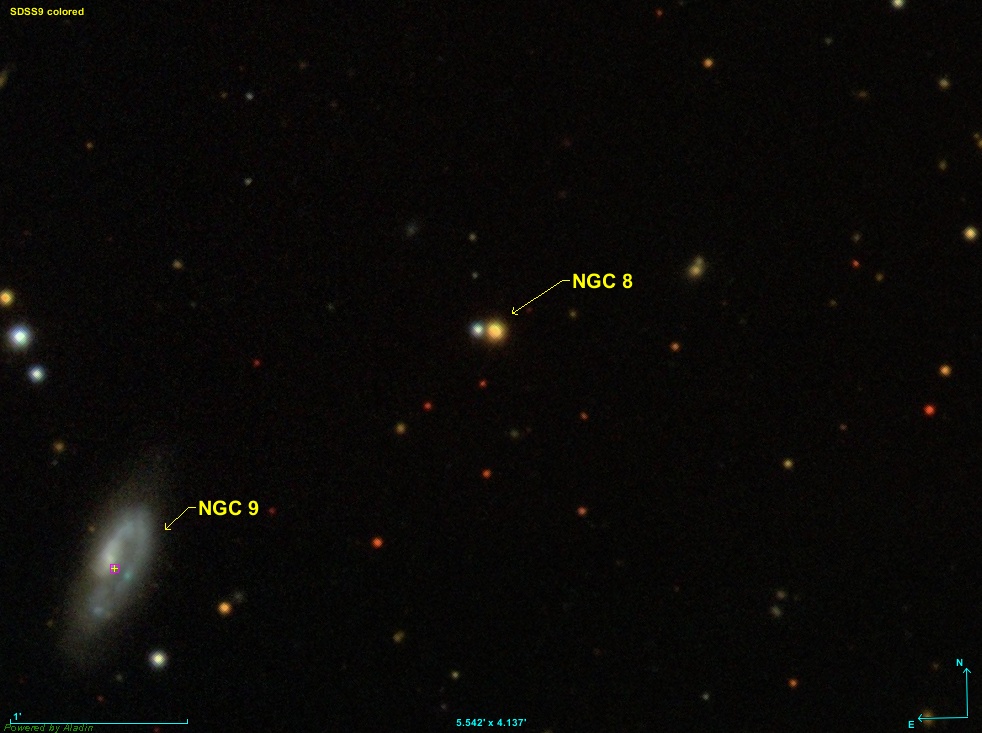
NGC 9
NGC 9 is a spiral galaxy about 140 million light-years away in the Pegasus constellation. It was discovered on 27 September 1865 by Otto Wilhelm von Struve Otto Wilhelm von Struve (May 7, 1819 (Julian calendar: April 25) – April 14, 1905) was a Russian astronomer of Baltic German origins. In Russian, his name is normally given as Otto Vasil'evich Struve (Отто Васильевич Струве .... References External links * * {{DEFAULTSORT:NGC 0009 Galaxies discovered in 1865 Unbarred spiral galaxies 0009 00078 00652 18650927 Discoveries by Otto Struve Pegasus (constellation) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Star
In observational astronomy, a double star or visual double is a pair of stars that appear close to each other as viewed from Earth, especially with the aid of optical telescopes. This occurs because the pair either forms a binary star (i.e. a binary system of stars in mutual orbit, gravitationally bound to each other) or is an ''optical double'', a chance line-of-sight alignment of two stars at different distances from the observer. Binary stars are important to stellar astronomers as knowledge of their motions allows direct calculation of stellar mass and other stellar parameters. The only (possible) case of "binary star" whose two components are separately visible to the naked eye is the case of Mizar and Alcor (though actually a multiple-star system), but it is not known for sure whether Mizar and Alcor are gravitationally bound. Since the beginning of the 1780s, both professional and amateur double star observers have telescopically measured the distances and angles between d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGC 8
NGC 8 is an asterism of two completely unrelated stars (spectral types K6I and G4) in the constellation Pegasus, discovered on 29 September 1865 by Otto Wilhelm von Struve. It is approximately 2.7 arc minutes away from NGC 9. The two stars are completely unrelated to each other, with the whiter, dimmer star (2MASS J00084563+2350186) being at a distance of light years, and the yellower, brighter star (2MASS J00084521+2350184) having a minimum distance of 215,000 light years. While both stars are technically outside the Milky Way's galactic disc A galactic disc (or galactic disk) is a component of disc galaxies, such as spiral galaxies and lenticular galaxies. Galactic discs consist of a stellar component (composed of most of the galaxy's stars) and a gaseous component (mostly composed ..., the nearer is light-years south of the 1,000-light-year-thick disc, and the further is not only at least 130,000 light-years south of the disk, but is located entirely outside the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sculptor (constellation)
Sculptor is a small and faint constellation in the southern sky. It represents a sculptor. It was introduced by Nicolas Louis de Lacaille in the 18th century. He originally named it Apparatus Sculptoris (the sculptor's studio), but the name was later shortened. History The region to the south of Cetus and Aquarius had been named by Aratus in 270 BC as ''The Waters'' – an area of scattered faint stars with two brighter stars standing out. Professor of astronomy Bradley Schaefer has proposed that these stars were most likely Alpha and Delta Sculptoris. The French astronomer Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille first described the constellation in French as ''l'Atelier du Sculpteur'' (the sculptor's studio) in 1751–52, depicting a three-legged table with a carved head on it, and an artist's mallet and two chisels on a block of marble alongside it. De Lacaille had observed and catalogued almost 10,000 southern stars during a two-year stay at the Cape of Good Hope, devising fourteen new con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barred Spiral Galaxy
A barred spiral galaxy is a spiral galaxy with a central bar-shaped structure composed of stars. Bars are found in about two thirds of all spiral galaxies, and generally affect both the motions of stars and interstellar gas within spiral galaxies and can affect spiral arms as well. The Milky Way Galaxy, where the Solar System is located, is classified as a barred spiral galaxy. Edwin Hubble classified spiral galaxies of this type as "SB" (spiral, barred) in his Hubble sequence and arranged them into sub-categories based on how open the arms of the spiral are. SBa types feature tightly bound arms, while SBc types are at the other extreme and have loosely bound arms. SBb-type galaxies lie in between the two. SB0 is a barred lenticular galaxy. A new type, SBm, was subsequently created to describe somewhat irregular barred spirals, such as the Magellanic Clouds, which were once classified as irregular galaxies, but have since been found to contain barred spiral structures. Among o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGC 7
NGC 7 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the Sculptor constellation. It was discovered by English astronomer John Herschel in 1834, who was using an 18.7 inch reflector telescope A reflecting telescope (also called a reflector) is a telescope that uses a single or a combination of curved mirrors that reflect light and form an image. The reflecting telescope was invented in the 17th century by Isaac Newton as an alternati ... at the time. Astronomer Steve Gottlieb described the galaxy as faint, albeit large, and edge-on from the perspective of the Milky Way; he also noted how the galaxy could only be observed clearly with peripheral vision, not by looking directly at it. References External links * Galaxies discovered in 1834 0007 18340927 Discoveries by John Herschel Sculptor (constellation) Barred spiral galaxies {{Spiral-galaxy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
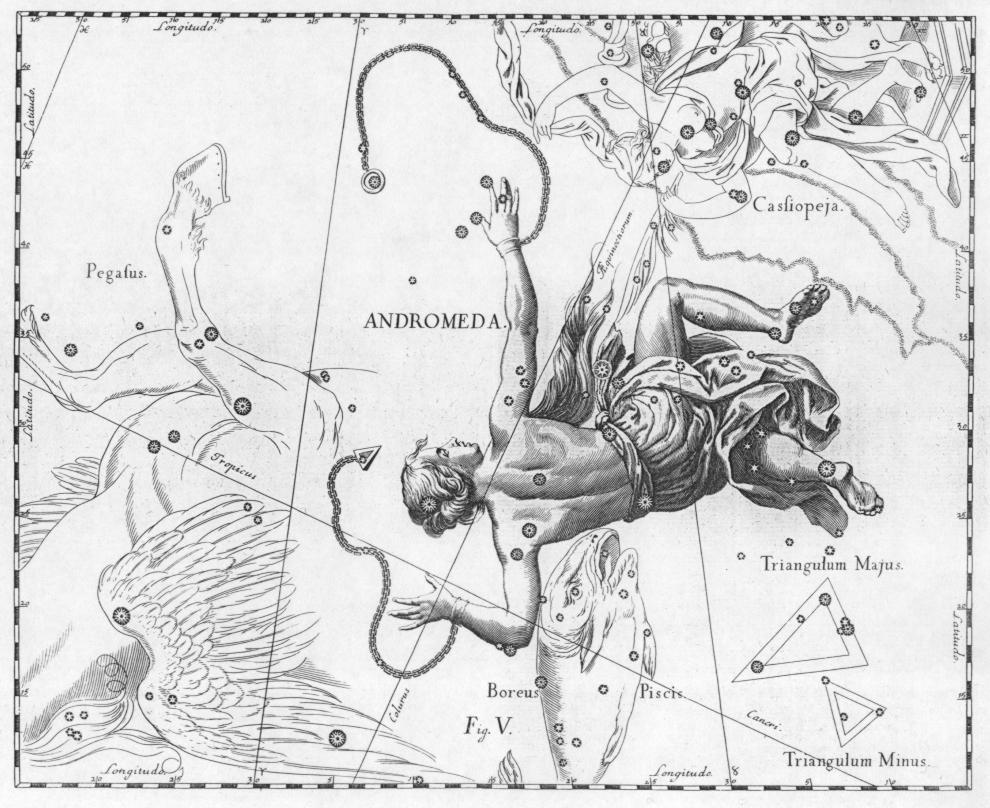
Andromeda (constellation)
Andromeda is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greco-Roman astronomer Ptolemy, and one of the 88 modern constellations. Located in the northern celestial hemisphere, it is named for Andromeda, daughter of Cassiopeia, in the Greek myth, who was chained to a rock to be eaten by the sea monster Cetus. Andromeda is most prominent during autumn evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with several other constellations named for characters in the Perseus myth. Because of its northern declination, Andromeda is visible only north of 40° south latitude; for observers farther south, it lies below the horizon. It is one of the largest constellations, with an area of 722 square degrees. This is over 1,400 times the size of the full moon, 55% of the size of the largest constellation, Hydra, and over 10 times the size of the smallest constellation, Crux. Its brightest star, Alpha Andromedae, is a binary star that has also been counted as a part of Pegasus, while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elliptical Galaxy
An elliptical galaxy is a type of galaxy with an approximately ellipsoidal shape and a smooth, nearly featureless image. They are one of the four main classes of galaxy described by Edwin Hubble in his Hubble sequence and 1936 work ''The Realm of the Nebulae'', with their intermediate scale disks, a subset of the "early-type" galaxy population. Most elliptical galaxies are composed of older, low-mass stars, with a sparse interstellar medium and minimal star formation activity, and they tend to be surrounded by large numbers of globular clusters. Elliptical galaxies are believed to make up approximately 10–15% of galaxies in the Virgo Supercluster, and they are not the dominant type of galaxy in the universe overall. They are preferentially found close to the centers of galaxy clusters. Elliptical galaxies range in size from dwarf ellipticals with tens of millions of stars, to supergiants of over one hundred trillion stars that dominate their galaxy clusters. Original ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |