|
LightSail
LightSail is a project to demonstrate controlled solar sailing within low Earth orbit using a CubeSat. The project was developed by The Planetary Society, a global non-profit organization devoted to space exploration. It consists of two spacecraft — LightSail 1 and LightSail 2. LightSail 1 was an engineering demonstration mission designed to test its new sail deployment method in space, it did not perform solar sailing. LightSail 2 was a fully functional spacecraft intended to demonstrate true solar sailing and incorporated the lessons learned from LightSail 1. LightSail is a follow-on project to '' Cosmos 1'' — a solar-sail spacecraft designed by The Planetary Society in the early 2000s, which was destroyed during a launch failure in 2005. Both LightSail spacecraft measured (3U CubeSat) in their stowed configuration. After sail deployment, the total area of each spacecraft was . History In 2005, The Planetary Society attempted to send a solar sail satellite named '' Cos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Sail
Solar sails (also known as light sails and photon sails) are a method of spacecraft propulsion using radiation pressure exerted by sunlight on large mirrors. A number of spaceflight missions to test solar propulsion and navigation have been proposed since the 1980s. The first spacecraft to make use of the technology was IKAROS, launched in 2010. A useful analogy to solar sailing may be a sailing boat; the light exerting a force on the mirrors is akin to a sail being blown by the wind. High-energy laser beams could be used as an alternative light source to exert much greater force than would be possible using sunlight, a concept known as beam sailing. Solar sail craft offer the possibility of low-cost operations combined with long operating lifetimes. Since they have few moving parts and use no propellant, they can potentially be used numerous times for delivery of payloads. Solar sails use a phenomenon that has a proven, measured effect on astrodynamics. Solar pressure aff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Planetary Society
The Planetary Society is an American internationally-active non-governmental nonprofit organization. It is involved in research, public outreach, and political space advocacy for engineering projects related to astronomy, planetary science, and space exploration. It was founded in 1980 by Carl Sagan, Bruce Murray, and Louis Friedman, and has about 60,000 members from more than 100 countries around the world. The Society is dedicated to the exploration of the Solar System, the search for near-Earth objects, and the search for extraterrestrial life. The society's mission is stated as: "Empowering the world’s citizens to advance space science and exploration." The Planetary Society is a strong advocate for space funding and missions of exploration within NASA. They lobby Congress and engage their membership in the United States to write and call their representatives in support of NASA funding. In addition to public outreach, The Planetary Society has sponsored solar sail and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CubeSat
A CubeSat is a class of miniaturized satellite based around a form factor consisting of cubes. CubeSats have a mass of no more than per unit, and often use commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) components for their electronics and structure. CubeSats are put into orbit by deployers on the International Space Station, or launched as secondary payloads on a launch vehicle. , more than 1,600 CubeSats have been launched. In 1999, California Polytechnic State University (Cal Poly) professor Jordi Puig-Suari and Bob Twiggs, a professor at Stanford University Space Systems Development Laboratory, developed the CubeSat specifications to promote and develop the skills necessary for the design, manufacture, and testing of small satellites intended for low Earth orbit (LEO) that perform a number of scientific research functions and explore new space technologies. Academia accounted for the majority of CubeSat launches until 2013, when more than half of launches were for non-academic purpose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmos 1
Cosmos 1 was a project by Cosmos Studios and The Planetary Society to test a solar sail in space. As part of the project, an unmanned solar-sail spacecraft named ''Cosmos 1'' was launched into space at 19:46:09 UTC (15:46:09 EDT) on 21 June 2005 from the submarine in the Barents Sea. However, a rocket failure prevented the spacecraft from reaching its intended orbit. Once in orbit, the spacecraft was supposed to deploy a large sail, upon which photons from the Sun would push, thereby increasing the spacecraft's velocity (the contributions from the solar wind are similar, but of much smaller magnitude). Had the mission been successful, it would have been the first ever orbital use of a solar sail to speed up a spacecraft, as well as the first space mission by a space advocacy group. The project budget was US$4 million. The Planetary Society planned to raise another US$4 million for ''Cosmos 2'', a reimplementation of the experiment provisionally to be launched on a Soyuz re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falcon Heavy
Falcon Heavy is a partially reusable heavy-lift launch vehicle that is produced by SpaceX, an American aerospace manufacturer. The rocket consists of two strap-on boosters made from Falcon 9 first stages, a center core also made from a Falcon 9 first stage, and a second stage on top. Falcon Heavy has the second highest payload capacity of any currently operational launch vehicle behind NASA's Space Launch System and the fourth-highest capacity of any rocket to reach orbit, trailing the Saturn V, Energia and Space Launch System. SpaceX conducted Falcon Heavy's maiden launch on 6 February 2018, at 20:45 UTC. The rocket carried Elon Musk's Tesla Roadster belonging to SpaceX founder Elon Musk, with a dummy dubbed "Starman" in the driver's seat, as a dummy payload. The second Falcon Heavy launch occurred on 11 April 2019, and all three booster rockets successfully returned to Earth. The third Falcon Heavy launch successfully occurred on 25 June 2019. Since then, Falcon Heavy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NanoSail-D2
NanoSail-D2 was a small satellite built by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center and Ames Research Center to study the deployment of a solar sail in space. It was a three-unit CubeSat, measuring with a mass of . Its solar sail had an area of , and was deployed in around five seconds. It was planned to be deployed from the FASTSAT satellite around 3 December 2010, two weeks after launch. The satellite did not eject at that time, but on 17 January 2011, it ejected on its own and deployed its sail three days later on 20 January 2011. The beacon signal began transmitting after ejection and was first received on the afternoon of 19 January 2011. Chronology NanoSail-D2 was originally built as a ground spare for the NanoSail-D satellite, which was launched aboard a Falcon 1 in 2008, and was subsequently lost when the launch vehicle malfunctioned during stage separation. Over the next two years improvements were made to the spare, and the satellite was incorporated into the FASTSAT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Test Program
The Space Test Program (STP) is the primary provider of spaceflight for the United States Department of Defense (DoD) space science and technology community. STP is managed by a group within the Advanced Systems and Development Directorate, a directorate of the Space and Missile Systems Center of the United States Space Force. STP provides spaceflight via the International Space Station (ISS), piggybacks, secondary payloads and dedicated launch services. Past activities STP has actually been in existence for 50 years as of 2019, with several thousand launches it has been responsible for. For example, the initial experiments that led to the modern Global Positioning System (GPS) satellite constellation were STP-launched projects. 2001 During August 2001, STP conducted two successful activities using the Space Shuttle and ISS. STS-105 delivered and successfully deployed the Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE) externally on the ISS. MISSE was a passive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Educational Launch Of Nanosatellites
Educational Launch of Nanosatellites (ELaNa) is an initiative created by NASA to attract and retain students in the science, technology, engineering and mathematics disciplines. The program is managed by the Launch Services Program (LSP) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Overview The ELaNa initiative has made partnerships with universities in the US to design and launch small research satellites called CubeSats (because of their cube shape). These low-cost CubeSat missions provide NASA with valuable opportunities to test emerging technologies that may be useful in future space missions, while university students get to be involved in all phases of the mission, from instrument and satellite design, to launch and monitoring. A CubeSat has a cubic shape measuring 10 × 10 × 10 cm (1 unit or 1U), and can be fabricated of multiple cubic units such as 2U, 3U and 6U, and weighing 1.33 kg per unit. Because of the high cost incurred by launching them to orbit, ELaN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NanoSail-D
NanoSail-D was a small satellite which was to have been used by NASA's Ames Research Center to study the deployment of a solar sail in space. It was a three-unit CubeSat measuring , with a mass of . The satellite was lost shortly after launch due to a problem with the launch vehicle carrying it; however, a replacement, NanoSail-D2, was launched in 2010 to complete its mission. Spacecraft NanoSail-D was to have been deployed on the third flight of the Falcon 1 launch vehicle, which was launched from Omelek Island at 03:34 UTC on 3 August 2008. One of two CubeSats aboard, along with PRESat, it was a secondary payload to the Trailblazer which was to have been operated by the Operationally Responsive Space Office of the United States Department of Defense. The launch was conducted by SpaceX, and also carried a space burial payload (Celestis-07) for Celestis. Two minutes and forty seconds after launch, the spent first stage of the rocket was jettisoned; however, unexpected res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
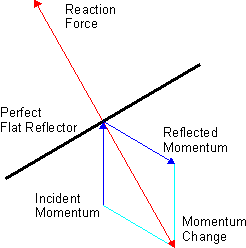
Radiation Pressure
Radiation pressure is the mechanical pressure exerted upon any surface due to the exchange of momentum between the object and the electromagnetic field. This includes the momentum of light or electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength that is absorbed, reflected, or otherwise emitted (e.g. black-body radiation) by matter on any scale (from macroscopic objects to dust particles to gas molecules). The associated force is called the radiation pressure force, or sometimes just the force of light. The forces generated by radiation pressure are generally too small to be noticed under everyday circumstances; however, they are important in some physical processes and technologies. This particularly includes objects in outer space, where it is usually the main force acting on objects besides gravity, and where the net effect of a tiny force may have a large cumulative effect over long periods of time. For example, had the effects of the Sun's radiation pressure on the spacecraft of the V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)